What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · D75.839 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D75.839 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D75.839 - other international versions of ICD-10 D75.839 may differ. Applicable To Thrombocythemia NOS
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D75.838. Other thrombocytosis. underlying condition, if known and applicable; Reactive thrombocytosis; Secondary thrombocytosis. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D75.838. Other thrombocytosis. 2022 - New Code Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Reactive thrombocytosis.
What are ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D75.83 Thrombocytosis 2022 - New Code Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code D75.83 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. ICD-10-CM D75.83 is a new 2022 ICD-10-CM code that became effective on October 1, 2021.
How many ICD 10 codes are there?
Oct 01, 2021 · When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code (D47.3) and the excluded code together. reactive thrombocytosis ( …
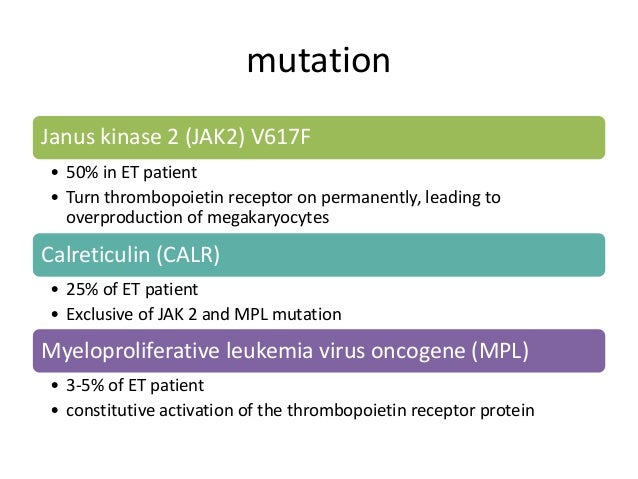
How do you code reactive thrombocytosis?
reactive thrombocytosis (D75.838)secondary thrombocytosis (D75.838)thrombocythemia NOS (D75.839)thrombocytosis NOS (D75.839)
What is meant by reactive thrombocytosis?
Reactive thrombocytosis, defined as an abnormally high platelet count in the absence of chronic myeloproliferative disease, secondary to an infection, inflammation, and hemorrhage. Secondary thrombocytosis is usually identified in routine laboratory testing, as most patients are asymptomatic.Aug 1, 2021
What is the ICD 10 code for secondary thrombocytosis?
Other secondary thrombocytopenia D69. 59 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is reactive thrombocytosis or essential thrombocythemia?
Thrombocytosis (throm-boe-sie-TOE-sis) is a disorder in which your body produces too many platelets. It's called reactive thrombocytosis or secondary thrombocytosis when the cause is an underlying condition, such as an infection.Oct 27, 2020
What is the platelet count for thrombocytosis?
Thrombocytosis is defined as a platelet count above 350,000 to 400,000/μL, which is the upper limit of the normal reference range.
What are the different types of thrombocytosis?
There are two types of thrombocytosis: primary and secondary. Primary thrombocytosis is a disease in which abnormal cells in the bone marrow cause an increase in platelets....What is thrombocytosis?Anemia due to iron deficiency.Cancer.Inflammation or infection,Surgery, especially splenectomy (removal of the spleen).Mar 2, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for hypercalcemia?
E83.52ICD-10 | Hypercalcemia (E83. 52)
Is thrombocytosis the same as thrombocythemia?
Thrombocythemia refers to a high platelet count that is not caused by another health condition. This condition is sometimes called primary or essential thrombocythemia. Thrombocytosis refers to a high platelet count caused by another disease or condition.Mar 24, 2022
How is pancytopenia diagnosis?
Doctors can diagnose pancytopenia with a complete blood count (CBC), a type of blood test that measures the levels of each blood cell type. Healthcare professionals may also make a peripheral blood smear by placing some blood on a slide and examining it under a microscope.
What infections cause reactive thrombocytosis?
The most common infectious causes of thrombocytosis were soft-tissue, pulmonary and GI infections.Nov 11, 2012
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
Is thrombocytosis a primary or secondary reaction?
Thrombocytosis (or thrombocythemia) is the presence of high platelet counts in the blood, and can be either primary (also termed essential and caused by a myeloproliferative disease) or reactive (also termed secondary). Although often symptomless (particularly when it is a secondary reaction), it can predispose to thrombosis in some patients.
What are the different types of blood disorders?
Types of blood disorders include. Platelet disorders, excessive clotting, and bleeding problems, which affect how your blood clots. Anemia, which happens when your blood does not carry enough oxygen to the rest of your body. Cancers of the blood, such as leukemia and myeloma.
What causes blood disorders?
Many blood disorders are inherited. Other causes include other diseases, side effects of medicines, and a lack of certain nutrients in your diet. Types of blood disorders include.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code D75.89 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is the liquid part of blood called?
Also called: Hematologic diseases. Your blood is living tissue made up of liquid and solids. The liquid part, called plasma , is made of water, salts and protein. Over half of your blood is plasma. The solid part of your blood contains red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
What is bone marrow?
Bone Marrow Diseases. Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside some of your bones, such as your hip and thigh bones. It contains stem cells. The stem cells can develop into the red blood cells that carry oxygen through your body, the white blood cells that fight infections, and the platelets that help with blood clotting.
What causes bone marrow disease?
Causes of bone marrow diseases include genetics and environmental factors. Tests for bone marrow diseases include blood and bone marrow tests. Treatments depend on the disorder and how severe it is. They might involve medicines, blood transfusions or a bone marrow transplant.
Does bone marrow make red blood cells?
In aplastic anemia, the bone marrow doesn't make red blood cells. In myeloproliferative disorders, the bone marrow makes too many white blood cells. Other diseases, such as lymphoma, can spread into the bone marrow and affect the production of blood cells. Causes of bone marrow diseases include genetics and environmental factors.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for parkinson's disease
- 2. icd 9 code for hereditary hemochromatosis
- 3. icd 10 code for s p incision and drainage
- 4. icd 10 diagnosis code for hip pain
- 5. icd 10 code for strep bovis bacteremia
- 6. icd 10 code for a recollection
- 7. icd 10 code for sepsis versus metabolic encephalopathy
- 8. icd 10 code for chronic ulcer of left lower extremity
- 9. icd 10 code for inury while deer hunting
- 10. icd 10 code for c67.9