Acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified
- J03.91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J03.91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J03.91 - other international versions of ICD-10 J03.91 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for tonsillitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified J03.91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J03.91 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J03.91 - other international ...
What are the signs and symptoms of tonsillitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · Acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified Billable Code J03.91 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic adenotonsillitis?
Acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified BILLABLE | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 J03.91 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code J03 is used to code Upper respiratory tract infection
What is the most common cause of tonsillitis?
J03.90 J03.91 J04 ICD-10-CM Code for Acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified J03.91 ICD-10 code J03.91 for Acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now
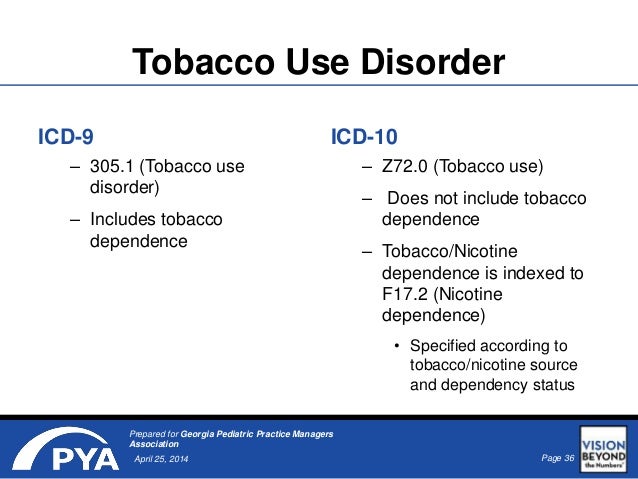
How do you code Acute and chronic tonsillitis?
Chronic tonsillitis and adenoiditisJ03.0 Streptococcal tonsillitis. J03.00 Acute streptococcal tonsillitis, unspecified. ... J03.8 Acute tonsillitis due to other specified organisms. J03.80 Acute tonsillitis due to other specified organisms. ... J03.9 Acute tonsillitis, unspecified. J03.90 Acute tonsillitis, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Acute and chronic tonsillitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Chronic tonsillitis J35. 01.
Is tonsillitis recurrent?
Recurrent tonsil infections are a common problem for adults. This is often seen when patients have frequent “sore throats” that last for weeks to even months. This is commonly due to a bacterial biofilm often caused by streptococcus.
What is the ICD-10 code for recurrent infections?
Acute recurrent sinusitis, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J01. 91 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J01.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R50 9?
ICD-10 code: R50. 9 Fever, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
What is exudative tonsillitis?
Tonsillar exudate is a fluid secreted by the tonsils in response to infection or inflammation. Various types of bacterial infections and viral infections cause tonsillitis, or the inflammation of the tonsils, which then results in secretion of tonsillar exudate.
What causes repeated tonsillitis?
Research from 2018 suggests that chronic and recurrent tonsillitis may occur due to biofilms in the folds of the tonsils. Biofilms are communities of microorganisms that have developed antibiotic resistance, and they can cause repeated infections. Genetics may also be a reason for recurrent tonsillitis.
How often can you get tonsillitis?
Frequent tonsillitis is usually defined as: more than seven episodes of tonsillitis in one year. more than four to five occurrences a year in each of the previous two years. more than three occurrences a year in each of the previous three years.
How do you stop recurrent tonsillitis?
The best way to prevent tonsillitis is through good hygiene, including:Washing your hands often.Not sharing food, drink, utensils, or personal items like toothbrushes with anyone.Staying away from someone who has a sore throat or tonsillitis.Aug 25, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code for ICD infection?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B99. 9: Unspecified infectious disease.
What is Urosepsis?
Urosepsis is sepsis caused by infections of the urinary tract, including cystitis, or lower urinary tract and bladder infections, and pyelonephritis, or upper urinary tract and kidney infections. Nearly 25 percent of sepsis cases originate from the urogenital tract.Feb 9, 2022
What is the ICD-10 code for bacterial infection?
ICD-10 code: A49. 9 Bacterial infection, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
What is the ICd 10 code for tonsillitis?
J03.91 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute recurrent tonsillitis, unspecified. The code J03.91 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code J03.91 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like chronic disease of tonsils and/or adenoids or recurrent acute tonsillitis.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like J03.91 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
How common is tonsillitis in children?
Tonsillitis is most common in children over age two. Almost every child in the United States gets it at least once. Tonsillitis caused by bacteria is more common in kids ages 5-15. Tonsillitis caused by a virus is more common in younger children. Adults can get tonsillitis, but it is not very common.
How do tonsils work?
The lymphatic system clears away infection and keeps body fluids in balance. Tonsils and adenoids work by trapping the germs coming in through the mouth and nose.
What does a doctor look for in a child's throat?
The provider will look at your child's throat and neck, checking for things such as redness or white spots on the tonsils and swollen lymph nodes. Your child will probably also have one or more tests to check for strep throat, since it can cause tonsillitis and it requires treatment.
Can antibiotics cause tonsillitis in children?
If treatment stops too soon, some bacteria may survive and re-infect your child. No matter what is causing the tonsillitis, there are some things you can do to help your child feel better. Make sure that your child.
How long does it take for a child to recover from tonsil surgery?
Very young children and people who have complications may need to stay in the hospital overnight. It can take a week or two before your child completely recovers from the surgery.
Can tonsillitis be treated with antibiotics?
Treatment for tonsillitis depends on the cause. If the cause is a virus, there is no medicine to treat it. If the cause is a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, your child will need to take antibiotics. It is important for your child to finish the antibiotics even if he or she feels better.
What are tonsils in the body?
The tonsils are part of the lymphatic and immunologic system. They are oval shaped, pink structures in the back of the throat and act as filters by trapping germs that pass through the nose and mouth. They also produce antibodies that help fight infection. They are the body’s first line of defense, and are similar to lymph nodes located in the neck, groin, and armpits.#N#Tonsillitis may be either viral or bacterial. Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria that causes strep throat, is a common bacterial cause, accounting for approximately 30 percent of tonsillitis in children and 10 percent in adults. Other causes include adenovirus, influenza virus, and Epstein-Barr virus.#N#ICD-10-CM codes for acute tonsillitis are contained in subcategory J03:
What causes strep throat in adults?
Streptococcus pyogenes, the bacteria that causes strep throat, is a common bacterial cause, accounting for approximately 30 percent of tonsillitis in children and 10 percent in adults. Other causes include adenovirus, influenza virus , and Epstein-Barr virus.
Where are lymph nodes located?
They are the body’s first line of defense, and are similar to lymph nodes located in the neck, groin, and armpits. Tonsillitis may be either viral or bacterial.
Who is John Verhovshek?
John Verhovshek. John Verhovshek, MA, CPC, is a contributing editor at AAPC. He has been covering medical coding and billing, healthcare policy, and the business of medicine since 1999. He is an alumnus of York College of Pennsylvania and Clemson University.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for gastric aorsiss
- 2. icd 10 code for abnormal ekg 3
- 3. icd 10 cm code for acute renal insufficiency
- 4. icd 10 code for sigmoid end colostomy
- 5. icd 10 cm code for outer ear infection right
- 6. icd 10 code for right fifth toe ulcer
- 7. icd 10 code for osteopenia multiple sites
- 8. icd-10 code for unstable gait
- 9. icd 10 code for sed rate
- 10. icd 10 code for complete heart block unspecified