What is the prognosis for renal cell cancer?
“For the first time in decades, we are seeing benefits to both survival and quality of life with these new treatments. People with kidney cancer have more effective treatment options than ever before. Not only are they living longer, they are living better.” In cancer treatment, quality of life matters more and more.
What is treatment for renal cell carcinoma?
- Treatment overview. ...
- Active surveillance. ...
- Surgery. ...
- Non-surgical tumor treatments. ...
- Therapies using medication. ...
- Radiation therapy. ...
- Physical, emotional, and social effects of cancer. ...
- Metastatic kidney cancer. ...
- Remission and the chance of recurrence. ...
- If treatment does not work. ...
What is renal cell carcinoma?
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), or renal cell cancer, is the most common type of kidney cancer, accounting for about 90% of all cases. In this type of cancer, malignant cells form in the lining of tubules (very small tubes) of the kidneys. What causes renal cell carcinoma? Cancer occurs when abnormal cells begin to grow or divide uncontrollably.
What is the treatment for renal cancer?
Treatment for renal cancer Surgery Surgery to remove part or all of the kidney is often used to treat renal cell cancer. The following types of surgery may be used: • Partial nephrectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the cancer within the kidney and some of the tissue around it. A partial nephrectomy may be done
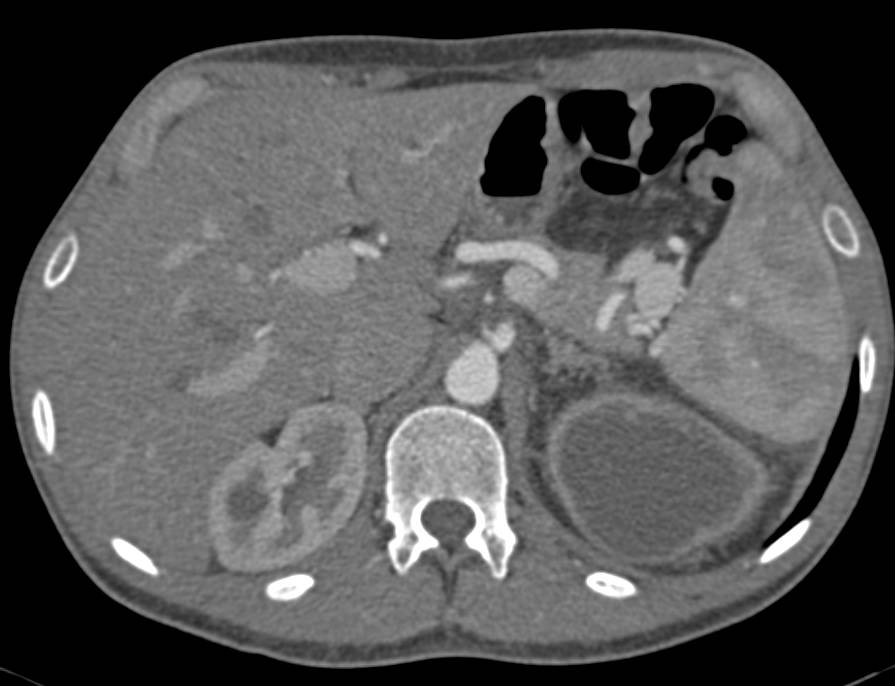
What is the diagnosis code for renal cell carcinoma left kidney?
C64. 2 - Malignant neoplasm of left kidney, except renal pelvis | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 10 code for renal cell carcinoma?
Kidney Cancer - Renal Cell Carcinoma (ICD-10: C64) - Indigomedconnect.
How do you code renal cell carcinoma?
Renal cell carcinoma (8312) is a group term for glandular (adeno) carcinomas of the kidney.
Is renal cell carcinoma the same as kidney cancer?
Renal cell cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tubules of the kidney. Renal cell cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal cell adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the lining of tubules (very small tubes) in the kidney.
What is the ICD-10 code for Wilms Nephroblastoma?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C64. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C64.
Why is it called clear cell carcinoma?
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma is named after how the tumor looks under the microscope. The cells in the tumor look clear, like bubbles.
Is renal cell carcinoma considered a solid tumor?
Solid tumors of the kidney are rare - approximately three-fourths of these tumors are cancerous with the potential to spread. The most common types of kidney cancer include: Renal cell carcinoma (adenocarcinoma)
Is clear cell renal carcinoma a solid tumor?
The tumor shows a solid growth pattern, but in some cases cystic appearance is seen. The cytoplasm is clear, due to an intensive intracytoplasmatic accumulation of glycogen and lipids. Usually, the nuclei are condensed and hyperchromatic.
What is total nephrectomy?
Total nephrectomy is done if the kidney does not work well enough or if there is a large tumor (mass) in the kidney that must be removed. The surgeon will tie off the blood supply to the kidney and the urine tube that goes to the bladder. Then he or she will take out the entire kidney and its attached urine tube.
What are the different types of renal cell carcinoma?
The types of RCC include:Clear cell. This is the most common type of RCC. ... Papillary. This is the second most common type of RCC. ... Chromophobe. This is a rare form of RCC. ... Collecting duct. This is also a rare form of RCC. ... Unclassified. This includes tumors that have cells from more than 1 type of cancer.
What is advanced renal cell carcinoma?
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is cancer in your kidneys that has spread to other parts of your body. It's also called stage IV renal cell cancer. Cancer is harder to treat after it spreads, but it's not impossible. You and your doctor still have many options.
What are the 4 types of kidney cancer?
Types of kidney cancerRenal cell carcinoma. Renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of adult kidney cancer, making up about 85% of diagnoses. ... Urothelial carcinoma. This is also called transitional cell carcinoma. ... Sarcoma. Sarcoma of the kidney is rare. ... Wilms tumor. ... Lymphoma.
What is metastatic renal cell carcinoma?
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma is cancer in your kidneys that has spread to other parts of your body. It's also called stage IV renal cell cancer. Cancer is harder to treat after it spreads, but it's not impossible. You and your doctor still have many options.
What is the ICD-10 code for squamous cell carcinoma?
ICD-10-CM Code for Squamous cell carcinoma of skin, unspecified C44. 92.
What is papillary renal cell carcinoma?
Papillary renal cell carcinoma, or PRCC, is a type of kidney cancer. The kidneys work by removing waste products from the blood. Papillary renal cell carcinoma is a cancer of the tubes that filter those waste products from the blood. There are two types of papillary renal cell carcinoma.
What is a Hypernephroma in medical terms?
Listen to pronunciation. (HY-per-neh-FROH-muh) Cancer that begins in the lining of the tiny tubes in the kidney that return filtered substances that the body needs back to the blood and remove extra fluid and waste as urine. Hypernephroma is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults.
What are some synonyms for cancer of the kidney?
Approximate Synonyms. Cancer of the kidney. Cancer of the kidney, primary, localized. Cancer of the kidney, renal cell. Cancer of the kidney, sarcoma. Cancer of the kidney, transitional cell carcinoma. Cancer of the kidney, wilms tumor. Clear cell carcinoma of kidney. Localized primary malignant neoplasm of kidney.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
Can multiple neoplasms be coded?
For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, ...
What is the ICd code for renal cell carcinoma?
The ICD code C64 is used to code Renal cell carcinoma. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC, also known as hypernephroma, Grawitz tumor, renal adenocarcinoma) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport waste molecules from the blood to the urine.
What is the most common type of kidney cancer?
RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90-95% of cases. Micrograph of the most common type of renal cell carcinoma (clear cell) - on right of the image, non-tumour kidney is on the left of the image. Nephrectomy specimen. H&E stain.
What is the ICd code for renal cell carcinoma?
The ICD code C64 is used to code Renal cell carcinoma. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC, also known as hypernephroma, Grawitz tumor, renal adenocarcinoma) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport waste molecules from the blood to the urine.
What is the ICD code for malignant neoplasm of kidney?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code C64 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the three child codes of C64 that describes the diagnosis 'malignant neoplasm of kidney, except renal pelvis' in more detail.
What is the most common type of kidney cancer?
RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90-95% of cases. Micrograph of the most common type of renal cell carcinoma (clear cell) - on right of the image, non-tumour kidney is on the left of the image. Nephrectomy specimen. H&E stain.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for cp
- 2. icd 10 code for abscess of right scrotum due to group b streptococcus
- 3. icd-10 code for spider veins
- 4. icd 10 code for aicd placement
- 5. icd 9 code for hemaotma to head
- 6. icd 10 code for cervical ca scree
- 7. icd 10 dx code for abdominal pain
- 8. icd 10 code for pre op surgical clearance
- 9. icd 10 code for personal history of non small cell cancer right lung
- 10. icd 10 code for delirium related to alcohol withdrawal