Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
What ICD 10 code will cover BNP for Medicare?
ICD-10 CODE DESCRIPTION 2019 MEDICARE LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (LCD) - L35526 PROCEDURE CODE: 83880 B-TYPE NATRIURETIC PEPTIDE (BNP) DLS TEST CODE AND NAME R06.00 Dyspnea, unspecified R06.01 Orthopnea R06.02 Shortness of breath R06.03 Acute respiratory distress R06.09 Other forms of dyspnea R06.2 Wheezing R06.82 Tachypnea, not elsewhere ...
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is the ICD 10 code for COPD with asthma?
- exposure to environmental tobacco smoke (Z77.22)
- history of tobacco use (Z87.891)
- occupational exposure to environmental tobacco smoke (Z57.31)
- tobacco dependence (F17.-)
- tobacco use (Z72.0)
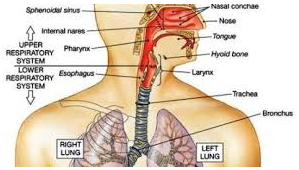
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for acute bronchitis?
9 – Acute Bronchitis, Unspecified.
Is acute respiratory infection the same as bronchitis?
Bronchitis (chest cold) is not an upper respiratory tract infection. Rather, it affects the air-transporting tubes of the lungs (bronchioles), which are a part of the lower respiratory tract.
What is the ICD 10 code for acute bacterial bronchitis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute bronchitis due to other specified organisms J20. 8.
Is bronchitis a lower respiratory infection?
Commonly known as bronchitis, acute bronchitis is a form of lower respiratory infection that affects the air tubes (bronchi) of the lungs. It usually comes on suddenly and lasts for a week to 10 days.
Can you have an upper respiratory infection and bronchitis at the same time?
Infectious bronchitis can also be due to bacteria, especially if it follows an upper respiratory viral infection. It is possible to have viral and bacterial bronchitis at the same time.
What is the difference between URI and bronchitis?
The upper respiratory tract includes the mouth, nose, sinus, throat, larynx (voice box), and trachea (windpipe). Upper respiratory infections are often referred to as "colds." The lower respiratory tract includes the bronchial tubes and the lungs. Bronchitis and pneumonia are infections of the lower respiratory tract.
What is the ICD 10 code for upper respiratory infection?
ICD-10 code J06. 9 for Acute upper respiratory infection, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is Acute bacterial bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis is inflammation of the windpipe (trachea) and the airways that branch off the trachea (bronchi) caused by infection. Acute bronchitis is usually caused by a viral upper respiratory tract infection. Symptoms are a cough that may or may not produce mucus (sputum).
What is acute bronchitis?
A chest cold, often called acute bronchitis, occurs when the airways of the lungs swell and produce mucus in the lungs. That's what makes you cough. Acute bronchitis can last less than 3 weeks.
Is acute bronchitis upper or lower respiratory infection?
Acute bronchitis is a lower respiratory tract infection that causes reversible bronchial inflammation. In up to 95 percent of cases, the cause is viral.
Is bronchiolitis upper or lower respiratory tract infection?
The most common cause of bronchiolitis is a virus. At first, the virus causes an infection in the upper respiratory tract. This includes the nose, mouth, and throat. It then spreads downward into the windpipe (trachea) and lungs (lower respiratory tract).
What is acute respiratory tract infection?
Acute respiratory infections (ARI) are defined as those infections of the respiratory system, caused by viruses or bacteria, with an evolution of less than 15 days, and which manifest with symptoms such as cough, nasal congestion and obstruction, sore throat, dysphonia or respiratory distress, accompanied or not by ...
What is a fibrinous bronchitis?
acute and subacute purulent bronchitis. acute and subacute septic bronchitis. Clinical Information. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to your lungs.
What is tobacco dependence?
tobacco dependence ( F17.-) "Includes" further defines, or give examples of, the content of the code or category. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to your lungs. It causes a cough that often brings up mucus, as well as shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness.
Do you need antibiotics for bronchitis?
You may need inhaled medicine to open your airways if you are wheezing. You probably do not need antibiotics. They don't work against viruses - the most common cause of acute bronchitis. If your healthcare provider thinks you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe antibiotics.
Can a virus cause bronchitis?
The same viruses that cause colds and the flu often cause acute bronchitis. These viruses spread through the air when people cough, or through physical contact (for example, on unwashed hands). Being exposed to tobacco smoke, air pollution, dusts, vapors, and fumes can also cause acute bronchitis.
What is J44.0 in pulmonary disease?
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with acute lower respiratory infection ( J44.0) Other acute lower respiratory infections. Clinical Information. Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to your lungs.
Do you need antibiotics for bronchitis?
You may need inhaled medicine to open your airways if you are wheezing. You probably do not need antibiotics. They don't work against viruses - the most common cause of acute bronchitis. If your healthcare provider thinks you have a bacterial infection, he or she may prescribe antibiotics.
Can a virus cause bronchitis?
The same viruses that cause colds and the flu often cause acute bronchitis. These viruses spread through the air when people cough, or through physical contact (for example, on unwashed hands). Being exposed to tobacco smoke, air pollution, dusts, vapors, and fumes can also cause acute bronchitis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for biopsy right lung
- 2. icd 10 code for ultrasound to confirm pregnancy
- 3. icd 10 code for plica
- 4. icd-10-cm code for gram negative septicemia
- 5. icd-10-cm code for diabetic nephropathy due to type 1 diabetes mellitus
- 6. icd 10 code for left elbow medial epicondylitis
- 7. icd 10 code for galactorrhea
- 8. icd 10 code for nail fungus
- 9. icd 9 cm code for low back pain
- 10. icd 10 code for struck by golf ball