What is the ICD 10 code for tonic pupil?
ICD Code H57.05 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the four child codes of H57.05 that describes the diagnosis 'tonic pupil' in more detail.
What is the ICD 10 code for dilatation of the pupil?
The code is valid for the year 2020 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code H57.04 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like bilateral fixed dilatation of pupil, congenital mydriasis, dilated pupil, episodic mydriasis of left pupil, episodic mydriasis of right pupil, fixed dilatation of left pupil, etc
What is the ICD 10 code for pupillary sphincter?
Pupillary disorder Rupture of sphincter of pupil ICD-10-CM H21.569 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 124 Other disorders of the eye with mcc
What is a blown pupil?
A blown, or blown out, pupil is characterized by a pupil that is largely dilated and unresponsive to light. When it occurs, a fixed dilated pupil may be present in one or both eyes. Typically, blown pupils are seen in response to brain damage caused by trauma or stroke, though less serious causes are possible.
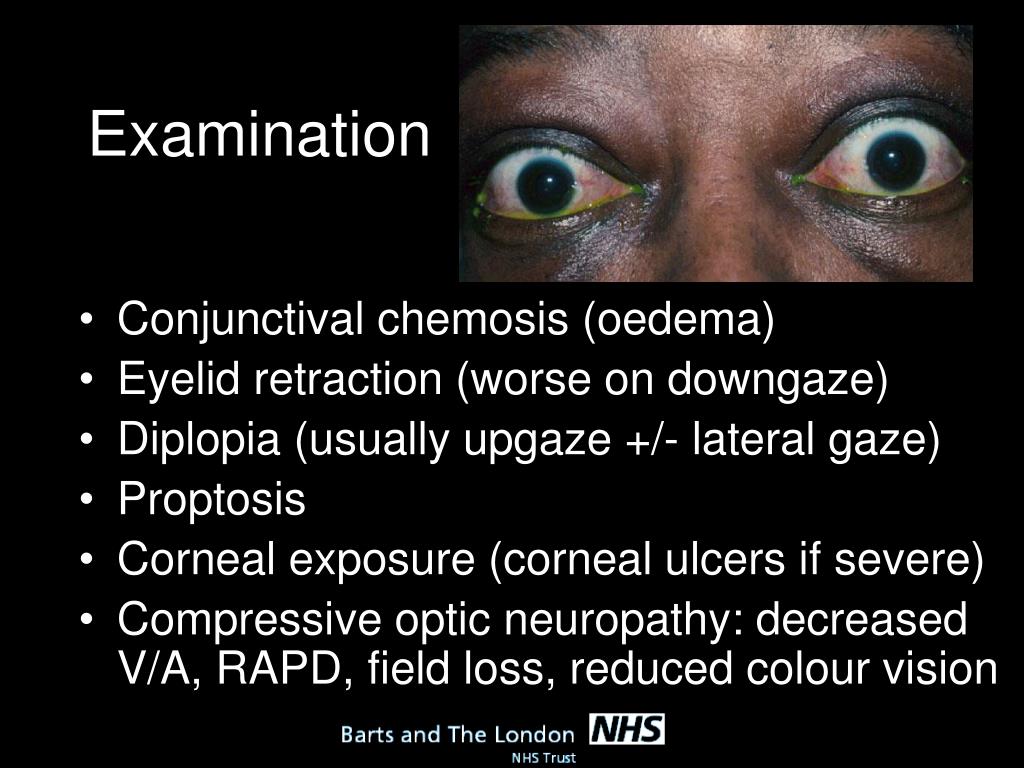
What is the ICD-10 code for dilated pupil?
ICD-10 | Mydriasis (H57. 04)
What is ICD-10 code for Anisocoria?
ICD-10-CM Code for Anisocoria H57. 02.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
Does mydriasis cause blurred vision?
Benign episodic unilateral mydriasis (BEUM) is a temporary condition that creates a dilated pupil in only one eye. Often individuals with this condition will also experience a mild headache, eye pain, light sensitivity, and blurred vision during these episodes.
What is the medical term for unequal pupils?
Uneven pupil size, or anisocoria, may be a normal variation in a person's eyes or may indicate an underlying problem.
What do unequal pupils mean?
Unequal pupil sizes of more than 1 mm that develop later in life and do not return to equal size may be a sign of an eye, brain, blood vessel, or nerve disease.
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
Is R51 a billable code?
R51. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R51. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does the first letter in the alphanumeric ICD 10 code represent?
Codes in the ICD-10-CM code set can have anywhere from three to seven characters. The more characters there are, the more specific the diagnosis. The first character is always alpha (i.e., a letter), but characters two through seven can be either alpha or numeric.
What does one dilated pupil mean?
Benign Episodic Unilateral Mydriasis This condition means only one pupil is dilated. It's called "benign" because it's not related to any serious conditions, but it can sometimes affect young women who get migraines. The pupil usually goes back to normal size within a few hours, but it can last for several days.
What is mydriasis caused by?
Dilated pupils (mydriasis) are when the black center of your eyes are larger than normal. The condition may be caused by dilating eye drops from an eye exam, the side effects from a drug/medication or traumatic injury.
What can dilated pupils mean?
This may be caused by an injury, psychological factors, or when someone takes certain drugs or medications. Doctors sometimes refer to more pronounced mydriasis, when the pupils are fixed and dilated, as “blown pupil.” This condition can be a symptom of an injury to the brain from physical trauma or a stroke.
How does mydriasis affect vision?
The characteristic symptom of mydriasis is dilated pupils that do not get bigger or smaller in response to changes in light. When the pupils are dilated, the eyes become more sensitive to light. This can lead to blurry vision, as well as, in some cases, a general feeling of constriction around the forehead and eyes.
How long does traumatic mydriasis last?
Both traumatic mydriasis and accommodation loss have been reported as long-term findings following a projectile injury. 2, 3, 4 However, there is limited published data regarding healing times or final outcomes. TM typically resolves in the weeks following the injury or is permanent.
What is the effect of Mydriatics on pupil size of eye?
Pupil diameter increased significantly in the subjects who received mydriatics ( ), but the extent of pupil diameter was found to be higher in the tropicamide and the cyclopentolate groups than in the phenylephrine group.
Does mydriasis increased intraocular pressure?
Mydriasis occurs with a rise in intraocular pressure due to the dilated iris blocking drainage of the intraocular fluid from the angle of the anterior chamber. An attack of glaucoma may be induced in eyes predisposed to primary angle (also called acute closed-angle or narrow-angle) closure and is a medical emergency.
What causes pupils to dilate?
This condition may occur due to injury of the pupillary fibers in the oculomotor nerve, in acute angle-closure glaucoma, and in adie syndrome.
When will the ICd 10-CM H57.04 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H57.04 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the symptoms of a blown pupil?
Blown pupil symptoms. The most obvious symptom of blown pupils is having one or both pupils that appear abnormally dilated (large) and do not react to light. Other symptoms associated with this include: Light sensitivity ( photophobia ). Headache.
What is a blown pupil?
In other words, mydriasis is a temporary dilation of the pupils in response to light. Blown pupils are dilated very widely and fixed, meaning they do not respond to an outside stimulus, such as light. The largely dilated pupil may affect one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral).
What does it mean when your eye is blown?
The largely dilated pupil may affect one eye (unilateral) or both eyes (bilateral). Unilateral cases, where only one pupil is dilated and fixed, is known as anisocoria, meaning unequal pupil size. Typically blown pupils occur as a response to a brain injury, such as head trauma or stroke. However, exposure to certain substances can also elicit ...
What does it mean when your pupil is blown out?
A blown, or blown out, pupil is characterized by a pupil that is largely dilated and unresponsive to light. When it occurs, a fixed dilated pupil may be present in one or both eyes. Typically, blown pupils are seen in response to brain damage caused by trauma or stroke, though less serious causes are possible.
Why do my pupils not react to light?
You have pupils of unequal size (one pupil is larger/smaller than the other). You suffer a serious head injury. You experience trauma to one or both of your eyes.
Why do pupils dilate when you step out of a dark room?
For instance, when you enter a dark room, your pupils will naturally dilate (get larger) to adjust to a low-light environment. However, once you step out of the dark room, your pupils will return to normal or adjust to the new level of brightness.
Is a blown pupil life threatening?
While some causes are non-life threatening and may resolve on their own , medical attention is recommended. The risk involved with a blown pupil is too great to go untreated. Serious causes of fixed, dilated pupils include:
What is the name of the disorder that causes a tonic pupil?
Adie syndrome (/ˈeɪdi/), sometimes known as Holmes–Adie syndrome or Adie's tonic pupil, is a neurological disorder characterized by a tonically dilated pupil that reacts slowly to light but shows a more definite response to accommodation (i.e., light-near dissociation). It is frequently seen in females with absent knee or ankle jerks and impaired sweating. It is named after the British neurologist William John Adie. It is caused by damage to the postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic innervation of the eye, usually by a viral or bacterial infection which causes inflammation, and affects the pupil of the eye and the autonomic nervous system.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H57.051 and a single ICD9 code, 379.46 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis.
What is the term for a pupillary dilation?
MYDRIASIS-. dilation of pupils to greater than 6 mm combined with failure of the pupils to constrict when stimulated with light. this condition may occur due to injury of the pupillary fibers in the oculomotor nerve in acute angle closure glaucoma and in adie syndrome.
What is retinal disorder?
Retinal disorders - problems with the nerve layer at the back of the eye
When is H57.04 due?
The code H57.04 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
The ICD code H570 is used to code Adie syndrome
Adie syndrome (/ˈeɪdi/), sometimes known as Holmes–Adie syndrome or Adie's tonic pupil, is a neurological disorder characterized by a tonically dilated pupil that reacts slowly to light but shows a more definite response to accommodation (i.e., light-near dissociation).
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'H57.05 - Tonic pupil'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code H57.05. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for malignant neoplasm of tongue
- 2. icd 10 code for fracture of right femoral neck
- 3. icd 10 code for ovarian dysfunction
- 4. 2017 icd 10 code for acute thrombus in cathetere
- 5. icd 10 code for open anterior frontal
- 6. icd 9 code for severe abdominal pain
- 7. icd 10 code for chest pain with shortness of breath
- 8. icd 10 code for mvc driver lost control
- 9. icd 10 code for acute kidney injury due to hypovolemia
- 10. icd 10 code for right axilla furuncle