What is the ICD 10 code for pupil dilation?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H57.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 H57.0 may differ. injury (trauma) of eye and orbit ( S05.-) Conditions in which the pupil does not react normally to dilation and constriction.
What is the ICD 10 code for pupillary abnormality right eye?
Pupillary abnormality, right eye 1 H21.561 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H21.561 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H21.561 - other international versions of ICD-10 H21.561 may differ. More ...
What is the CPT code for eye dilation?
Medical and Surgical, Eye, Dilation The Dilation root operation is identified by the character code 7 in the 3 rd position of the procedure code. It is defined as Expanding an orifice or the lumen of a tubular body part. The orifice can be a natural orifice or an artificially created orifice.
What is the ICD 10 code for Adie's tonic pupil?
The ICD code H570 is used to code Adie syndrome. Adie syndrome (/ˈeɪdi/), sometimes known as Holmes–Adie syndrome or Adie's tonic pupil, is a neurological disorder characterized by a tonically dilated pupil that reacts slowly to light but shows a more definite response to accommodation (i.e., light-near dissociation).
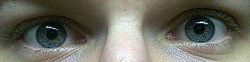
What is the ICD-10 code for dilated pupil?
H57. 04 - Mydriasis | ICD-10-CM.
What is ICD-10 code for Anisocoria?
ICD-10-CM Code for Anisocoria H57. 02.
What is miosis and mydriasis?
Miosis can occur in one or both eyes. When it affects only one eye, it's also called anisocoria. Another name for miosis is pinpoint pupil. When your pupils are excessively dilated, it's called mydriasis.
What is the code for right eye?
41 for Blindness, right eye, normal vision left eye is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
What is the medical term for unequal pupils?
Uneven pupil size, or anisocoria, may be a normal variation in a person's eyes or may indicate an underlying problem.
What is the ICD-10 code for small pupil left eye?
Pupillary abnormality, unspecified eye H21. 569 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H21. 569 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does it mean when one pupil is more dilated?
If there are no other symptoms and if the pupils return to normal, then it is nothing to worry about. Unequal pupil sizes of more than 1 mm that develop later in life and do not return to equal size may be a sign of an eye, brain, blood vessel, or nerve disease.
What is dilated pupil?
Dilated pupils (mydriasis) are when the black center of your eyes are larger than normal. The condition may be caused by dilating eye drops from an eye exam, the side effects from a drug/medication or traumatic injury.
What causes unilateral pupil dilation?
Causes include Adie's tonic pupil, oculomotor nerve palsy, traumatic injury to the iris, or pharmacologic dilation from mydriatics/cycloplegics (atropine, tropicamide, cyclopentolate), or cocaine. The use of pilocarpine can be diagnostic in this setting.
What is the ICD-10 code for ophthalmology?
Encounter for examination of eyes and vision without abnormal findings. Z01. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z01.
What is the ICD-10 code for legally blind right eye?
Blindness right eye, category 5 The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H54. 0X5 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H54.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What are the signs of pupillary abnormalities?
Signs of pupillary abnormalities originate from the pupil's shape, position, and response to stimulation. Code History.
Is H57.0 a reimbursement code?
H57.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H57.0 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H57.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 H57.0 may differ.
What is the name of the eye disorder that causes a pupil to dilate?
Adie syndrome (/ˈeɪdi/), sometimes known as Holmes–Adie syndrome or Adie's tonic pupil, is a neurological disorder characterized by a tonically dilated pupil that reacts slowly to light but shows a more definite response to accommodation (i.e., light-near dissociation). It is frequently seen in females with absent knee or ankle jerks and impaired sweating. It is named after the British neurologist William John Adie. It is caused by damage to the postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic innervation of the eye, usually by a viral or bacterial infection which causes inflammation, and affects the pupil of the eye and the autonomic nervous system.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H57.051 and a single ICD9 code, 379.46 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H21.41 and a single ICD9 code, 364.74 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is PPM in the eye?
Persistent pupillary membrane (PPM) is a condition of the eye involving remnants of a fetal membrane that persist as strands of tissue crossing the pupil. The pupillary membrane in mammals exists in the fetus as a source of blood supply for the lens. It normally atrophies from the time of birth to the age of four to eight weeks. PPM occurs when this atrophy is incomplete. It generally does not cause any symptoms. The strands can connect to the cornea or lens, but most commonly to other parts of the iris. Attachment to the cornea can cause small corneal opacities, while attachment to the lens can cause small cataracts. Using topical atropine to dilate the pupil may help break down PPMs.
What is the ICd 9 code for a swollen eye?
Specialty: Ophthalmology. MeSH Code: D015845. ICD 9 Code: 379.46.
What is the ICD code for Adie syndrome?
The ICD code H570 is used to code Adie syndrome. Adie syndrome (/ˈeɪdi/), sometimes known as Holmes–Adie syndrome or Adie's tonic pupil, is a neurological disorder characterized by a tonically dilated pupil that reacts slowly to light but shows a more definite response to accommodation (i.e., light-near dissociation).

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2016 icd 10 code for acl repair
- 2. icd code for carpal tunnel bi lat hands
- 3. icd 10 code for burns to the face fireworks
- 4. icd 10 code for eididymal cyst
- 5. icd 9 code for multiple therapy
- 6. icd code for dvt prophylaxis
- 7. icd 10 code for hand wart
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for acute respiratory insufficiency post op
- 9. icd 10 code for unspecified pulmonary embolism
- 10. icd 10 code for delirium tremens due to chronic alcoholism