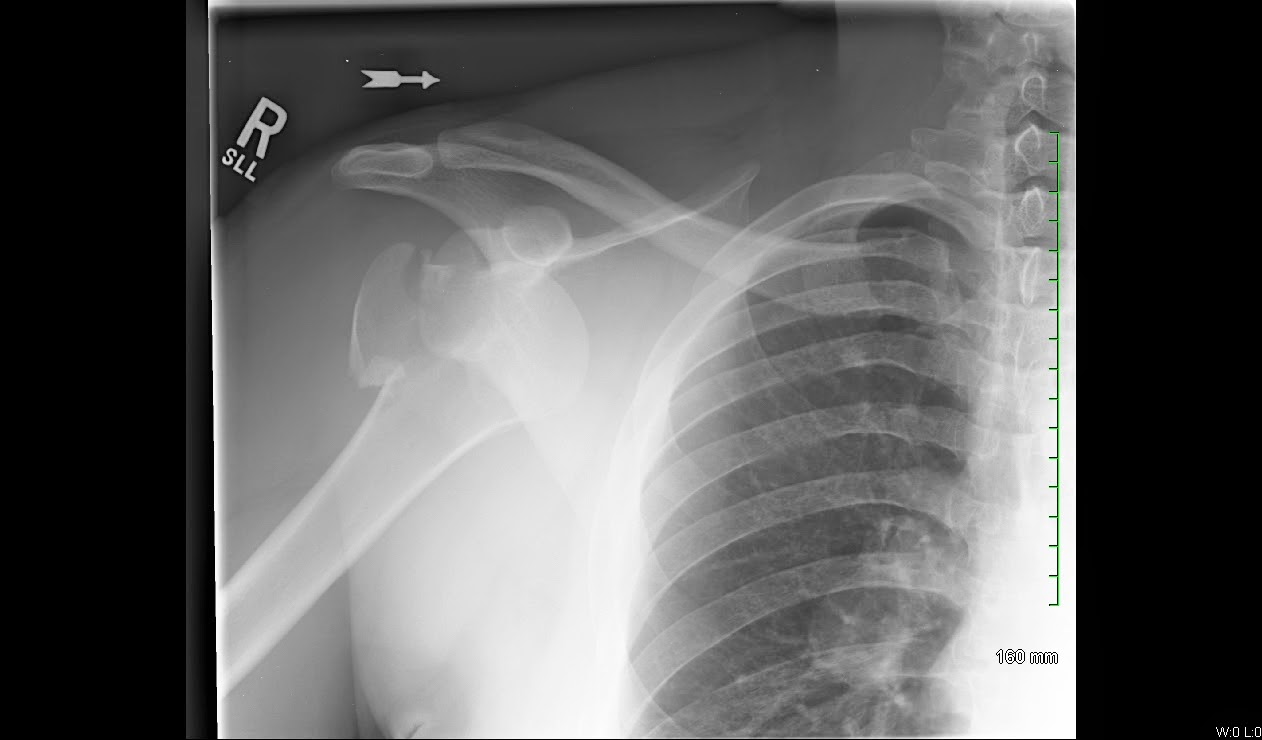
ICD-10-CM Code S42.254. Nondisplaced fracture of greater tuberosity of right humerus. S42.254 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Nondisplaced fracture of greater tuberosity of right humerus.
What is the ICD 10 code for displaced fracture of greater tuberosity?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S42.25 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S42.25 Fracture of greater tuberosity of humerus 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code S42.25 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is the ICD 10 code for tuberosity of humerus?
Oct 01, 2021 · Nondisplaced fracture of greater tuberosity of right humerus, initial encounter for closed fracture. S42.254A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S42.254A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for fracture of the right humerus?
Oct 01, 2021 · Displaced fracture of greater tuberosity of right humerus, initial encounter for closed fracture. S42.251A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S42.251A became effective on October 1, 2021.
Which ICD-10 code should not be used for reimbursement purposes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Displaced fracture of greater tuberosity of right humerus, subsequent encounter for fracture with routine healing. S42.251D is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S42.251D became effective on October 1, 2021.
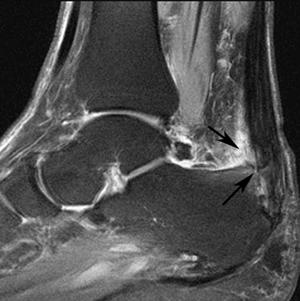
What is the greater tuberosity?
The greater tuberosity is the “bump” of bone at the top of the humerus that serves as the attachment for two rotator cuff muscles. This attachment is why a fracture can also interfere with the functioning of the rotator cuff.
Where is a greater tuberosity fracture?
This condition is a fracture of the bony bump that is located opposite of the head of the humerus. This type of fracture can interfere with the rotator cuff. Fractures of the greater tuberosity are often caused by direct trauma to the shoulder.
What is greater tuberosity of humerus fracture?
The greater tuberosity is the prominent area of bone at the top of the humerus and is the attachment for the two large, powerful rotator cuff muscles - supraspinatus and infraspinatus. It is injured/fractured in a fall by either landing directly onto the side of your shoulder or landing with your arm outstretched.Jan 19, 2022
What is a displaced fracture of the greater tuberosity?
Greater Tuberosity Fractures may occur due to trauma or shoulder dislocation, and represent a boney disruption to the rotator cuff tendons around the shoulder. They can occur in any age group, although they are most commonly due to a fall in older individuals or due to athletic injuries.
What is a tuberosity?
Tuberosity - A moderate prominence where muscles and connective tissues attach. Its function is similar to that of a trochanter. Examples include the tibial tuberosity, deltoid tuberosity, and ischial tuberosity. Tubercle - A small, rounded prominence where connective tissues attach.Nov 21, 2021
Is tubercle and tuberosity the same?
Tubercle vs tuberosity A tubercle is a small rounded prominence, often a site of tendon or ligament attachment e.g. adductor tubercle of the femur. A tuberosity is larger, found in varying shapes and often rough in texture. The ulnar tuberosity is one example.
What is a nondisplaced greater tuberosity fracture?
The fracture is completely un-displaced (the bone has not moved), this means you do not need a routine follow up appointment. You have however been referred to your local physiotherapy service for rehabilitation to start approximately 3 weeks after your injury.
What tendon attaches to greater tuberosity?
The greater tuberosity it is located lateral to the head. The lesser tuberosity is located inferior to the head, on the anterior part of the humerus, Its very prominent and palpable. Bicipital (intertubercular) groove is located between the two tuberosities. The Biceps tendon is placed here.
How do you treat a fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus?
Nonoperative treatment for a nondisplaced greater tuberosity fracture has been reported to in- clude passive range of motion (PROM) starting at 1 week postinjury, active range of motion (AROM) starting at 6 weeks postinjury, followed by gradually progressed strengthening once full PROM is reached.
What does sclerosis of greater tuberosity mean?
Greater tuberosity sclerosis was defined as cortical thickening and subchondral sclerosis, ex- tending from the articular cartilage of humeral head to the lateral humeral cortex on a true AP Shoulder radio-graph.
What is a greater tuberosity avulsion fracture?
Tuberosity avulsion or fracture may occur after a fall onto an outstretched upper extremity due to an eccentric load applied by the attached rotator cuff on the tuberosity, often in the setting of a traumatic glenohumeral dislocation.Aug 31, 2018
What is a minimally displaced fracture?
Minimally displaced: where there is a slight shift in the position, usually not significant. Displaced: where the bone has significantly shifted, the degree of which is described in percentages. Depression: an intra-articular (joint) fracture which has been pushed out of alignment with the bone.Jul 8, 2020
The ICD code S422 is used to code Humerus fracture
A humerus fracture is a bone fracture of the arm. Fractures of the humerus may be classified by the location and divided into fractures of the upper end, the shaft, or the lower end.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #559-561 - Aftercare, musculoskeletal system and connective tissue with MCC.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code S42.251D and a single ICD9 code, V54.11 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for status post foreign body left eye
- 2. icd-10 code for osteopenia left hip
- 3. icd 9 code for osteoarthritis of the hip
- 4. icd 10 code for thrombophlebitis upper extremity
- 5. icd-10 code for dry mouth
- 6. icd 10 code for weakness bilateral lower extremities
- 7. icd 9 code for diabetic hyperlipidemia
- 8. icd 10 code for type 1 diabetes cataract
- 9. what is the icd 10 code for venous insufficiency
- 10. icd 9 code for severe obstructive sleep apnea