What is the ICD 10 code for otalgia right ear?
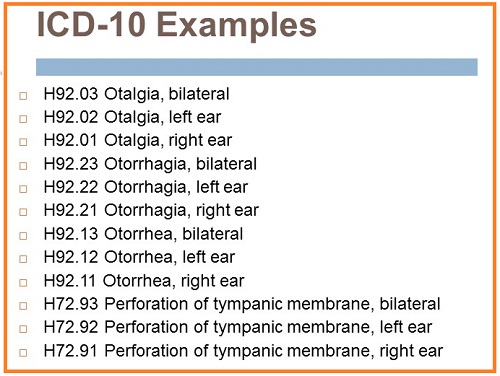
Oct 01, 2021 · Otalgia, right ear. H92.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H92.01 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H92.01 - other international versions of ICD-10 H92.01 may differ.
What is bilateral referred otalgia ICD 10?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otalgia, right ear H92.01 ICD-10 code H92.01 for Otalgia, right ear is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is otalgia of the ear?
Otalgia, right ear BILLABLE | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 H92.01 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of otalgia, right ear. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. MS-DRG Mapping DRG Group #154-156 - Other …
What is the new ICD 10 for ear pain?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H92.0 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H92.0 Otalgia 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code H92.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H92.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #154-156 - Other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with MCC.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H92.01 and a single ICD9 code, 388.70 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What does "other specified" mean in a tabular list?
This abbreviation in the Tabular List represents “other specified”. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the “other specified” code.
What does "excludes2" mean?
An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together.
What are the two types of pain?
There are two types of pain: acute and chronic. Acute pain usually comes on suddenly, because of a disease, injury, or inflammation. It can often be diagnosed and treated. It usually goes away, though sometimes it can turn into chronic pain. Chronic pain lasts for a long time, and can cause severe problems.
Why does my ear roar?
Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud noises, medicines or a variety of other causes. Meniere's disease may be the result of fluid problems in your inner ear; its symptoms include tinnitus and dizziness.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code H92.01 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
How do sound waves travel?
You use all of them in hearing. Sound waves come in through your outer ear. They reach your middle ear, where they make your eardrum vibrate. The vibrations are transmitted through three tiny bones, called ossicles, in your middle ear. The vibrations travel to your inner ear, a snail-shaped organ.
What organ controls balance?
The inner ear makes the nerve impulses that are sent to the brain. Your brain recognizes them as sounds. The inner ear also controls balance. A variety of conditions may affect your hearing or balance:
Is pain always curable?
Pain is not always curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment depends on the cause and type of pain. There are drug treatments, including pain relievers. There are also non-drug treatments, such as acupuncture, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for encounter for weight management
- 2. icd 10 code for rt foot verruca
- 3. icd 10 dx code for familial cardiomyopathy
- 4. icd 10 code for postive ccp
- 5. icd-10 code for follow up work comp injury
- 6. icd 10 code for decreased recurrent eruptation
- 7. icd 10 code for left facial weakness
- 8. 2015 icd 10 code for diabetes type 11
- 9. icd 10 code for elevated bicarbonate
- 10. icd 10 pcs code for gastric lavage