Which knee ligament is the worst to tear?
Oct 01, 2021 · Right scapholunate ligament rupture ICD-10-CM S63.391A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 562 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh with mcc 563 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh without mcc 963 Other multiple significant trauma with mcc
What is meniscus tear diagnosis and treatment?
Oct 01, 2021 · Right scapholunate ligament tear; ICD-10-CM S63.519A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 39.0): 562 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh with mcc; 563 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh without mcc; 963 Other multiple significant trauma with mcc
What is a complete tear of a ligament?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S63.519A [convert to ICD-9-CM] Sprain of carpal joint of unspecified wrist, initial encounter Sprain of carpal joint of unspecified wrist, init encntr; Right scapholunate ligament tear ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S83.511A [convert to ICD-9-CM] Sprain of anterior cruciate ligament of right knee, initial encounter
How do I treat a torn wrist ligament?
Oct 01, 2021 · S63.392A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S63.392A became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S63.392A - other international versions of ICD-10 S63.392A may differ.

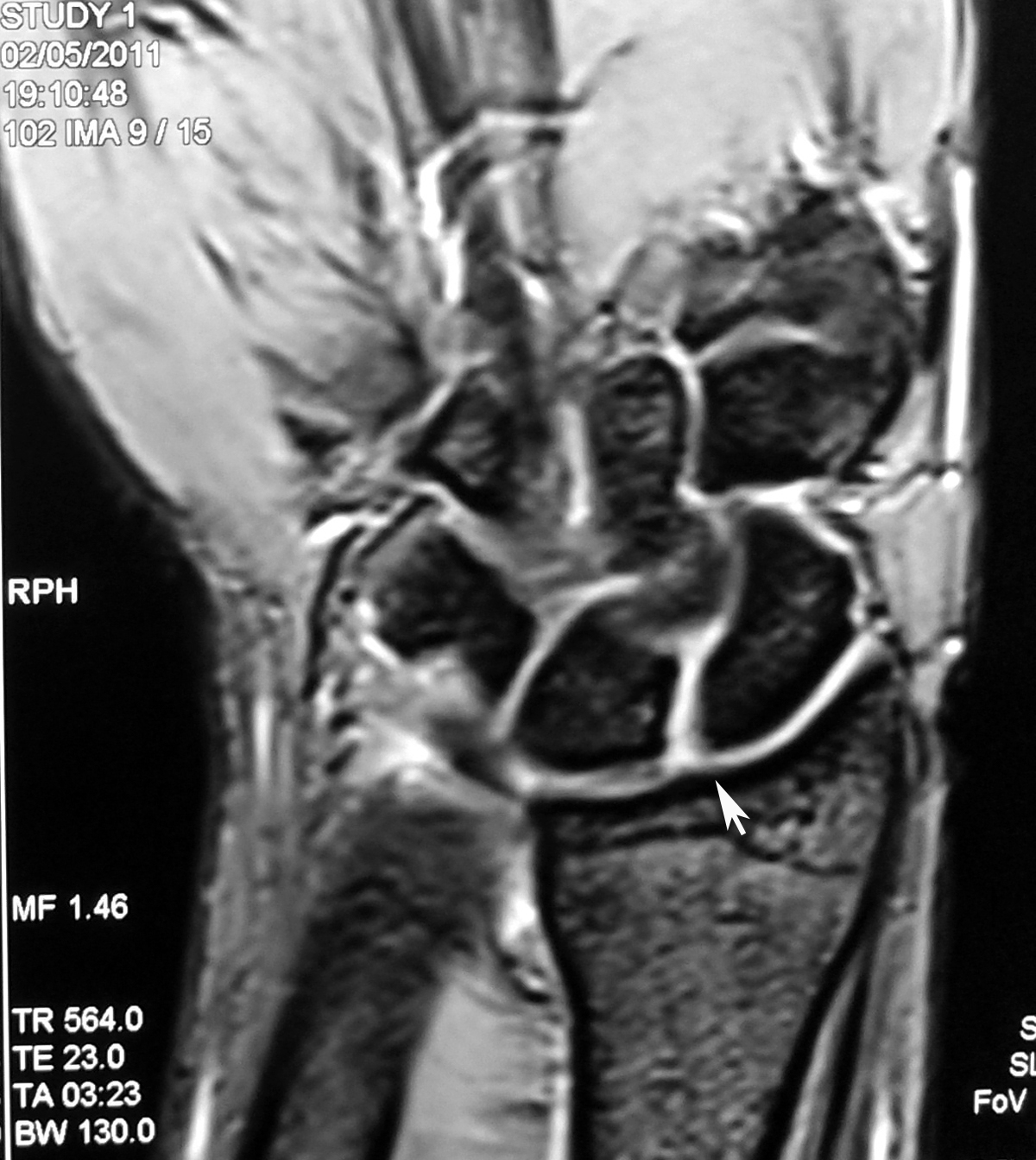
What is the scapholunate ligament?
Is scapholunate ligament extra articular?
What is a chronic scapholunate ligament tear?
What is a scapholunate injury?
Where is the scapholunate ligament?
What is a partial tear of the scapholunate ligament?
How do you diagnose a scapholunate ligament tear?
Is scaphoid hand or wrist?
What is the scapholunate interval?
What are the ligaments of the wrist?
The Ulnocarpal and radioulnar ligaments are two sets of ligaments that provide the main support for the wrist. The scapholunate interosseous ligament and the lunotriquetral interosseous ligament provide stability to the proximal carpal row.
How do you treat a scapholunate ligament injury?
What is SLAC wrist?
What is a scapholunate advanced collapse?
A wrist defect often requiring surgical intervention is scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC.) SLAC is a condition of progressive instability that causes advanced radiocarpal and midcarpal osteoarthritis. SLAC describes a specific pattern of progressive subluxation with loss of articulation between the scaphoid and lunate bones. SLAC usually results from trauma to the wrist, but may be caused by a degenerative process such as calcinosis or as a sequela of a prior injury. SLAC is estimated to account for more than half of all non-traumatic wrist osteoarthritis cases.#N#Signs and symptoms of SLAC include:
What is the name of the inflammation of the first dorsal extensor compartment?
De Quervain’s disease (radial styloid tenosynovitis) is an inflammation of the first dorsal extensor compartment; this is entrapment tendinitis causing tendon thickening, which leads to restricted motion and a grinding sensation with tendon movement (crepitus).
What are some examples of unbundling?
It’s important to understand payer guidelines and National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) bundling rules. Common examples of unbundling and miscoding errors include: 1 Reporting a ganglion cyst excision (25111 Excision of ganglion, wrist (dorsal or volar); primary) in addition to a synovectomy of the wrist (25118 Synovectomy, extensor tendon sheath, wrist, single compartment ): 25111 is bundled into the 25118. 2 Reporting a partial synovectomy (29844 Arthroscopy, wrist, surgical; synovectomy, partial) in addition to an arthroscopic TFCC repair (29846 Arthroscopy, wrist, surgical; excision and/or repair of triangular fibrocartilage and/or joint debridement) when the synovectomy is included in the repair. 3 Reporting 25215 Carpectomy; all bones of proximal row for a carpectomy of all proximal row bones when not all three bones (scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum) are excised. 4 Reporting a trapezium excision (25210 Carpectomy; 1 bone) in addition to a carpometacarpal joint arthroplasty (25447 Arthroplasty, interposition, intercarpal or carpometacarpal joints ). 5 Separately reporting bone grafts (20900 Bone graft, any donor area; minor or small (eg, dowel or button) or 20902 Bone graft, any donor area; major or large) with procedures that include these grafts. 6 Billing for initial application of a short-arm cast (29075 Application, cast; elbow to finger (short arm)) or short-arm splint (29125 Application of short arm splint (forearm to hand); static) with a surgical procedure on the wrist. 7 Coding fracture of carpal bone (S62.1- Fracture of other and unspecified carpal bone (s)) when the diagnosis is a distal radius fracture (S52.5- Fracture of lower end of radius ).
What are the bones of the wrist?
The wrist, or carpus, contains eight carpal bones. There are three bones in the proximal row (scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum) and five bones in the distal row (trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate, and pisiform). The trapezium is also known as the greater multangular, the trapezoid as the lesser multangular, and the scaphoid as the navicular bone.#N#In ICD-10-CM, most wrist conditions coded from chapter 13 (M codes) have a “3” in the fifth position of the code such as M19.031 Primary osteoarthritis, right wrist. Common conditions of the wrist and distal radius from chapters 13 and 19 (M and S codes) are: 1 Wrist drop (M21.33-) 2 Contracture of wrist (M24.53-) 3 Flail joint of wrist (M25.23-) 4 Infective tenosynovitis of wrist (M65.13-) 5 DeQuervain’s disease (radial styloid tenosynovitis) (M65.4) 6 Ganglion cyst of wrist (M67.43-) 7 Crepitant synovitis of wrist (M70.03-) 8 Abscess of wrist bursa (M71.03-) 9 Carpal idiopathic aseptic necrosis (M87.037, M87.038) 10 Fracture of lower (distal) end of radius (S52.5-) 11 Physeal (Salter-Harris) fracture of lower end of radius (S59.2-) 12 Fracture of ulnar styloid process (S52.61-) 13 Fracture of navicular (scaphoid) bone (S62.0-) 14 Fracture of (other) carpal bone (S62.1-) 15 Subluxation and dislocation of wrist (S63.0-) 16 Wrist sprain (S63.5-)
Is the wrist a joint?
The wrist is classified as an “intermediate” joint, but consists of many intricate structures and bones. Accurate coding of wrist diagnoses, services, and procedures requires a solid working knowledge of wrist, hand, and distal forearm anatomy.
How many carpal bones are there in the wrist?
The wrist, or carpus, contains eight carpal bones. There are three bones in the proximal row (scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum) and five bones in the distal row (trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate, and pisiform). The trapezium is also known as the greater multangular, the trapezoid as the lesser multangular, and the scaphoid as the navicular bone.#N#In ICD-10-CM, most wrist conditions coded from chapter 13 (M codes) have a “3” in the fifth position of the code such as M19.031 Primary osteoarthritis, right wrist. Common conditions of the wrist and distal radius from chapters 13 and 19 (M and S codes) are:
What is the function of TFCC?
A primary function of the TFCC is to facilitate forearm rotation with a flexible connection between the distal radius and ulna, stabilizing the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) and supporting the ulnocarpal structures. The TFCC provides a continuous gliding surface across the distal radius/ulna for flexion, extension, supination, pronation, and radial/ulnar deviation. Damage to the TFCC is often caused by:
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for abnormal smeel
- 2. icd 10 code for influenza a virus
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for psa screening
- 4. office visit for bronchitis icd 10 code
- 5. icd 10 code for food impaction
- 6. icd-10-cm code for lumbar disc herniation
- 7. icd 10 code for wound on unspecified buttocks
- 8. icd code 10 for aspiration pneumonia
- 9. icd 10 code for heme positive stool
- 10. icd 10 code for fall from chair (initial encounter)