What is the ICD 10 code for dislocated shoulder?
Nontraumatic tear of flexor tendon of bilateral shoulders; Nontraumatic tear of flexor tendon of right shoulder; Spontaneous rupture of flexor tendon of right shoulder; Spontaneous rupture of flexor tendons of right shoulder. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M66.311. Spontaneous rupture of flexor tendons, right shoulder.
What is the ICD 10 code for total shoulder replacement?
Nov 22, 2016 · Best answers 0 Nov 22, 2016 #1 What ICD10 code do you use for Posterior Inferior Labral Tear? This was the diagnosis on an MRI result. J jkunsag Guest Messages 7 Best answers 0 Nov 22, 2016 #2 I assume this was a shoulder MRI. For left shoulder S43492A, right shoulder S43491A, which are Other sprain of left/right shoulder joint, initial encounter.
Could I have a labral tear in my shoulder?
Oct 01, 2021 · S43.431A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder, init. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S43.431A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is intrasubstance tear to right shoulder?
May 22, 2015 · ICD-10 Codes. S43.431 SLAP lesion of right shoulder. S43.432 SLAP lesion of left shoulder. S43.439 SLAP lesion of unspecified shoulder. Add seventh character for episode of care (A—initial encounter, D—subsequent encounter, S—sequela encounter) M75.80 Other shoulder lesions, unspecified shoulder. M75.81 Other shoulder lesions, right shoulder
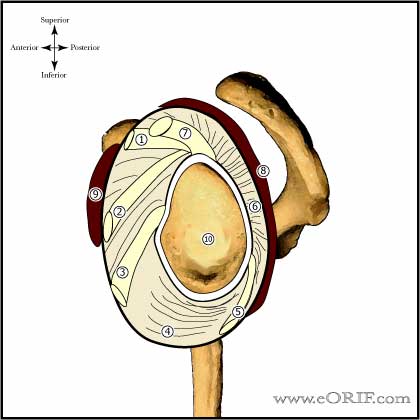
What is the ICD 10 code for posterior labral tear?
The ICD-10-CM code S43. 432A might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anterior to posterior tear of superior glenoid labrum of left shoulder or glenoid labrum tear.
What is the ICD 10 code for left posterior labral tear?
S43.432AICD-10-CM Code for Superior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder, initial encounter S43. 432A.
What is the ICD 10 code for labral tear?
S43.432ASuperior glenoid labrum lesion of left shoulder, initial encounter. S43. 432A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is a posterior labral tear shoulder?
Posterior Labral Tear (Lesion) This is a condition of the shoulder which usually affects younger people. It is most commonly caused by a fall onto the arm or a direct blow e.g. a rugby tackle. It is also seen in people who do a lot of throwing. The glenoid has a rim of tissue (the labrum) around its edge.
What is the ICD-10 code for right shoulder pain?
ICD-10 | Pain in right shoulder (M25. 511)
What is the ICD-10 code for right shoulder synovitis?
M65.811ICD-10 | Other synovitis and tenosynovitis, right shoulder (M65. 811)
What can cause a labral tear in the shoulder?
Common causes of labral tears in the shoulder include:Trauma, such as a fracture or dislocated shoulder.Overuse.Repetitive motion.
What is the ICD-10 code for right shoulder instability?
M25.311ICD-10 | Other instability, right shoulder (M25. 311)
What is ICD-10 code for rotator cuff tear?
A traumatic rotator cuff diagnosis is defined as an injury of the rotator cuff ligaments, muscles, and tendons and maps to rotator cuff sprain/strain and/or tear/rupture. ICD-10 codes S46. 011A (right shoulder) and S46. 012A (left shoulder) are for strain/tear/rupture OR S43.
What is a posterior superior labral tear?
A Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior (SLAP) tear is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder, which is the ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint. The term SLAP stands for Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior.
What is a posterior inferior labrum tear?
A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes.Mar 7, 2022
Where is the posterior labrum?
The labrum is a type of cartilage found in the shoulder joint. The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint where the arm meets the body.
What is posterior shoulder instability?
Posterior shoulder instability may result in injury to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament as well as the posterior labrum, or a reverse Bankart lesion. Tears can extend to involve multiple regions of the labrum and have other associated injuries.
What is the effect of the labrum on the shoulder?
If the labrum or capsule is injured, such as in the Bankart lesion, this suction is lost, and this decreases the stability of the shoulder.
What is SLAP tear?
The most studied injury to the labrum is the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear. Anterior dislocations of the shoulder can be associated with a disruption of the anteroinferior labrum and anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament, also known as a Bankart lesion.
What is the labrum?
The labrum also serves as an attachment point for the long head of the biceps tendon, the glenohumeral ligaments, and the long head of the triceps tendon, forming a periarticular system of fibers that gives the shoulder joint much needed stability [ 4 ]. The vascular supply to the labrum is from the posterior humeral circumflex artery, ...
Where is the glenoid labrum located?
The glenoid labrum is a densely fibrous tissue that is located along the periphery of the glenoid bone [ 1] ( Fig. 15.1 ). As the outer labrum transitions from the periphery to its articulation with the glenoid, the histology changes from fibrous to a small fibrocartilaginous zone at the junction with the glenoid [ 2 ].
Where does the vascular supply to the labrum come from?
The vascular supply to the labrum is from the posterior humeral circumflex artery, the circumflex scapular branch of the subscapular artery, and the suprascapular artery. These arteries come from the periphery of the labrum, making the articular margins of the labrum avascular [ 2 ]. It has also been shown that the superior labrum has less vascular ...
What are the symptoms of a slap tear?
Patients may have mechanical symptoms, such as catching, popping, or grinding with rotation of the shoulder. Many patients with a SLAP tear will also have other shoulder disease, making clinical diagnosis challenging [ 11 ].
What is the labrum of the shoulder?
The glenoid labrum is a densely fibrous tissue that is located along the periphery of the glenoid portion of the scapula. It functions to provide increased stability, while still allowing great range of motion. In addition, it serves as an attachment point for tendons and ligaments. Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum. The two most common sites include the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear, occurring with forced traction of the shoulder and/or direct compression, and the Bankart lesion, created by episodes of anterior instability. Symptoms of deep-seated pain (SLAP tears) or anterior instability (Bankart lesions) are the most common presentations, but concomitant shoulder pathology makes diagnosis challenging and clouds many physical exam findings. Physical exam includes several clinical tests, with the O’Brien’s test being the most common for SLAP tears and the surprise test as the most accurate for Bankart lesions. As in any case of shoulder pain, the initial imaging of choice is plain radiography. With a high clinical likelihood of labral disease, this should be followed by either magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance arthrography. Initial management of SLAP tears involves exhausting non-operative treatment, focusing on stretching and strengthening of the dynamic shoulder stabilizers. Initial management of Bankart lesions (after reduction) may be conservative or operative and depends on demographic and radiographic factors. Surgical management of SLAP tears are reserved for those who have failed conservative management. Operative treatment of Bankart tears are reserved for those with recurrent instability despite conservative treatment.
What is posterior shoulder instability?
Posterior shoulder instability may result in injury to the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament as well as the posterior labrum, or a reverse Bankart lesion. Tears can extend to involve multiple regions of the labrum and have other associated injuries.
What is the labrum?
The labrum also serves as an attachment point for the long head of the biceps tendon, the glenohumeral ligaments, and the long head of the triceps tendon, forming a periarticular system of fibers that gives the shoulder joint much needed stability .
What is the effect of the labrum and capsule on the shoulder?
If the labrum or capsule is injured, such as in the Bankart lesion, this suction seal is lost, and this decreases the stability of the shoulder.
What happens to the labrum as it transitions from the periphery to the articulation?
As the outer labrum transitions from the periphery to its articulation with the glenoid, the histology changes from fibrous to a small fibrocartilaginous zone at the junction with the glenoid articular cartilage. The labrum increases the height and width of the glenoid while also giving extra depth to the joint.
What is the most studied injury to the labrum?
Tears can occur in all regions of the labrum. The most studied injury to the labrum is the superior labral anterior-posterior (SLAP) tear.
Where does the vascular supply to the labrum come from?
The vascular supply to the labrum is from the posterior humeral circumflex artery, the circumflex scapular branch of the subscapular artery, and the suprascapular artery. These arteries come from the periphery of the labrum, making the articular margins of the labrum avascular.
What is the ICd 10 code for glenoid labrum tear?
S43.431A is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder, initial encounter. The code S43.431A is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code S43.431A might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anterior to posterior tear of superior glenoid labrum of right shoulder or glenoid labrum tear.#N#S43.431A is an initial encounter code, includes a 7th character and should be used while the patient is receiving active treatment for a condition like superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder. According to ICD-10-CM Guidelines an "initial encounter" doesn't necessarily means "initial visit". The 7th character should be used when the patient is undergoing active treatment regardless if new or different providers saw the patient over the course of a treatment. The appropriate 7th character codes should also be used even if the patient delayed seeking treatment for a condition.
How to diagnose shoulder pain?
Health care providers diagnose shoulder problems by using your medical history, a physical exam, and imaging tests. Often, the first treatment for shoulder problems is RICE. This stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Other treatments include exercise and medicines to reduce pain and swelling.
What is shoulder MRI?
Shoulder MRI scan (Medical Encyclopedia) Shoulder pain (Medical Encyclopedia) Using your shoulder after surgery (Medical Encyclopedia) [ Learn More in MedlinePlus ] Sprains and Strains. A sprain is a stretched or torn ligament. Ligaments are tissues that connect bones at a joint.
Why are the shoulders unstable?
Your shoulders are the most movable joints in your body. They can also be unstable because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the shoulder socket that holds it. To remain in a stable or normal position, the shoulder must be anchored by muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
What is the ICd 10 code for glenoid labrum tear?
S43.431D is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder, subsequent encounter. The code S43.431D is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code S43.431D might also be used to specify conditions or terms like anterior to posterior tear of superior glenoid labrum of right shoulder or glenoid labrum tear. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.#N#S43.431D is a subsequent encounter code, includes a 7th character and should be used after the patient has completed active treatment for a condition like superior glenoid labrum lesion of right shoulder. According to ICD-10-CM Guidelines a "subsequent encounter" occurs when the patient is receiving routine care for the condition during the healing or recovery phase of treatment. Subsequent diagnosis codes are appropriate during the recovery phase, no matter how many times the patient has seen the provider for this condition. If the provider needs to adjust the patient's care plan due to a setback or other complication, the encounter becomes active again.
What are the bones of the shoulder?
Your shoulder joint is composed of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone). Your shoulders are the most movable joints in your body. They can also be unstable because the ball of the upper arm is larger than the shoulder socket that holds it. To remain in a stable or normal position, the shoulder must be anchored by muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Is S43.431D a POA?
S43.431D is exempt from POA reporting - The Present on Admission (POA) indicator is used for diagnosis codes included in claims involving inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals. POA indicators must be reported to CMS on each claim to facilitate the grouping of diagnoses codes into the proper Diagnostic Related Groups (DRG). CMS publishes a listing of specific diagnosis codes that are exempt from the POA reporting requirement. Review other POA exempt codes here.
What is posterior labral tear?
Posterior Labral Tear. A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex , and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder.
What are the symptoms of a posterior shoulder?
vague, nonspecific posterior shoulder pain is the most common symptoms. worsens with provocative activities that apply a posteriorly directed force to the shoulder. ex: pushing heavy doors, bench press, push-ups. clicking or popping in the shoulder with range of motion . sense of instability.
Which branch of the axillary nerve is at risk during arthroscopic stabilization?
posterior branch of the axillary nerve is at risk during arthroscopic stabilization. travels within 1 mm of the inferior shoulder capsule and glenoid rim. at risk during suture passage at the posterior inferior glenoid. Overtightening of posterior capsule. can lead to anterior subluxation or coracoid impingement.

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2013 icd 9 code for hyperlipoproteinemia
- 2. icd 10 code for cyst in sacral coccyx
- 3. icd 10 code for multiple rib fracture subsequent encounter
- 4. icd 10 code for gastric pancreatitis
- 5. icd 10 code for generalized seizure
- 6. icd 9 code for chronic hepatitis
- 7. 2017 icd 10 code for hallux valgus
- 8. icd code for suprapubic region abcess
- 9. icd code 10 for diverticulitis s/p resection
- 10. icd 10 code for lung cancer stage 4