What causes hearing loss in the right ear?
Causes of hearing loss in one ear. There are a number of potential causes of hearing loss in just one ear, including but not limited to: Meniere’s disease; acoustic neuroma; viral or bacterial infection; physical damage to the ear; head trauma; circulatory system disorders; genetic or inherited disorders
What are the early signs of hearing loss?
What are the early signs of hearing loss?
- Sound which is stifled or unclear in children. ...
- Feeling tired, especially after a social gathering. ...
- You read lips more than making eye contact. ...
- You cannot hear voices in noisy places. ...
- You are hearing it loud. ...
- Your ears are choked. ...
- You notice tinnitus, or ringing in the ears. ...
How do doctors diagnose hearing loss?
- Prevention and Early Detection of Hearing Loss are Important. Don’t wait until you show signs of hearing loss. ...
- Children Should Have Their Hearing Tested. ...
- Regular Check-Ups Can Help Identify Early Hearing Loss. ...
- Learn More about Hearing Tests
- For More Information. ...
What caused my hearing loss?
While causes vary from individual to individual ... head injuries and infections can play a role in hearing loss.” But this isn’t all. Common signs include difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds, trouble understanding conversations over background ...
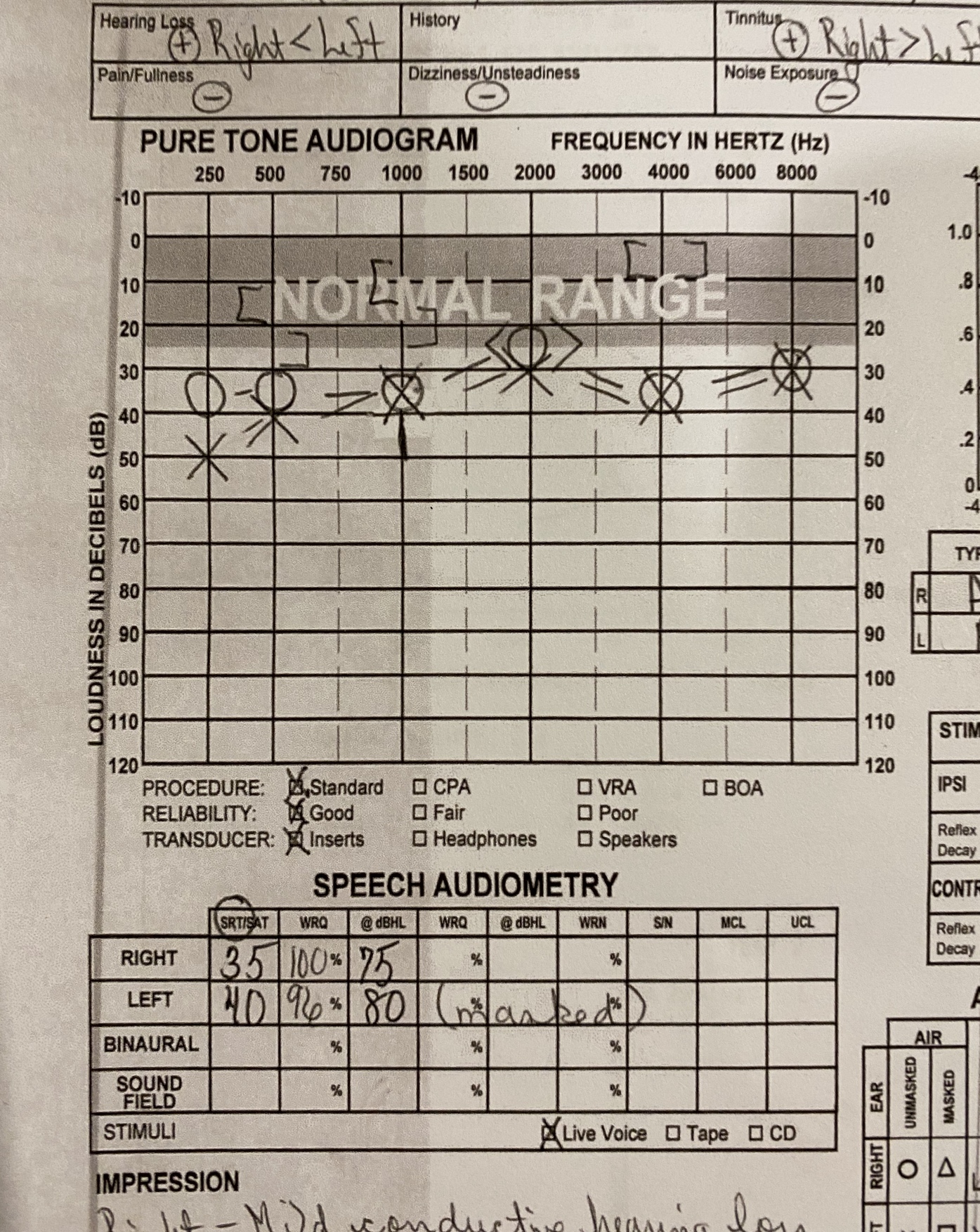
What is conductive hearing loss?
When will the ICd 10-CM H90.2 be released?
About this website
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H90.0
Free, official coding info for 2022 ICD-10-CM H90.0 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD-9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping and more.
Conductive hearing loss – Find causes, symptoms & treatment here
A conductive hearing loss occurs when the ability to conduct sound from the external and middle ear into the inner ear is reduced or lost. You can have a conductive hearing loss in one ear or in both ears. In this article, you can read more about the causes and the symptoms of conductive hearing loss and find information about treatment options.
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D72.829
Free, official coding info for 2022 ICD-10-CM D72.829 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD-9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping and more.
When will the ICD-10-CM H90.A1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H90.A1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can H90.A1 be used for reimbursement?
H90.A1 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is occupational hearing loss?
Occupational hearing loss (Medical Encyclopedia) Otosclerosis (Medical Encyclopedia) Sensorineural deafness (Medical Encyclopedia) Nonsyndromic hearing loss Nonsyndromic hearing loss is a partial or total loss of hearing that is not associated with other signs and symptoms.
What causes hearing loss?
This type is usually permanent. The other kind happens when sound waves cannot reach your inner ear. Earwax buildup, fluid, or a punctured eardrum can cause it. Treatment or surgery can often reverse this kind of hearing loss.
What is the name of the bone that helps transfer sound from the eardrum to the inner ear?
The middle ear contains three tiny bones that help transfer sound from the eardrum to the inner ear. Some forms of nonsyndromic hearing loss, particularly a type called DFNX2, involve changes in both the inner ear and the middle ear.
What is the H90.41 code?
H90.41 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of sensorineural hearing loss, unilateral, right ear, with unrestricted hearing on the contralateral side. The code H90.41 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
Which part of the brain processes sound?
The inner ear processes sound and sends the information to the brain in the form of electrical nerve impulses. Less commonly, nonsyndromic hearing loss is described as conductive, meaning it results from changes in the middle ear.
Can hearing loss affect both ears?
Hearing loss can affect one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral). Degrees of hearing loss range from mild (difficulty understanding soft speech) to profound (inability to hear even very loud noises). The term "deafness" is often used to describe severe-to-profound hearing loss.
Can hearing problems get worse?
Untreated, hearing problems can get worse. If you have trouble hearing, you can get help. Possible treatments include hearing aids, cochlear implants, special training, certain medicines, and surgery.
What is hearing loss?
Hearing loss due to damage or impairment of both the conductive elements (hearing loss, conductive) and the sensorineural elements (hearing loss, sensorineural) of the ear.
When will the ICd 10-CM H90.8 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H90.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is conductive hearing loss?
Right conductive hearing loss due to disorder of middle ear. Right middle ear conductive hearing loss. Clinical Information. Hearing loss caused by a problem in the outer ear or middle ear. Conductive losses usually affect all frequencies to the same degree.
When will the ICd 10-CM H90.2 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H90.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for chronic opiate dependence
- 2. icd 9 code for orif
- 3. icd-10 code for alpha-fetoprotein tumor marker
- 4. icd-10 code for screening blood horomone levels
- 5. icd 10 code for encounter to establish care
- 6. icd 10 code for nondisplaced distal right clavicle fracture
- 7. icd 10 code for wide qrs
- 8. icd-10-cm code for encounter for reprogramming of aicd
- 9. icd 10 code for right ankle fx
- 10. icd 10 code for tear duct stenosis