What is artery flows into right subclavian?
The Anatomy of the Subclavian Artery
- Anatomy. The left and right subclavian arteries are located in the thorax (chest) underneath the clavicles (commonly known as the collarbones).
- Function. The primary function of the subclavian artery is to provide oxygen-rich blood to certain areas of the upper body.
- Clinical Significance. ...
Is aberrant right subclavian artery hereditary?
Aberrant subclavian artery is a rare vascular anomaly that is present from birth. It usually causes no symptoms and is often discovered as an incidental finding (such as through a barium swallow or echocardiogram ). Occasionally the anomaly causes swallowing difficulty ( dysphagia lusoria).
What does subclavian artery mean?
The subclavian artery is a large, major blood vessel that supplies oxygen -rich blood to the chest and upper limbs of the body. There are right and left subclavian arteries, and they received their name from the fact that they are both located under the clavicles, commonly known as the collar bones.
Is the subclavian artery an elastic artery?
Elastic arteries (conducting vessels) Small veins (capacitance vessels) Lymph node Capillaries (exchange vessels) Thoroughfare Precapillary sphincter channel Lymphatic ... Subclavian artery Subclavian artery Aortic arch Ascending aorta Coronary artery Thoracic aorta (above diaphragm) Renal artery Superficial palmar arch Radial artery
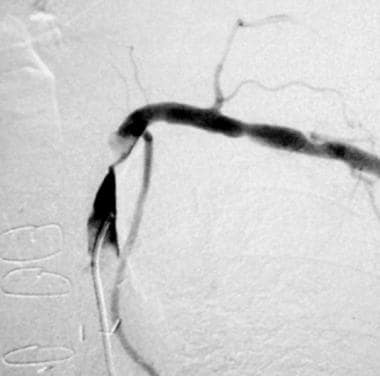
What is the ICD 10 code for subclavian stenosis?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I65. 22 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I65.
What is subclavian stenosis?
In subclavian stenosis, the artery is simply narrowed, leading to decreased blood flow beyond the area of blockage. When the subclavian blockage is severe, or if the artery is completely blocked, a condition called 'subclavian steal' can occur (Figure 4).
Where is the right subclavian artery located?
Branches of the Subclavian Artery The left and right subclavian arteries are located in the thorax (chest) underneath the clavicles (commonly known as the collarbones).
What is the ICD 10 code for arterial stenosis?
ICD-10 code I65. 2 for Occlusion and stenosis of carotid artery is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What causes stenosis of the subclavian artery?
The most common cause of subclavian artery stenosis is atherosclerosis but other causes include congenital abnormalities such as arteria lusoria (aberrant subclavian artery) or right sided aortic arch that can cause compression of the right subclavian artery leading to congenital subclavian steal syndrome,,.
How do you diagnose subclavian stenosis?
A meticulous examination of segmental pulses and pressures, as well as judicious use of duplex ultrasonography, magnetic resonance angiography, computed tomography angiography, or conventional angiography can confirm the presence of subclavian stenosis.
What is the right subclavian artery?
The right subclavian artery is a branch of the brachiocephalic trunk and the left arises directly from the arch of the aorta. It lies posterior to the insertion of the scalenus anterior on the first rib. The subclavian vein runs parallel to the artery but in front of the scalenus anterior slightly at a lower level.
Is there a right and left subclavian artery?
The subclavian artery is a paired arterial vessel of the thorax. The right and left arteries have different origins; the left subclavian artery originates directly from the aortic arch, while the right subclavian artery originates from the brachiocephalic trunk.
What does the right subclavian artery branch into?
The main branches of the subclavian artery include the vertebral artery, the internal thoracic artery, the thyrocervical trunk, the costocervical trunk, and the dorsal scapular artery. Once the subclavian artery reaches the axilla, it becomes known as the axillary artery.
What is the ICD-10 code for left subclavian artery occlusion?
ICD-10 code I82. B22 for Chronic embolism and thrombosis of left subclavian vein is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is stenosis of the arteries?
Stenosis, in general, refers to any condition in which a blood vessel -- such as an artery -- or other tubular organ becomes abnormally narrow.
What is the ICD-10 code for right common femoral artery stenosis?
213.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for administration of flu vaccine
- 2. icd-10-pcs code for percutaneous fetal spinal tap to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid
- 3. icd-10-cm code for acute peritonitis
- 4. icd 10 code for mass in brain
- 5. icd 9 code for right sided weakness
- 6. icd 10 code for superficial bite bite left leg
- 7. icd code for viral uri
- 8. icd 10 code for vena cava syndrome post placement of hickman catheter
- 9. icd 10 code for tendonitis crepitans back
- 10. icd 10 code for stop taking medication