Cutaneous abscess of right hand
- L02.511 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L02.511 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L02.511 - other international versions of ICD-10 L02.511 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for intracranial abscess?
Intracranial abscess and granuloma 1 G06.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM G06.0 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G06.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 G06.0 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for cutaneous abscess of face?
Cutaneous abscess of face 1 L02.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM L02.01 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L02.01 - other international versions of ICD-10 L02.01 may differ. More ...
What is the ICD 10 code for abscess of right ear?
H60.02 ICD-10-CM Code for Abscess of right external ear H60.01 ICD-10 code H60.01 for Abscess of right external ear is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process. Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the ICD 10 code for abscess and granuloma?
Intracranial abscess and granuloma 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code G06.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM G06.0 became effective on October 1, 2020.
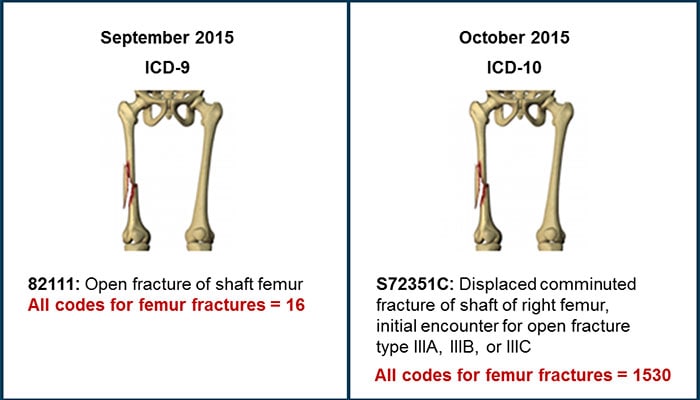
What is the ICD-10 code for facial abscess?
ICD-10 code L02. 01 for Cutaneous abscess of face is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 DX code for abscess?
L02. 91 - Cutaneous abscess, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for abscess forehead?
L02. 01 - Cutaneous abscess of face | ICD-10-CM.
What is L02 611?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cutaneous abscess of right foot L02. 611.
What is the code for abscess?
Group 1CodeDescription10060INCISION AND DRAINAGE OF ABSCESS (EG, CARBUNCLE, SUPPURATIVE HIDRADENITIS, CUTANEOUS OR SUBCUTANEOUS ABSCESS, CYST, FURUNCLE, OR PARONYCHIA); SIMPLE OR SINGLE6 more rows
What is the ICD 10 code for multiple abscess?
L02. 91 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L02.
What is cutaneous abscess of face?
A cutaneous abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface. Symptoms and signs are pain and a tender and firm or fluctuant swelling. Diagnosis is usually obvious by examination. Treatment is incision and drainage.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the CPT code for incision and drainage of abscess?
Procedure codes 10060 and 10061 represent incision and drainage of an abscess involving the skin, subcutaneous and/or accessory structures.
How do you describe an abscess?
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
What is the ICD-10 code for cellulitis?
ICD-10 code L03. 90 for Cellulitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 code for right foot infection?
Direct infection of right ankle and foot in infectious and parasitic diseases classified elsewhere. M01. X71 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the CPT code for paronychia?
Paronychia, when sufficiently treated with avulsion of the nail only, should be billed with CPT code 11730 and not as an incision and drainage. Permanent correction of recurring ingrown toenail by nail resection or wedge excision of the nail lip should be billed with CPT code 11750 or 11765 and not as an incision and drainage.
What is the ICd 10 code for suppurative hidradenitis?
Claims for CPT codes 10060 or 10061 with diagnosis of furuncle/carbuncle (ICD-10-CM code L02.621, L02.622, L02.631, L02.632), suppurative hidradenitis (ICD-10-CM code L73.2) will be subject to review, as these diagnoses are not commonly found in the foot.
Does ICD-10-CM code assure coverage?
The correct use of an ICD-10-CM code listed below does not assure coverage of a service. The service must be reasonable and necessary in the specific case and must meet the criteria specified in the attached determination.
What is CPT 31040?
Have your provider look at CPT 31040, I think this might be the way to go.#N#31040 - Pterygomaxillary fossa surgery, any approach#N#In this procedure, the provider uses any approach for a surgery involving the pterygomaxillary fossa, a trench–like structure roughly located between the upper jaw and orbit of the eye.#N#Clinical Responsibility#N#When the patient is appropriately prepped and anesthetized, the provider begins the approach to the pterygomaxillary fossa. In a typical procedure, he makes an intraoral incision in the parapharyngeal space. The provider carries this incision across the maxilla exposing the anterior wall of the maxilla, which is the upper jaw. He then also creates an opening in the posterior wall of the maxilla, approaching the pterygomaxillary fossa. He then performs the required surgery, such as removing a lesion in the fossa and tying the vidian nerves and maxillary artery in the fossa. The provider then closes the incision in the mouth with sutures in a single layer. The goal of the procedure is to treat any tumor or abscess present in the parapharyngeal space.
Where is the pterygomaxillary fossa located?
In this procedure, the provider uses any approach for a surgery involving the pterygomaxillary fossa, a trench–like structure roughly located between the upper jaw and orbit of the eye.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for sepsis secondary to pneumonia
- 2. icd 10 code for aggressive behavior of adult
- 3. icd 9 code for behavioral disorder
- 4. icd 10 code for uti due to enterococcus
- 5. icd 10 code for osteopenia hip
- 6. icd 10 code for hemachezia
- 7. icd 10 code for pressure ulcer stage 2 coccyx
- 8. icd 9 code for .pathological facture, neck of femur
- 9. icd 10 cm code for sialadenitis)
- 10. icd 10 code for i21.3