How to confirm an ectopic pregnancy?
To find out if you have an ectopic pregnancy, your doctor will likely do:
- A pelvic exam to check the size of your uterus and feel for growths or tenderness in your belly.
- A blood test that checks the level of the pregnancy hormone (hCG). This test is repeated 2 days later. ...
- An ultrasound. This test can show pictures of what is inside your belly. ...
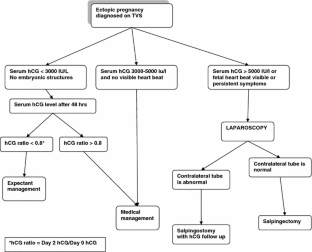
How to recognize and treat an ectopic pregnancy?
Treatment
- Medication. An early ectopic pregnancy without unstable bleeding is most often treated with a medication called methotrexate, which stops cell growth and dissolves existing cells.
- Laparoscopic procedures. Salpingostomy and salpingectomy are two laparoscopic surgeries used to treat some ectopic pregnancies.
- Emergency surgery. ...
Who is at risk of tubal ectopic pregnancy?
Women conceiving at or after 35 years of age have a much higher risk of having an ectopic pregnancy. Women with a history of pelvic surgery, abdominal surgery, or multiple abortions are also at risk. Women with pelvic inflammatory disease are at risk of having an ectopic pregnancy.
What are the chances of having an ectopic pregnancy?
The following are all associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) – inflammation of the female reproductive system, usually caused by a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- previous ectopic pregnancy – the risk of having another ectopic pregnancy is around 10%
- previous surgery on your fallopian tubes – such as an unsuccessful female sterilisation procedure
What is the ICD-10 code for ectopic tubal pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM O00. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of O00.
What is right tubal pregnancy?
A tubal pregnancy — the most common type of ectopic pregnancy — happens when a fertilized egg gets stuck on its way to the uterus, often because the fallopian tube is damaged by inflammation or is misshapen. Hormonal imbalances or abnormal development of the fertilized egg also might play a role.
How do you code an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy is reported using an ICD-10-CM code from category O00. - (ectopic pregnancy), which is divided into five subcategories: O00. 0, abdominal pregnancy....Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include:Light or heavy vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain (mild or severe)Light headedness.Shoulder pain.
What is right tubal pregnancy without intrauterine pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy — In an ectopic pregnancy, the developing embryo does not implant on the endometrial wall, but instead attaches to some other surface. For ninety eight percent of pregnancies outside the uterus, that surface is within the fallopian tube. This is also called a tubal pregnancy.
What are the types of ectopic pregnancy?
Conclusion. Six unusual types of ectopic pregnancy were illustrated and discussed in this article. These are heterotopic pregnancy (combined intra- and extra uterine pregnancies), scar pregnancy, interstitial pregnancy, cervical pregnancy, abdominal pregnancy and ovarian pregnancy.
What are 3 causes of an ectopic pregnancy?
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes from a previous medical condition, infection, or surgery.hormonal factors.genetic abnormalities.birth defects.medical conditions that affect the shape and condition of the fallopian tubes and reproductive organs.
What is the ICD 9 code for ectopic pregnancy?
ECTOPIC AND MOLAR PREGNANCY ICD-9 Code range 630-633.
What is adnexal ectopic pregnancy?
An adnexal mass is more specific for an ectopic pregnancy when it contains a yolk sac or a living embryo (,Fig 2) or when it moves independently from the ovary (,Fig 3) (,22). However, an extrauterine mass may not be detected at transvaginal US in 15%–35% of patients with an ectopic pregnancy (,12).
What ICD-10-CM code is reported for rupture of fallopian tube due to pregnancy?
6 Damage to pelvic organs and tissues following abortion and ectopic and molar pregnancy.
Can you have intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy?
Heterotopic pregnancy is a rare complication in which both an extra-uterine (ectopic pregnancy) and an intrauterine pregnancy occur simultaneously. In common person terms, it's two pregnancies happening at the same time, one in the uterus and one outside the uterus.
What is the discriminatory zone for ectopic?
The discriminatory zone is the serum hCG level above which a gestational sac should almost always be visualized on ultrasound when an IUP is present. This level varies by laboratory and institution. For TVUS, we use a discriminatory zone of 3510 milli-international units/mL.
Can intrauterine pregnancy become ectopic?
A heterotopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which both extrauterine (ectopic) pregnancy and intrauterine pregnancy occur simultaneously. It may also be referred to as a combined ectopic pregnancy, multiple‑sited pregnancy, or coincident pregnancy.
Where does ectopic pregnancy occur?
The most common (>96%) type of ectopic pregnancy in which the extrauterine embryo implantation occurs in the fallopian tube, usually in the ampullary region where fertilization takes place.
What causes ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy that occurs in the fallopian tube instead of the uterine corpus. Causes include pelvic inflammatory disease and prior pelvic surgery. It may result in severe abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and tubal rupture.
Can O00.1 be used for reimbursement?
O00.1 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is the ICd 10 code for right tubal pregnancy?
Right tubal pregnancy with intrauterine pregnancy 1 O00.111 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM O00.111 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of O00.111 - other international versions of ICD-10 O00.111 may differ.
When will the ICD-10-CM O00.111 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM O00.111 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is ruptured ectopic pregnancy?
ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Clinical Information. A condition in which a fertilized egg grows outside of the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. Symptoms include sharp pain on one side of the abdomen and bleeding from the vagina.
Where do most ectopic pregnancies occur?
Most ectopic pregnancies (>96%) occur in the fallopian tubes , known as tubal pregnancy. They can be in other locations, such as uterine cervix; ovary; and abdominal cavity (pregnancy, abdominal). An abnormal pregnancy in which the egg is implanted anywhere outside the corpus uteri. Development of a fertilized ovum outside of the uterine cavity.
Where does the baby grow when a woman is pregnant?
The uterus, or womb, is an important female reproductive organ. It is the place where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. If you have an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg grows in an abnormal place, outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes.
What is renal failure?
Renal failure after ectopic pregnancy. Clinical Information. A condition in which a fertilized egg grows outside of the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. Symptoms include sharp pain on one side of the abdomen and bleeding from the vagina.
What is the Z34 code?
supervision of normal pregnancy ( Z34.-) mental and behavioral disorders associated with the puerperium ( F53.-) code from category Z3A, Weeks of gestation, to identify the specific week of the pregnancy, if known. A condition in which a fertilized egg grows outside of the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy (not in uterus) with urinary tract infection. Ectopic pregnancy (not in uterus)with intrauterine pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy with cardiac arrest. Ectopic pregnancy with damage to pelvic organs. Ectopic pregnancy with genital tract infection.
Where do ectopic pregnancies occur?
Most ectopic pregnancies (>96%) occur in the fallopian tubes , known as tubal pregnancy. They can be in other locations, such as uterine cervix; ovary; and abdominal cavity (pregnancy, abdominal). An abnormal pregnancy in which the egg is implanted anywhere outside the corpus uteri.
What is the code for weeks of gestation?
code from category Z3A, Weeks of gestation, to identify the specific week of the pregnancy, if known. A condition in which a fertilized egg grows outside of the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. Symptoms include sharp pain on one side of the abdomen and bleeding from the vagina.
Where does the baby grow when a woman is pregnant?
The uterus, or womb, is an important female reproductive organ. It is the place where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. If you have an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg grows in an abnormal place, outside the uterus, usually in the fallopian tubes.
How many weeks are in the first trimester?
Trimesters are counted from the first day of the last menstrual period. They are defined as follows: 1st trimester- less than 14 weeks 0 days. 2nd trimester- 14 weeks 0 days to less than 28 weeks 0 days. 3rd trimester- 28 weeks 0 days until delivery. Type 1 Excludes.
What is the ICD-10 code for ectopic pregnancy?
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include: Light or heavy vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain (mild or severe) An ectopic pregnancy is reported using an ICD-10-CM code from category O00.- (ectopic pregnancy), which is divided into five subcategories: An abdominal pregnancy is a rare type of ectopic pregnancy, occurring in about 1% of ectopic cases, ...
Where does an unspecified ectopic pregnancy occur?
An unspecified ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized ovum implants itself anywhere other than the uterus, but the location is not specified.
What is ectopic pregnancy?
A: An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants itself outside the uterus (e.g., in a fallopian tube, ovary, or within the abdomen). It can cause life-threatening bleeding and requires immediate medical attention. In more than 90% of cases, the egg implants in a fallopian tube (i.e., tubal pregnancy).
Can a tubal pregnancy be treated?
A tubal pregnancy can sometimes be treated with drug therapy or with surgery to remove the incorrectly implanted egg. If a patient is diagnosed with the condition early, the affected fallopian tube can be preserved. In other cases, the mass will cause irreversible damage to the fallopian tube and the tube may need to be removed.
Is abdominal pregnancy rare?
An abdominal pregnancy is a rare type of ectopic pregnancy, occurring in about 1% of ectopic cases, in which the fertil ized ovum implants itself somewhere within the peritoneal cavity but outside of the fallopian tube, ovary, uterus, or broad ligament.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for close head injury
- 2. icd 10 code for intervertebral disc syndrome
- 3. icd 10 code for acute kidney injury superimposed on ckd
- 4. icd 9 code for elevated platelets
- 5. icd 10 code for severe sepsis
- 6. icd 9 code for ventral hernia repair
- 7. icd 10 code for lung cancer post cryosurgery
- 8. icd 10 code for dmi1
- 9. icd 10 code for alien abduction
- 10. what is the correct icd 10 code for peripheral edema