What is suspicious opacity in the right upper lobe?
This could be due to:
- the air spaces becoming partially filled with fluid, pus, or cells
- the walls of the alveoli, which are the tiny air sacs in the lungs, thickening
- the space between the lungs thickening
What are the causes of lung lesions?
What Is Inflammation of the Lungs?
- Lung Inflammation Symptoms. Symptoms of lung inflammation can come on very suddenly or take a little longer to develop. ...
- Causes. Your lungs can become inflamed when they are infected, irritated, or damaged. ...
- Diagnosis. ...
- Treatment. ...
- Summary. ...
- A Word From Verywell. ...
What is suspicious densities in upper lobe?
Those densities could be a focal lesion in the upper lobe or apical lobes of lung,so it can be revealed by the apicolordotic view,but if your symptoms has disappeared and you do not have coughing or any other symptoms then it could have been artifact..
Is lung infiltrate in upper right lobe an infection?
Summary: Right middle lobe (RML) syndrome is defined as recurrent or chronic obstruction or infection of the middle lobe of the right lung. Nonobstructive causes of middle lobe syndrome include inflammatory processes and defects in the bronchial anatomy and collateral ventilation. Then, can lung infiltrates be cancer?
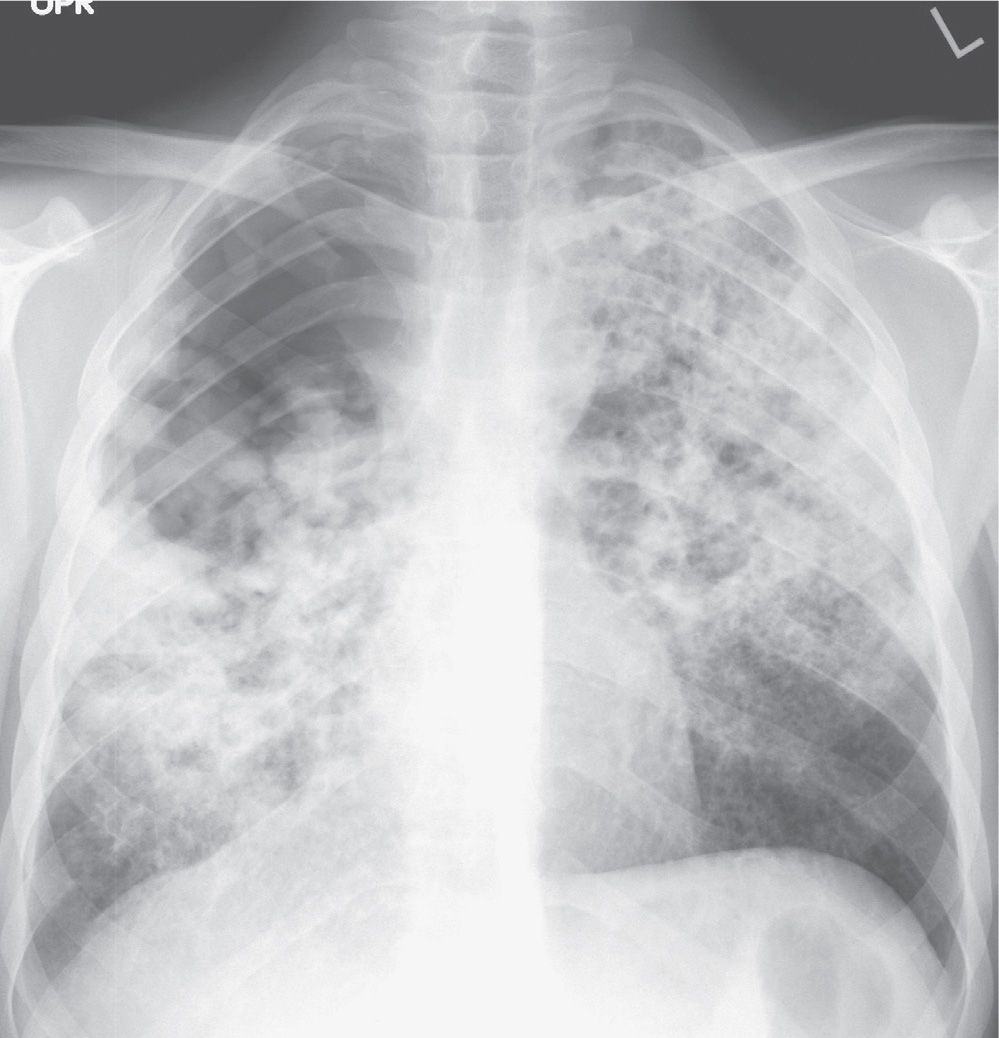
What is the ICD-10 code for lung lesion?
ICD-10-CM Code for Solitary pulmonary nodule R91. 1.
What is the ICD-10 code for right upper lobe?
ICD-10-CM Code for Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe, right bronchus or lung C34. 11.
What is the ICD-10 code for right lung nodule?
R91. 1 - Solitary pulmonary nodule. ICD-10-CM.
What is Malignant neoplasm of upper lobe right bronchus or lung?
Bronchogenic carcinoma is a malignant neoplasm of the lung arising from the epithelium of the bronchus or bronchiole. Accounts for 14% of all new cancers in males and 13% of all new cancers in females. Seventy percent of all lung cancer deaths occur between the ages of 55 and 74.
Where is the right upper lobe?
the lungThe right upper lobe of the lung is located in the right superior corner of the thoracic cavity lateral to the trachea and esophagus. It is superior to the horizontal and oblique fissures, which separates the upper lobe from the middle and lower lobes of the right lung.
Is a lobectomy an excision or resection?
Resection includes all of a body part or any subdivision of a body part having its own body part value in ICD-10-PCS, while excision includes only a portion of a body part. Examples of resection are total nephrectomy, total lobectomy of lung, total mastectomy, resection cecum, prostatectomy, or cholecystectomy.
What is cavitary lesion of lung?
Right upper lobe cavitary lung lesion. A lung cavity is defined radiographically as a lucent area contained within a consolidation, mass, or nodule. 1. Cavities usually are accompanied by thick walls, greater than 4 mm.
What is ICD 10 code for cavitary lesion?
J98. 4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J98. 4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a pulmonary nodule in the lung?
A lung (pulmonary) nodule is an abnormal growth that forms in a lung. You may have one nodule on the lung or several nodules. Nodules may develop in one lung or both. Most lung nodules are benign (not cancerous). Rarely, pulmonary nodules are a sign of lung cancer.
What is a malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung?
A malignant neoplasm of the bronchus and lung, also known as bronchogenic carcinoma or lung cancer, is a malignant cancer that originates in the bronchi, bronchioles, or other parts of the lung. The cancer begins when the cells of the lung begin to mutate.
What is a malignant neoplasm in the lung?
A malignant neoplasm, or lung cancer, is much more concerning. It requires immediate attention. Malignant lung neoplasms are characterized by abnormal-looking cells that divide uncontrollably, leading to tumors in the lungs (primary neoplasms) that may spread to other parts of the body (metastatic neoplasm).
What is the difference between Nsclc and SCLC?
The pace of treatment for SCLC is generally faster than NSCLC due to the tumors' ability to quickly spread. NSCLC is less aggressive; however, it is typically identified at a later stage. In fact, only an approximate 25% of NSCLC patients are diagnosed at stage 1 or 2.
Open Approach
Cutting through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to expose the site of the procedure
Percutaneous Approach
Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach the site of the procedure
Percutaneous Endoscopic Approach
Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach and visualize the site of the procedure
Via Natural or Artificial Opening Approach
Entry of instrumentation through a natural or artificial external opening to reach the site of the procedure
Via Natural or Artificial Opening Endoscopic Approach
Entry of instrumentation through a natural or artificial external opening to reach and visualize the site of the procedure

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for myocardiopathy
- 2. icd 10 code for right dermoid cyst
- 3. icd 10 code for dehydration with hypernatremia
- 4. icd 10 code for status urostomy
- 5. icd 10 code for palsy due to cerebral infarction
- 6. icd 10 code for paoxysmal afib
- 7. icd 10 code for left hip prosthetic joint infection
- 8. icd 10 code for ua c&s
- 9. icd 10 code for positive ppd skin test
- 10. icd 10 code for fell off bed