How do you get rid of salivary gland stones?
Method 2 Method 2 of 3: Clearing the Blocked Salivary Duct at Home
- Drink a lot of water to keep the mouth hydrated. ...
- Take over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and swelling. If you’re experiencing intense pain from a blocked salivary gland, relieve your symptoms with an over-the-counter pain reliever.
- Suck on citrus fruits or hard candies to dislodge a stone. ...
- Massage the salivary gland with your fingers. ...
How do you remove a salivary gland stone?
- Stay hydrated.
- Massage the areas where salivary glands are located several times a day.
- Suck on hard candy or lollipops. To avoid cavities, try a sugar-free candy, like lemon heads.
- Take medications that increase saliva flow.
What is the treatment for salivary stone?
- Gender (being male)
- Age (30-60 years old)
- Dehydration
- Malnutrition
- Smoking
- Gum disease
- Anticholinergic medicine
- Trauma to the inside of the mouth
What happens when a salivary gland is removed?
Removal of a salivary gland doesn’t affect overall saliva production, but radiation therapy often causes dry mouth, which can increase your risk for cavities and mouth infections. Here are some tips to keep your mouth moist: Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day and take a water bottle with you wherever you go.

What is the ICD-10 code for sialadenitis?
K11. 20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K11.
Is parotid gland a salivary gland?
The parotid glands are two salivary glands that sit just in front of the ears on each side of the face. Salivary glands produce saliva to aid in chewing and digesting food. There are many salivary glands in the lips, cheeks, mouth and throat.
Is submandibular gland a salivary gland?
You have three pairs of major salivary glands — parotid, sublingual and submandibular. Each gland has its own tube (duct) leading from the gland to the mouth.
What are the 4 types of salivary glands?
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous, or seromucous (mixed).
What are the three types of salivary glands?
The three main pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands, the sublingual glands, and the submandibular glands.
What causes salivary gland stone?
The cause is not known, but several factors are associated with salivary stone formation: Dehydration, due to inadequate fluid intake, illness, or medications such as diuretics (water pills) and anticholinergic drugs. Trauma to the inside of the mouth. Smoking.
What are the two glands under your jaw?
Submandibular glands -- These two glands are located just under both sides of the lower jaw and carry saliva up to the floor of the mouth under the tongue. Sublingual glands -- These two glands are located just under the front most area of the floor of the mouth.
How do you treat salivary gland stones?
If a stone is detected, the goal of treatment is to remove it. For small stones, stimulating saliva flow by sucking on a lemon or sour candies may cause the stone to pass spontaneously. In other cases where stones are small, the doctor or dentist may massage or push the stone out of the duct.
How can you tell the difference between a lymph node and a submandibular gland?
0:542:37Parotid Gland and Submandibular Triangle - Lymph Nodes - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOne is typically anterior to the submandibular gland. Which you can see here. And then you will haveMoreOne is typically anterior to the submandibular gland. Which you can see here. And then you will have and note that the lymph node is typically darker than and separate from the gland.
Where are the 3 salivary glands located?
There are three pairs of large salivary glands. Parotid glands are found in front of and just below each ear. Submandibular glands are below the jaw. Sublingual glands are under the tongue.
Which salivary gland is the largest?
The parotid glandsThe parotid glands are the largest salivary glands. There are 2 parotid glands, one in front of each ear on either side of the face. The parotid gland is divided into 2 lobes, one on each side of the facial nerve. The superficial lobe is closest to the front of the neck.
What gland is under your chin?
Submandibular glands -- These two glands are located just under both sides of the lower jaw and carry saliva up to the floor of the mouth under the tongue.
What glands make saliva?
Your salivary glands make saliva - sometimes called spit - and empty it into your mouth through openings called ducts. Saliva makes your food moist, which helps you chew and swallow. It helps you digest your food. It also cleans your mouth and contains antibodies that can kill germs.
When will the ICd 10-CM K11 be effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM K11 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
Which of the three pairs of salivary glands is a condition in which there is a deviation from or interruption
Condition in which there is a deviation from or interruption of the normal structure or function of any of the three pairs of salivary glands, which are the parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands .
What glands make saliva?
Your salivary glands make saliva - sometimes called spit - and empty it into your mouth through openings called ducts. Saliva makes your food moist, which helps you chew and swallow. It helps you digest your food. It also cleans your mouth and contains antibodies that can kill germs.
What is the ICD code for sialolithiasis?
K11.5 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of sialolithiasis. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
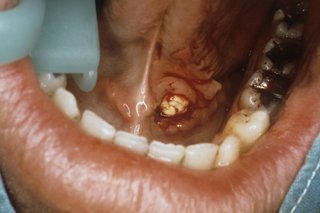
Where is the sialolith located?
Sialolithiasis (also termed salivary calculi, or salivary stones), is a condition where a calcified mass or sialolith forms within a salivary gland, usually in the duct of the submandibular gland (also termed "Wharton's duct").
What is the ICD code for acute care?
K11. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code K11 is a non-billable code.
What is an additional code note?
Use Additional Code note means a second code must be used in conjunction with this code. Codes with this note are Etiology codes and must be followed by a Manifestation code or codes.
What is the code for salivary gland atrophy?
K11.0 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of atrophy of salivary gland. The code K11.0 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
How does saliva work?
They make saliva (spit) and empty it into your mouth through openings called ducts. Saliva makes your food moist, which helps you chew and swallow. It helps you digest your food. It also cleans your mouth and contains antibodies that can kill germs.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for displaced ulnar styloid fracture
- 2. icd 10 code for diastolic heart failure unspecified
- 3. icd 10 code for digoxin use
- 4. icd code 10 for angiomyolipoma
- 5. icd 9 code for follow up after circulatory surgery
- 6. icd 10 code for antisocial personality traits
- 7. icd 9 code for lymphomas
- 8. icd 9 code for diabetic cataract
- 9. icd 10 code for history of vf arrest
- 10. icd 10 pcs code for watchman procedure