ICD-10-CM Code S99.13. Salter-Harris Type III physeal fracture of metatarsal. S99.13 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Salter-Harris Type III physeal fracture of metatarsal. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
What is the ICD 10 code for Salter Harris physeal fracture?
Salter-Harris Type III physeal fracture of lower end of right tibia, initial encounter for closed fracture. S89.131A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S89.131A became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is Salter-Harris type III physeal fracture?
Salter-Harris Type III physeal fracture of lower end of tibia ICD-10-CM S89.131A is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 562 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh with mcc 563 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh without mcc
What is the ICD 10 code for SLTR-Haris type III?
S99.231A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Sltr-haris Type III physeal fx phalanx of right toe, init The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S99.231A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for left tibia fracture?
2021 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S89.122A Salter-Harris Type II physeal fracture of lower end of left tibia, initial encounter for closed fracture 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code S89.122A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
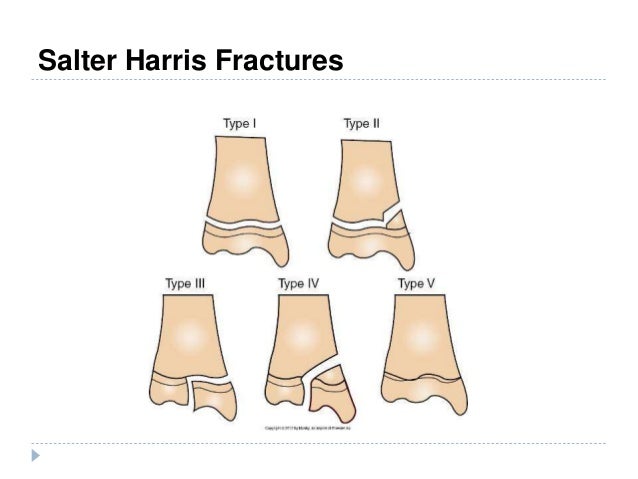
What is a Salter-Harris III fracture?
Salter-Harris type III fractures are an uncommon, intraarticular fracture physeal fractures that occur in children. The fracture line is often obliquely oriented through the epiphysis to the physis where it will take a horizontal orientation extending to the edge of the physis.
How many types of Salter-Harris fractures are there?
There are five common types of Salter-Harris fractures, which range in severity according to their potential for growth disturbance. Type I fractures are least likely to impair bone growth, while type V is the most likely to disturb a child's bone growth.
What is a Salter-Harris IV fracture?
Salter-Harris type IV fractures are relatively uncommon injuries that occur in children. They are intra-articular injuries in which the fracture extends through the epiphysis, across the physis and through the metaphysis. Salter-Harris fractures are a group childhood injuries where a fracture involves the physis.
What is a Level 3 fracture?
A type III fracture (see the images below) is a fracture through the physis and epiphysis. This fracture passes through the hypertrophic layer of the physis and extends to split the epiphysis, inevitably damaging the reproductive layer of the physis.
Where do Salter-Harris fractures occur?
The reason a Salter-Harris fracture is concerning in kids is that it typically occurs on or near the growth plate. 5 The growth plate is situated near the ends of the long bones where growth literally occurs, enabling them to grow longer, larger, and stronger.
What is Salter-Harris fracture classification?
The Salter-Harris classification system is a method used to grade fractures that occur in children and involve the growth plate, which is also known as the physis or physial plate. The classification system grades fractures according to the involvement of the physis, metaphysis, and epiphysis.
What are the 4 types of fractures?
Although there are many types of bone fractures, there are four main categories a fracture usually falls under: displaced, non-displaced, open and closed. We'll start with the most grueling first: open and closed fractures. A closed fracture describes the bone breaking with no puncture through the skin.
What's the difference between a fracture and a break?
The terms are actually interchangeable and both refer to a bone that has been shattered, often by excessive force. Your doctor may be more likely to use the term fracture. To be frank, the term fracture is more “professional” sounding. To say break would still be correct but more colloquial.
What are the three types of fractures?
What types of bone fractures are there?Closed or open fractures: If the injury doesn't break open the skin, it's called a closed fracture. ... Complete fractures: The break goes completely through the bone, separating it in two.Displaced fractures: A gap forms where the bone breaks.More items...•
What is a 3 column fracture?
When all three columns are involved, the fracture is by definition considered unstable, because of the loss of the integrity of the posterior stabilizing ligaments. The table below shows the types of fractures, the part or parts of the spine involved, and whether or not it is a stable or unstable injury.
What are the 7 types of fractures?
The Different Types of Bone FracturesTransverse fracture. A transverse fracture occurs when a bone breaks at a 90-degree angle to the long axis of the bone. ... Oblique fracture. ... Comminuted fracture. ... Greenstick fracture. ... Stress fracture. ... Pathologic fracture.
What is a Grade 4 stress fracture?
grade 4: severe marrow edema on both fat-suppressed T2WI and T1WI or periosteal edema plus visible fracture line on T1WI or T2WI.
What are the three types of hip fractures?
There are three broad categories of hip fractures based on the location of the fracture: femoral neck fractures, intertrochanteric fractures, and subtrochanteric fractures. The femoral neck is the most common location for a hip fracture, accounting for 45% to 53% of hip fractures.
What is the ICD-10 code for Salter Harris fracture?
Salter-Harris Type III physeal fracture of lower end of ulna, unspecified arm, initial encounter for closed fracture 1 S59.039A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Sltr-haris Type III physl fx lower end ulna, unsp arm, init 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S59.039A became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S59.039A - other international versions of ICD-10 S59.039A may differ.
When will the ICD-10-CM S59.039A be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S59.039A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
When will the ICD-10-CM S99.231A be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S99.231A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
When will the ICD-10-CM S89.131A be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S89.131A became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
What is the ICd 9 code for a fracture of the distal femur?
So a physeal fracture of the distal femur would be reported as 821.22 for a closed fracture or 821.32 for an open fracture. It should be noted that these codes are not specific to Salter-Harris fractures. These codes are used for any fracture or separation of the epiphysis in the lower end of the femur. These codes are reported both for adults (who have closed growth plates) and children and adolescents (who have open growth plates) even though the potential for complications, including arrested bone growth, is much greater for children and adolescents.
What is type 1 fracture?
Type I: Fracture of the bone through the growth plate with separation of the epiphysis from the diaphysis.
What is S79.111?
S79.111- Salter-Harris Type I physeal fracture of lower end of right femur
What happens when a physeal fracture occurs?
When a physeal fracture occurs, the cartilaginous tissue of the growth plate becomes disrupted or separated, and when this occurs, bone growth may be affected. In the United States, physeal fractures are classified by severity using a system developed in 1963 by Robert Salter and W. Robert Harris; the system is known as ...
What type of injury involves only the growth plate without a fracture of either the diaphysis or epiphy?
Type V: This is a crush- or compression-type injury that involves only the growth plate without a fracture of either the diaphysis or epiphysis.
What is type III in biology?
Type III: Fracture through the growth plate and epiphysis with a complete break through the epiphysis.
Can you use Salter Harris classification as documentation?
However, these codes should be used rarely as documentation ; in most instances, identification of the Salter-Harris classification will be possible, as well as the side affected. If the documentation does not include this information, the physician should be queried so that the most specific code can be assigned.
What is the ICD-10 code for Salter Harris fracture?
Salter-Harris Type II physeal fracture of lower end of left tibia, initial encounter for closed fracture 1 S89.122A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Sltr-haris Type II physeal fx lower end of left tibia, init 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S89.122A became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S89.122A - other international versions of ICD-10 S89.122A may differ.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
When will the ICD-10-CM S89.122A be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S89.122A became effective on October 1, 2021.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for status post left hip revision
- 2. icd 9 code for status post knee surgery
- 3. icd-10 code for polypharmacy abuse
- 4. icd 10 cm code for cytomegalovirus infection
- 5. icd 10 code for k20
- 6. icd 10 code for medication overuse headache
- 7. icd 9 code for eye cataract
- 8. icd 10 code for neuropathy left upper extremity
- 9. icd 10 code for tenosynovitis wrist
- 10. icd 10 code for secondary cancer of liver