Sarcoidosis, unspecified
- D86.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM D86.9 became effective on October 1, 2020.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D86.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 D86.9 may differ.
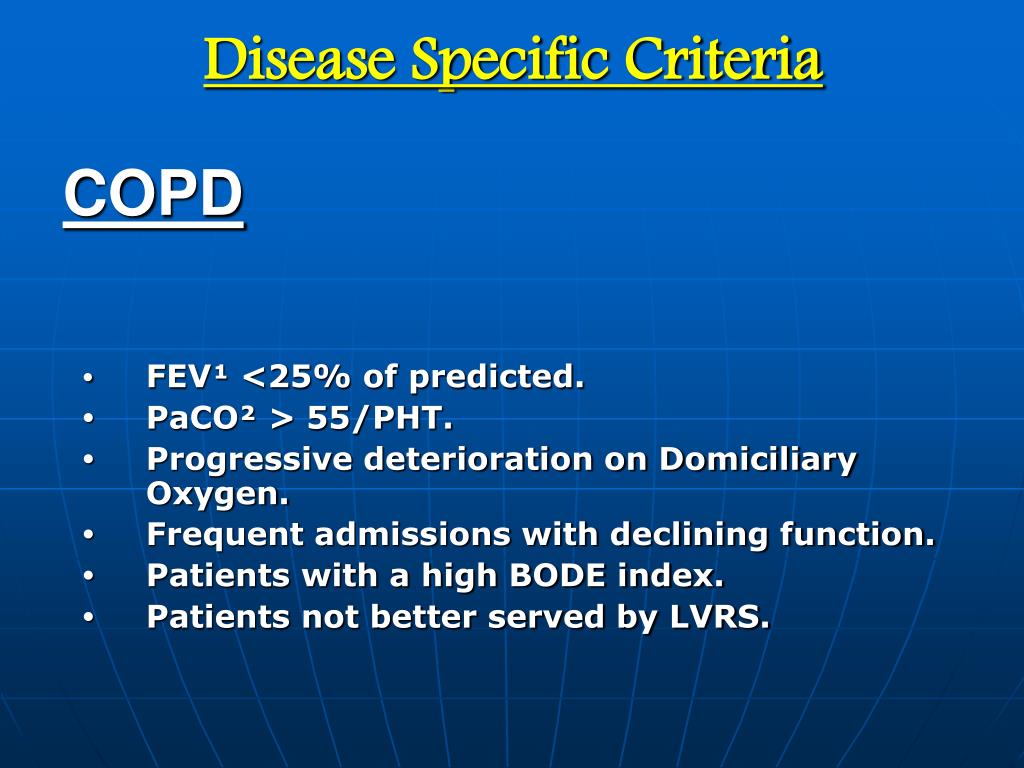
How many codes in ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · Sarcoidosis, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. D86.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What are ICD 10 codes?
Sarcoidosis. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. D86 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D86 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes D86*: Sarcoidosis. ICD-10-CM Codes. ›. D50-D89 Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. ›.
What does ICD 10 mean?
Oct 01, 2021 · Sarcoidosis of lung. D86.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D86.0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D86.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 D86.0 may differ.
What sarcoidosis mean?
Sarcoidosis is a disease characterized by the growth of tiny collections of inflammatory cells (granulomas) in any part of your body — most commonly the lungs and lymph nodes. But it can also affect the eyes, skin, heart and other organs.Jan 30, 2019
What is sarcoidosis and how do you get it?
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which immune cells form small lumps, called granulomas, in your organs. Experts believe that inflammation causes these granulomas to form. The inflammation could be triggered by an infection or exposure to certain substances in your environment.Jul 11, 2018
How is sarcoidosis of the lungs treated?
Corticosteroids. These powerful anti-inflammatory drugs are usually the first line treatment for sarcoidosis. In some cases, corticosteroids can be applied directly to an affected area — via a cream to a skin lesion or drops to the eyes. Medications that suppress the immune system.Jan 30, 2019
What diagnosis code is D86 9?
ICD-10 code: D86. 9 Sarcoidosis, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
What are the 4 stages of sarcoidosis?
Stage I: Lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes) Stage II: Enlarged lymph nodes with shadows on chest X-ray due to lung infiltrates or granulomas. Stage III: Chest X-ray shows lung infiltrates as shadows, which is a progressive condition. Stage IV (Endstage): Pulmonary fibrosis or scar-like tissue found on a chest X-ray ...Sep 24, 2020
Is sarcoid autoimmune?
Sarcoidosis has a wide variety of clinical phenotypes wherein many of them remind “classic” autoimmune diseases. About half of the patients have no symptoms, while in severe clinical cases, sarcoidosis can lead to a failure of the internal organ functions with the development of fibrosis and pulmonary hypertension.Jan 8, 2020
What foods should be avoided with sarcoidosis?
Things to Avoid in Your Diet Refrain from eating foods with refined grains, such as white bread and pasta. Cut back on red meat. Avoid foods with trans-fatty acids, such as commercially processed baked goods, french fries, and margarine. Stay away from caffeine, tobacco, and alcohol.Jul 19, 2018
What is the life expectancy of a person with sarcoidosis?
Most people with sarcoidosis live normal lives. About 60% of people with sarcoidosis recover on their own without any treatment, 30% have persistent disease that may or may not require treatment, and up to 10% with progressive long-standing disease have serious damage to organs or tissues that can be fatal.
What is the leading cause of sarcoidosis?
The cause of pulmonary sarcoidosis is unknown. Experts think that bacteria, viruses, or chemicals might trigger the disease. It may also be genetic. This means a person is more likely to develop sarcoidosis if someone his or her close family has it.
What is sarcoidosis D86 9?
ICD-10 code D86. 9 for Sarcoidosis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism .
What is icd10 code for fibromyalgia?
ICD-10 | Fibromyalgia (M79. 7)
What is sarcoid Iridocyclitis?
Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of noncaseating granulomas in affected organs, most commonly the lungs, lymph nodes, skin, and eyes. The disease was first described in 1878 by noted surgeon Sir Jonathan Hutchinson as a dermatologic disorder.Mar 8, 2022
What age group is most affected by sarcoidosis?
No one is sure what causes sarcoidosis. It affects men and women of all ages and races. It occurs mostly in people ages 20 to 50, african americans, especially women, and people of northern european origin. Many people have no symptoms.
What is granulomatous idiopathic?
An idiopathic systemic inflammatory granulomatous disorder comprised of epithelioid and multinucleated giant cells with little necrosis. It usually invades the lungs with fibrosis and may also involve lymph nodes, skin, liver, spleen, eyes, phalangeal bones, and parotid glands.
Does sarcoidosis go away?
Sarcoidosis may be acute and go away by itself, or it may be chronic and progressive. Inflammatory disease characterized by small lumps or granulomas in lymph nodes and other organs. Sarcoidosis is a disease that leads to inflammation, usually in your lungs, skin, or lymph nodes.
What is a giant cell?
An idiopathic inflammatory disorder characterized by the formation of non-necrotizing epithelioid granulomas which contain giant cells. It usually affects the lungs, lymph nodes, liver, and skin. Cardiac involvement is also possible.
What is sarcoidosis D86?
Sarcoidosis D86-. Clinical Information. A disease that produces messes especially in the liver, lungs, skin, and lymph nodes. An idiopathic inflammatory disorder characterized by the formation of non-necrotizing epithelioid granulomas which contain giant cells. It usually affects the lungs, lymph nodes, liver, and skin.
What is granulomatous idiopathic?
An idiopathic systemic inflammatory granulomatous disorder comprised of epithelioid and multinucleated giant cells with little necrosis. It usually invades the lungs with fibrosis and may also involve lymph nodes, skin, liver, spleen, eyes, phalangeal bones, and parotid glands.
What is a lump in the body called?
It starts as tiny, grain-like lumps, called granulomas. Sarcoidosis can affect any organ in your body. No one is sure what causes sarcoidosis. It affects men and women of all ages and races. It occurs mostly in people ages 20 to 50, african americans, especially women, and people of northern european origin.
Does sarcoidosis need treatment?
Not everyone who has the disease needs treatment. If you do, prednisone, a type of steroid, is the main treatment. What: sarcoidosis: sarcoidosis: a disorder of unknown etiology that affects many organ systems with noncaseating epithelioid cell granulomas. It has a special predilection for the lung and lymph tissues.
Does sarcoidosis go away?
Sarcoidosis may be acute and go away by itself, or it may be chronic and progressive. Inflammatory disease characterized by small lumps or granulomas in lymph nodes and other organs. Sarcoidosis is a disease that leads to inflammation, usually in your lungs, skin, or lymph nodes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for low dose ct lung screening
- 2. icd 10 code for broken toy
- 3. icd 10 code for acute peritonitis due to peritoneal dialysis
- 4. icd 10 code for other specified gastritis
- 5. icd 10 code for hunter's syndrome
- 6. icd 10 pcs code for the one therapeutic nuclear medicine procedure is which root type?
- 7. icd 10 code for history of blood in urine
- 8. icd 10 code for venous doppler upper extremity
- 9. icd 10 code for irritable
- 10. icd 10 code for proteus bacteremia