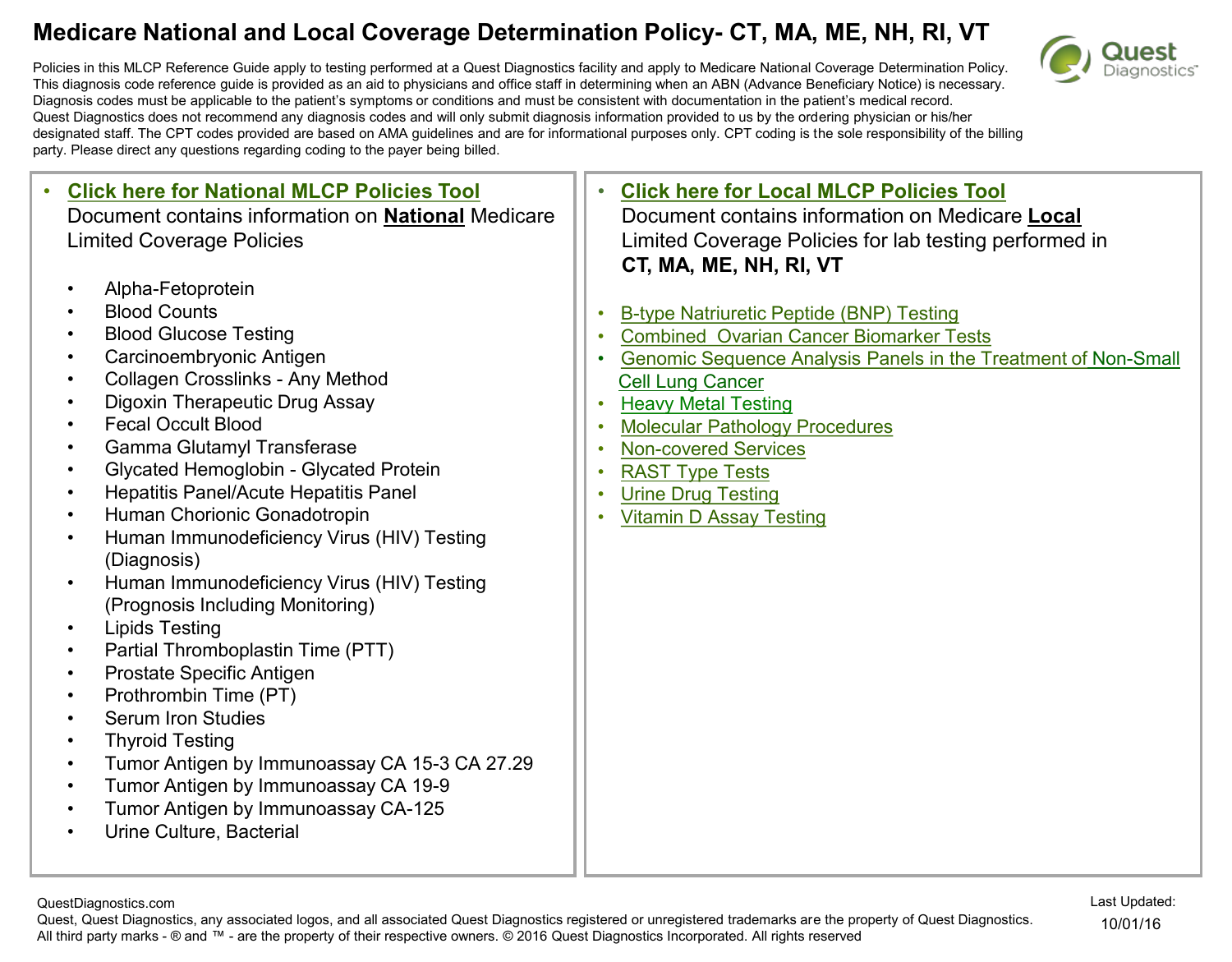
SARS-associated coronavirus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. B97.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM B97.21 became effective on October 1, 2018.
Full Answer
What is the CPT number for the SARS-Cov-2 vaccine?
Oct 01, 2021 · SARS-associated coronavirus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere B97.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: SARS-associated coronavirus causing diseases classd elswhr The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM ...
What does a negative SARS-Cov-2 mean?
Apr 01, 2020 · R05 Cough R06.02 Shortness of breath R50.9 Fever, unspecified
What is the ICD 10 code for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
For the full ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, effective January 1, 2021, see: https://www.cms.gov/medicare/icd-10/2021-icd-10-cm. 1. Chapter 1: Certain Infectious and Parasitic Diseases (A00-B99), U07.1 g. Coronavirus infections 1) COVID-19 infection (infection due to SARS-CoV-2) (a) Code only confirmed cases Code only a confirmed diagnosis of the …
Can serum tests detect SARS-Cov-2 infection?
New ICD-10-CM code for Post-COVID Conditions, following the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Effective: October 1, 2021 In March 2020 the Novel Coronavirus Disease, COVID-19, was declared a pandemic by the
What is the Directive 2000/54/EC?
Directive 2000/54/EC of the European Parliament and Council of 18 September 2000 on the protection of workers from risks related to exposure to biological agents at work. EUR-Lex web site. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32000L0054. Accessed May 2020.
How long does it take for antibodies to develop?
Current literature suggests that detectable antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 develop approximately 8 to 11 days following onset of symptoms. Correlation with epidemiologic risk factors and other clinical and laboratory findings is recommended. A positive serologic result is not diagnostic but indicates that an individual has likely been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and produced an immune response to the virus. It is not known at this time whether detectable antibody correlates with immunity. A negative serologic result indicates that an individual has not developed detectable antibodies at the time of testing. While contingent on a variety of factors, this could be due to testing too early in the course of infection, the absence of exposure to the virus, or the lack of adequate immune response, which can be due to conditions or treatments that suppress immune function.
Can IgG antibodies be detected?
While this assay in principle can detect high affinity antibodies of all isotypes (i.e., IgG, IgA, IgM), it preferentially detects IgG antibodies since these are more likely to evolve to become high affinity. Serologic results should not be used as the sole basis to diagnosis or exclude recent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Special Instructions
On May 19, 2021, the FDA issued a safety communication reiterating that "antibody testing should not be used to evaluate a person's level of immunity or protection from COVID-19 at any time, and especially after the person received a COVID-19 vaccination." Visit http://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/antibody-testing-not-currently-recommended-assess-immunity-after-covid-19-vaccination-fda-safety#N#(link is external)#N#for more information..
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Container
Gel-barrier tube, red-top tube, or serum transfer tube, or plasma from lithium heparin tube, EDTA, or sodium citrate tube
Use
Qualitative and semi-quantitative detection of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD). Aid in identifying individuals with an adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2, indicating recent or prior infection.
Limitations
This test should not be used to diagnose or exclude acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. The results should always be assessed in conjunction with patient's medical history, clinical presentation, and other findings. A negative test result does not rule out the possibility of an infection with SARS-CoV-2.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for nausea without vomiting
- 2. icd 10 code for left knee replacement using uncemented metal prosthesis.
- 3. icd 10 code for uncontrolled hypertension
- 4. icd 10 code for lazy
- 5. icd 10 code for history of hemorrhoidectomy surgery
- 6. icd 10 code for acute migraine headache
- 7. icd 10 code for :other assault by crashing of motor vehicle, initial encounter
- 8. icd 10 code for glucose intolerance
- 9. icd-10 code for urine drug screen
- 10. icd 10 code for leiomyoma of uterus in pregnancy