Is spontaneous pneumothorax life threatening?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J93.12 Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code J93.12 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J93.12 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are symptoms of spontaneous pneumomediastinum?
Oct 01, 2021 · ICD-10-CM Code. J93.12. Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax Billable Code. J93.12 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
How often does spontaneous pneumothorax happen?
ICD-10 code J93.12 for Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
Can ultrasound rule out a pneumothorax?
ICD-10-CM Code. J93.12. Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. J93.12 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.

How do you code a spontaneous pneumothorax?
ICD-10-CM Code for Primary spontaneous pneumothorax J93. 11.
What is code J93 83?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J93. 83: Other pneumothorax.
How does secondary pneumothorax occur?
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) occurs in people with a wide variety of parenchymal lung diseases. These individuals have underlying pulmonary pathology that alters normal lung structure (see the image below). Air enters the pleural space via distended, damaged, or compromised alveoli.
Which is the most common cause of a secondary spontaneous pneumothorax?
Secondary spontaneousOther Section Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs due to underlying chest diseases. Most commonly they are observed in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which accounts for approximately 70% of cases.
What is the ICD-10 code for iatrogenic pneumothorax?
512.1512.1 - Iatrogenic pneumothorax. ICD-10-CM.
What is the correct code for Hemopneumothorax?
J94.2ICD-10-CM Code for Hemothorax J94. 2.
What are the three types of pneumothorax?
OverviewPrimary spontaneous pneumothorax: Collapsed lung sometimes happens in people who don't have other lung problems. ... Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax: Several lung diseases may cause a collapsed lung. ... Injury-related pneumothorax: Injury to the chest can cause collapsed lung.More items...•May 11, 2021
What is the cause of spontaneous pneumothorax?
Primary spontaneous pneumothorax is likely due to the formation of small sacs of air (blebs) in lung tissue that rupture, causing air to leak into the pleural space. Air in the pleural space creates pressure on the lung and can lead to its collapse.
How do you classify pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax can be categorised as primary, secondary, iatrogenic or traumatic according to aetiology. Occasionally, individuals may develop a concomitant haemothorax due to bleeding caused by shearing of adjacent subpleural vessels when the lung collapses.
What are four clinical manifestations of a pneumothorax?
What are the Symptoms of Pneumothorax?Sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens when trying to breath in.Shortness of breath.Bluish skin caused by a lack of oxygen.Fatigue.Rapid breathing and heartbeat.A dry, hacking cough.Apr 10, 2020
What is the difference between blebs and bullae?
'Blebs' are blister-like air pockets that form on the surface of the lung. Bulla (or Bullae for pleural) is the term used for air-filled cavities within the lung tissue.Feb 8, 2012
What is the purpose of thoracentesis?
Thoracentesis is a procedure to remove fluid or air from around the lungs. A needle is put through the chest wall into the pleural space. The pleural space is the thin gap between the pleura of the lung and of the inner chest wall.
The ICD code J93 is used to code Pneumothorax
A pneumothorax (pneumo- + thorax; plural pneumothoraces) is an abnormal collection of air or gas in the pleural space that causes an uncoupling of the lung from the chest wall. Like pleural effusion (liquid buildup in that space), pneumothorax may interfere with normal breathing.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'J93.12 - Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code J93.12. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 512.82 was previously used, J93.12 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is the pleura in the chest?
Pleural Disorders. Your pleura is a large, thin sheet of tissue that wraps around the outside of your lungs and lines the inside of your chest cavity. Between the layers of the pleura is a very thin space. Normally it's filled with a small amount of fluid.
What causes pleural effusion?
The most common cause of pleural effusion is congestive heart failure. Lung diseases, like COPD, tuberculosis, and acute lung injury, cause pneumothorax. Injury to the chest is the most common cause of hemothorax.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code J93.12:
What is the code for pneumothorax?
J93.12 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of secondary spontaneous pneumothorax. The code J93.12 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the term for the condition where air leaks into the lungs?
February 13, 2020. February 13, 2020. by Natalie Tornese. Pneumothorax is a condition which occurs when air leaks into the space between your lungs and the chest wall – called the pleural space. This buildup of air puts pressure on the lungs, so it cannot expand as much as it normally does when a person takes breath.
What is secondary spontaneous pneumothorax?
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax (SSP) – SSP is caused by a variety of lung diseases like – chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, thoracic endometriosis, lung infections such as tuberculosis, and certain forms of pneumonia. Tension pneumothorax – This is caused by a leak in the pleural space.
What are the different types of pneumothorax?
Types of Pneumothorax. Pneumothorax is generally categorized into different types which include the following –. Traumatic pneumothorax – This type is often the result of an injury (sports injuries, car accidents, and punctures or stab wounds) that damages the chest wall and pleural space. Certain medical procedures like inserting a catheter ...
What causes a lung to collapse?
Also called lung collapse, the condition can be caused by a blunt or penetrating chest injury, ruptured air blisters, mechanical ventilation, certain medical procedures or lung damage from many types of underlying diseases (including COPD, cystic fibrosis and pneumonia). ...
How old is too old to get pneumothorax?
Generally, men are far more likely to develop pneumothorax than women. It is more likely to develop in people between the age group of 20 – 40 years, particularly among tall and underweight people.
What tests are done to determine the severity of pneumothorax?
Imaging tests like chest X-ray, CT scan and ultrasound may be performed to view the size and severity of the pneumothorax. Treatment of pneumothorax aims to relieve the pressure on your lungs, allowing it to re-expand.
How many times more likely is a smoker to develop PSP than a non smoker?
According to a review in the medical journal BMJ, men who smoke tobacco are 22 times more likely to develop PSP than non-smokers. Women who smoke tobacco are nine times more likely than nonsmokers to develop PSP. If treated promptly, PSP is usually not fatal.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as J93. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. spontaneous pneumothorax ( J93.-)
What is Z72.0?
tobacco use ( Z72.0) Diseases of the respiratory system. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by abnormal presence of air in the pleural cavity resulting in the collapse of the lung. Abnormal presence of air in the pleural cavity.
Is J93 a reimbursement code?
Pneumothorax and air leak. J93 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM J93 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is pleural air?
A disorder characterized by abnormal presence of air in the pleural cavity resulting in the collapse of the lung. Abnormal presence of air in the pleural cavity. Accumulation of air or gas in the pleural space, which may occur spontaneously or as a result of trauma or a pathological process.
What is pneumothorax gas?
Pneumothorax; abnormal presence of air in the pleural cavity resulting in the collapse of the lung.
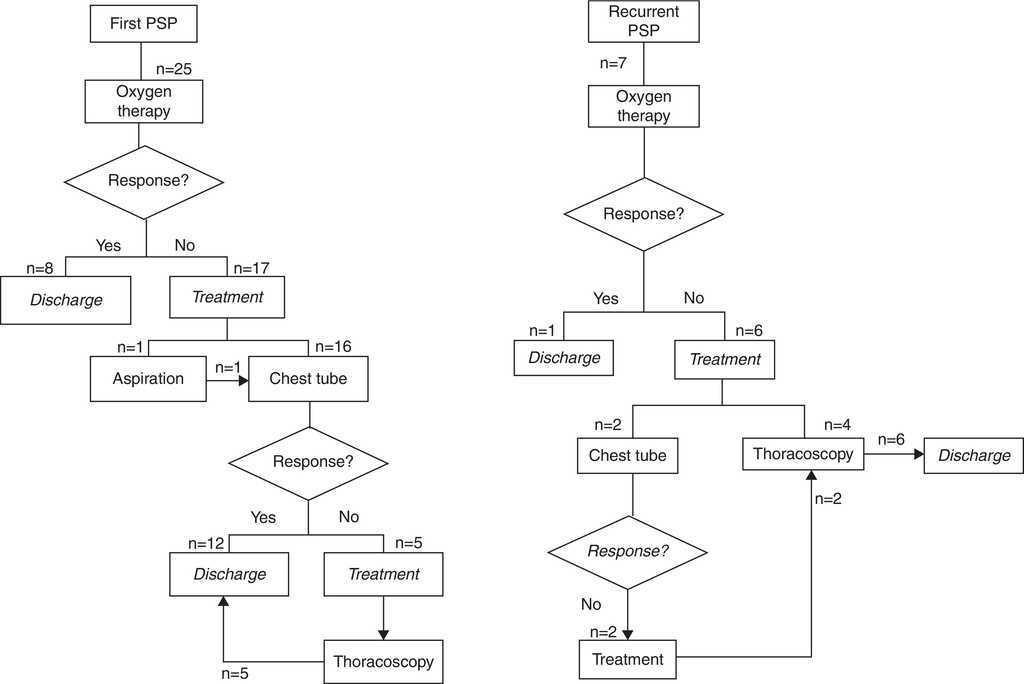
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for renal ultrasound?
- 2. icd 10 code for throat cancer in remission
- 3. icd 10 code for goals of care discussion
- 4. 2016 icd 10 code for decubitus ulcer right foot
- 5. icd 9 code for hyperhomocysteinemia
- 6. 2018 icd 10 code for edema right kidney
- 7. icd-10 code for lumbar stenosis
- 8. icd-10 code for long term use of lipitor
- 9. icd 10 code for immunocompromised due to medication
- 10. icd 10 code for arthrocentesis of ganglion cyst of joint both injection and aspiration