Failed moderate sedation during procedure, initial encounter. T88.52XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM T88.52XA became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for sedative toxicity?
Moderate sedation/analgesia (conscious sedation) Codes 99151-99157, is a drug-induced depression of consciousness during which patients respond purposefully to verbal commands, either alone or accompanied by light tactile stimulation. No interventions are required to maintain a patent airway, and spontaneous ventilation is adequate.
What is the CPT code for sedation?
ICD10 codes matching "Sedation" Codes: = Billable. O29 Complications of anesthesia during pregnancy; O74 Complications of anesthesia during labor and delivery; O89 Complications of anesthesia during the puerperium; T88.52 Failed moderate sedation during procedure; T88.52XA Failed moderate sedation during procedure, initial encounter
What is the ICD 10 code for anesthesia?
Oct 01, 2021 · Sedative, hypnotic or anxiolytic dependence, uncomplicated 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code F13.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F13.20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is moderate sedation?
ICD-10-CM Codes › F01-F99 Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders › F10-F19 Mental and behavioral disorders due to psychoactive substance use › Sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic related disorders F13 Sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic related disorders F13-
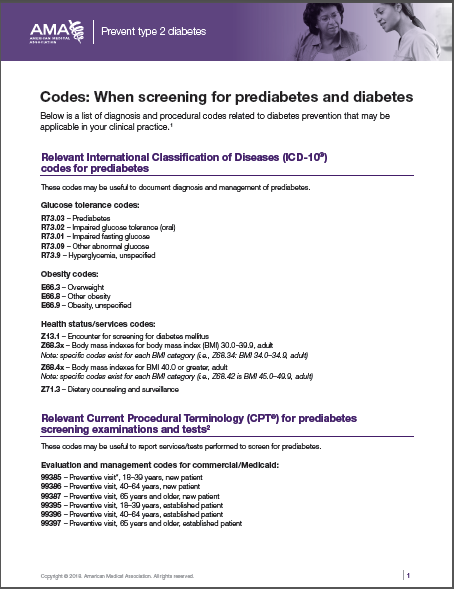
What is the ICD-10 code for anesthesia?
R20. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for drowsiness?
Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness.
What is the ICD-10 code Z51 89?
Encounter for other specified aftercareICD-10 code Z51. 89 for Encounter for other specified aftercare is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is Sedative, hypnotic or anxiolytic dependence uncomplicated?
Sedative, Hypnotic, or Anxiolytic Use Disorder is a substance use disorder characterized by repeated use of substances including benzodiazepines, benzodiazepine-like drugs (e.g. - zolpidem, zaleplon), carbamates (e.g. - glutethimide, meprobamate), barbiturates (e.g. - phenobarbital, secobarbital), and barbiturate-like ...Mar 29, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for weakness and fatigue?
ICD-10-CM Code for Other malaise and fatigue R53. 8.
What is the ICD-10 code for agitation?
R45.1ICD-10 code: R45. 1 Restlessness and agitation - gesund.bund.de.
Can Z51 89 be a primary DX?
The code Z51. 89 describes a circumstance which influences the patient's health status but not a current illness or injury. The code is unacceptable as a principal diagnosis.
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
9.
What is the diagnosis code for physical therapy?
Z51. 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z51. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for sedative-hypnotic or anxiolytic dependence?
Sedative, hypnotic or anxiolytic dependence, uncomplicated F13. 20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Which of the following compound belongs to category of sedative and hypnotic?
The benzodiazepines include chlordiazepoxide (Librium), diazepam (Valium), alprazolam (Xanax), oxazepam (Serax), and triazolam (Halcion).
What are sedative-hypnotic or anxiolytic?
Anxiolytics are a class of medications aimed at treating patients with panic disorders, generalized anxiety, and various other uses. Sedatives(hypnotics) are a class of drugs used in different situations ranging from treating insomnia to treating someone connected to a mechanical ventilator.Sep 1, 2021
What is United Healthcare Dental Coverage Guideline?
This Dental Coverage Guideline provides assistance in interpreting UnitedHealthcare standard dental benefit plans. When deciding coverage, the member specific benefit plan document must be referenced as the terms of the member specific benefit plan may differ from the standard dental plan. In the event of a conflict, the member specific benefit plan document governs. Before using this guideline, please check the member specific benefit plan document and any applicable federal or state mandates. UnitedHealthcare reserves the right to modify its Policies and Guidelines as necessary. This Dental Coverage Guideline is provided for informational purposes. It does not constitute medical advice.
Is local anesthesia safe for dental patients?
The administration of local anesthetic is common and used for most routine dental procedures. For some patients, Moderate/ Conscious Sedation, non-intravenous sedation and Deep Sedation/General Anesthesia may be necessary to safely provide dental care. These procedures generally are safe when administered by trained, certified providers in the appropriate setting, but are not without risk. According to the American Dental Association (ADA), dentists must comply with their state laws, rules and/or regulations when providing sedation and anesthesia, and follow the educational and training requirements for the level of sedation intended. The ADA maintains clinical guidelines and educational/training requirements for all levels of sedation and includes specific information for the following:
What is a moderate sedation?
Moderate Sedation Coding. Moderate sedation, also sometimes referred to as conscious sedation, is a drug-induced depression of consciousness. A patient who has been sedated in this way is relaxed and generally insensitive to pain, but remains awake and able to respond to verbal instruction. If medically necessary and properly documented, moderate ...
What is sedating agent?
The sedating agent (s), with or without an analgesic agent, is administered, and the patient is assessed continuously until an effective and safe level of moderate sedation and/or analgesia is achieved. The patient is closely monitored by the sedating physician and additional doses of sedating and/or analgesic agent (s) are delivered as needed.
What is intraservice time?
Intraservice time begins with the administration of the sedation agent, and ends when the procedure is completed, the patient is stable for recovery status, and the provider performing the sedation ends personal continuous face-to-face time with the patient.
What is a 99152?
Description of Procedure (99152)#N#The physician or other qualified health care professional performs presedation patient assessment; supervises or personally provides the administration of the sedating agent, with or without an analgesic; and supervises an independent, trained observer who monitors the patient’s level of consciousness and physiologic status throughout the procedure. The patient is assessed continuously throughout the procedure to achieve an effective and safe level of moderate sedation. Additional doses of the sedating agent (s) are ordered or provided by the physician as needed. The physician’s intraservice time ends when the procedure is complete, the patient is physiologically stable, and face-to-face physician time is no longer required.
What is a clinical example?
Clinical Example (99157) A patient undergoes a procedure that requires a physician other than the physician providing the procedure to provide moderate sedation, in order to complete the procedure safely and with minimal emotional trauma.
Who is John Verhovshek?
John Verhovshek, MA, CPC, is a contributing editor at AAPC. He has been covering medical coding and billing, healthcare policy, and the business of medicine since 1999. He is an alumnus of York College of Pennsylvania and Clemson University.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for fall from roller skating
- 2. icd 10 code for lower respiratory culture
- 3. icd 10 code for decompressive craniectomy
- 4. icd 10 code for left middle finger phalanx fracture
- 5. icd 10 code for metatarsalgia right great toe
- 6. icd-10 code for laryngeal penetration without aspiration
- 7. icd 10 code for pain from right femur fx
- 8. icd 10 cm code for hep b carrier
- 9. icd 10 code for e78.1
- 10. icd 10 code for paresthesia right arm