Septic arterial embolism. I76 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I76 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for septic embolism?
Septic arterial embolism. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code. I76 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I76 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is the ICD 10 code for cerebral infarction with embolism?
I63.40 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Cerebral infarction due to embolism of unsp cerebral artery The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I63.40 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for embolism and thrombosis?
I76 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. I74.9 Embolism and thrombosis of unspecified artery... Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology. For such conditions,...
What is the ICD 10 code for sepsis without acute cor pulmonale?
Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code I26.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I26.90 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the code for septic pulmonary embolism?
How do septic emboli occur?
About this website
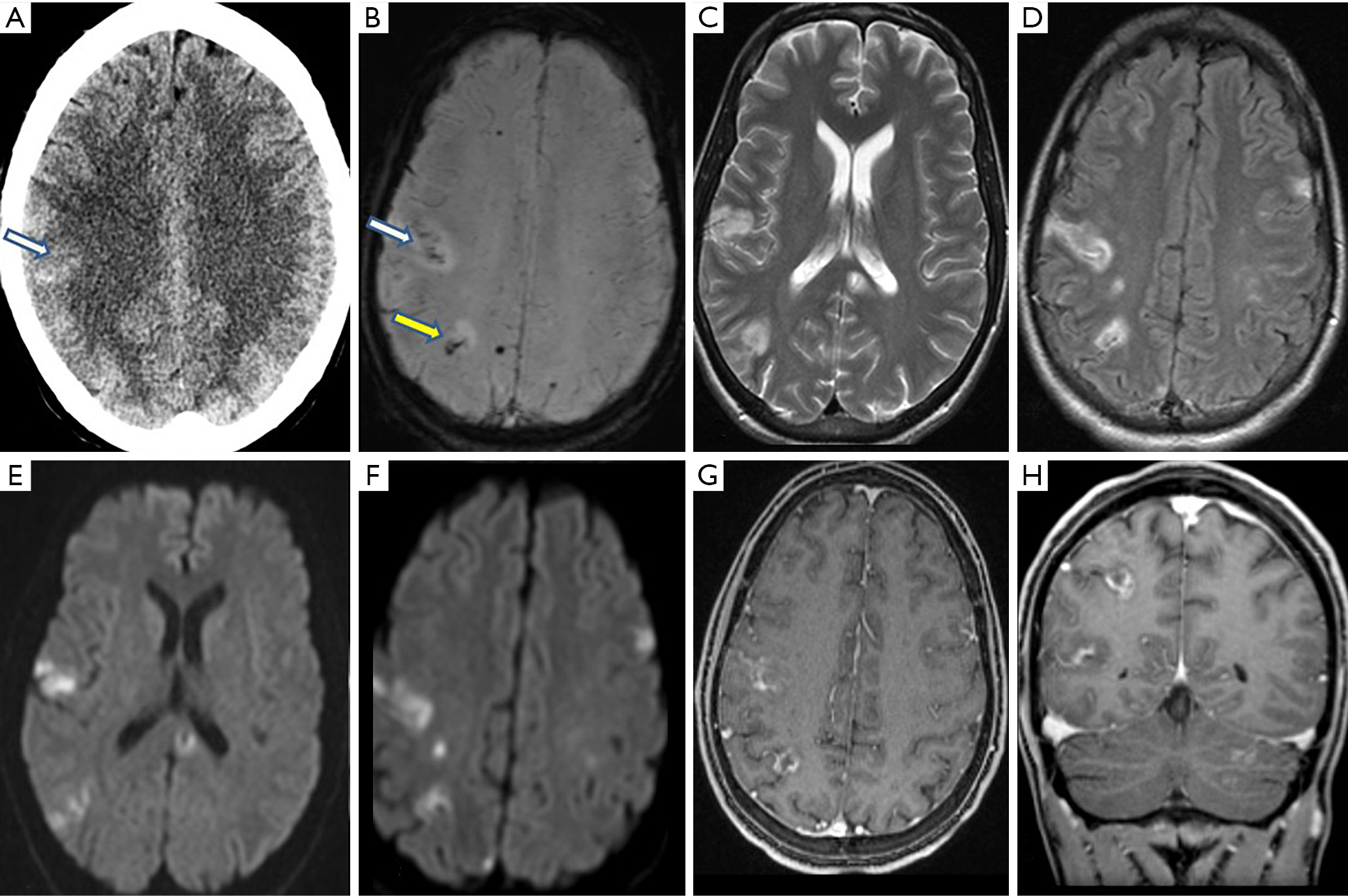
What is septic emboli to the brain?
Septic-embolic encephalitis, also known as septic-embolic brain abscess, refers to a focal or diffuse brain infection, ischemic and hemorrhagic damages following infective thromboembolism from any part of the body. It is usually caused by bacterial infections from endocarditis.
What is the ICD 10 code for septic emboli?
I26.90ICD-10-CM Code for Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale I26. 90.
Is septic emboli a stroke?
Septic emboli typically originate in a heart valve. An infected heart valve can yield a small blood clot that can travel almost anywhere in the body. If it travels to the brain and blocks a blood vessel, it's called a stroke. If the clot is infected (septic emboli), it's classified as a septic stroke.
What is the ICD 10 code for embolic CVA?
ICD-10 code I63. 40 for Cerebral infarction due to embolism of unspecified cerebral artery is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
How do you code a septic embolism?
Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonaleI26. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I26. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I26.
What is the ICD-10 code for PE?
ICD-10 code I26. 9 for Pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
Can sepsis cause brain lesions?
A brain MRI should be considered in case of persistent brain dysfunction after control of sepsis and exclusion of major confounding factors. Recent MRI studies suggest that septic shock can be associated with acute cerebrovascular lesions and white matter abnormalities.
Does sepsis cause stroke?
Sepsis is a leading cause of death in the United States, particularly among patients in the intensive care unit. Sepsis patients are at long-term increased risk of death and major adverse cardiovascular events. Additionally, sepsis is associated with an increased intermediate and long-term risk for stroke.
Can endocarditis affect the brain?
As a result, endocarditis can cause several complications, including: Heart problems, such as heart murmur, heart valve damage and heart failure. Stroke. Pockets of collected pus (abscesses) that develop in the heart, brain, lungs and other organs.
Is an embolic stroke An ischemic stroke?
An embolic stroke occurs when a blood clot that forms elsewhere in the body breaks loose and travels to the brain via the bloodstream. When the clot lodges in an artery and blocks the flow of blood, this causes a stroke. This is a type of ischemic stroke.
How do you code a CVA in ICD-10?
I63. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of CVA with residual deficits?
Cognitive deficits following cerebral infarction The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I69. 31 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I69. 31 - other international versions of ICD-10 I69.
What is a septic embolus?
A septic embolus is a type of bacterial infection inside a blood vessel due to a thrombus or fat globule or air or foreign material.
What is the underlying infection of a septic embolism?
The physician diagnoses the patient with septic arterial embolism. His underlying infection is acute infective endocarditis. Also, according to the documentation, the patient has an embolism and thrombosis of the thoracic aorta.
What is the treatment for septic pulmonary embolism?
Treatment: When the diagnosis is confirmed, antibiotic therapy is used to manage the infection with the thrombolytic treatment of the embolus. Depending on the cause of the septic pulmonary embolic, treatment with anticoagulants may be considered. Note: Do not Sequence Embolism as Primary Diagnosis (pdx)
Where does pulmonary embolism go?
The embolic material travels through the venous system to the right side of the heart and goes into the pulmonary arterial system where it lodges in small vessels. Septic pulmonary emboli may cause subsequent lung abscess or necrotizing pneumonia.
Where does septic embolus originate?
Arterial: A septic arterial embolus may originate from a central infection, such as in the heart, and then travel through the systemic arterial system to lodge in small vessels anywhere in the body, such as the brain, the retina, or the digits. It can block a blood vessel in the brain, causing a stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), cerebral hemorrhage, meningitis, brain abscess, or a mycotic aneurysm.
What is the meaning of I74.11?
I74.11 (Embolism and thrombosis of thoracic aorta) to identify the site of the embolism.
Can a septic pulmonary embolus cause a stroke?
Pulmonary: A septic pulmonary embolus originates from a localized infection such as localized cellulitis or a central venous catheter infection.
What is the code for septic pulmonary embolism?
Effective October 1, 2007, codes 415.12 , Septic pulmonary embolism, and 449, Septic arterial embolism, have been created. A septic pulmonary embolus occurs when the infectious material from a localized infection breaks off enters the venous system, travels through the heart and lodges in the arteries of the lung. The risk for septic pulmonary embolism increases with the presence of an indwelling catheter or device, intravenous drug use, pelvic thrombophlebitis and suppurative conditions in the head and neck such as sinusitis or tonsillopharyngitis. Septic pulmonary embolism is an uncommon disorder that is difficult to diagnose because of its nonspecific...
How do septic emboli occur?
Septic arterial emboli occur when embolic material from the localized infection travels through the systemic arterial system and lodges in the small vessels of the body. The embolus may originate from an infection in the heart such as infective endocarditis or an abscess of the lung, and travel anywhere in the body, including the brain, retina or digits. Tissue damage may result from the lack of oxygen and blood flow to the affected area. There may be muscle pain, tingling or numbness. Multiple areas of infection or abscesses may occur. The most important treatment is to eliminate the infection with antibiotics.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for foreign body in stomach
- 2. what is the icd 10 cm code for labyrinthine hydrops.
- 3. icd 10 code for long term use of plaquenil
- 4. icd 9 code for history of fatigue
- 5. florida requires icd-10 code for pharmacy billing
- 6. icd 10 code for salzmann's nodule
- 7. icd 10 code for snowboarding fall
- 8. icd 10 code for chronic pain disorder
- 9. icd 9 code for bipolar with mania
- 10. icd-10-cm code for nausea and vomiting