What is the ICD 10 code for septic pulmonary embolism?
Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale I26.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I26.90 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I26.90 - other ...
What is the ICD 10 code for sepsis without acute cor pulmonale?
Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code I26.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I26.90 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for embolism and thrombosis?
I76 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. I74.9 Embolism and thrombosis of unspecified artery... Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology. For such conditions,...
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary insufficiency following surgery?
pulmonary insufficiency following surgery ( ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J95.1. Acute pulmonary insufficiency following thoracic surgery 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. Type 2 Excludes Functional disturbances following cardiac surgery (I97.0, I97.1-) J95.1- ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J95.2.
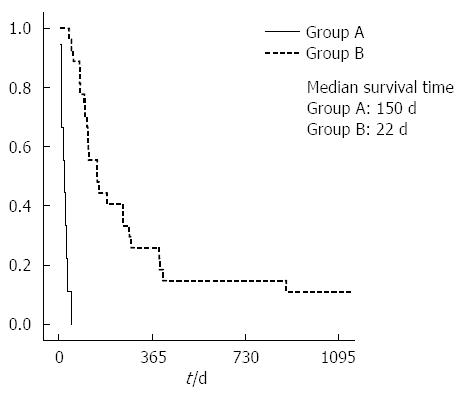
What is the ICD-10 code for pulmonary septic emboli?
ICD-10-CM Code for Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale I26. 90.
How do you code a septic embolism?
Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonaleI26. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I26. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I26.
What is a septic pulmonary embolism?
Septic pulmonary embolism is an uncommon disease in which septic thrombi are mobilised from an infectious nidus and transported in the vascular system of the lungs. It is usually associated with tricuspid valve vegetation, septic thrombophlebitis or infected venous catheters.
How do you treat septic embolism in lungs?
Septic emboli treatment Treating the infection with antibiotics is typically the primary treatment for septic emboli. Depending on the location of the original source of the infection, treatment could also include: draining an abscess. removing or replacing infected prostheses.
Do you Anticoagulate septic pulmonary emboli?
Although anticoagulation therapy is important for treating noninfective pulmonary embolism, it is not typically used in cases of septic embolization due to the increased risk of bleeding in the area of the infected embolus.
How does endocarditis affect the lungs?
The lungs are especially at risk when IE affects the right side of the heart. This is called right-sided infective endocarditis. A vegetation or blood clot going to the lungs can cause a pulmonary embolism and lung damage. Other lung complications include pneumonia and a buildup of fluid or pus around the lungs.
What is the difference between sepsis and septic?
ANSWER: Sepsis is a serious complication of an infection. It often triggers various symptoms, including high fever, elevated heart rate and fast breathing. If sepsis goes unchecked, it can progress to septic shock — a severe condition that occurs when the body's blood pressure falls and organs shut down.
Can sepsis cause blood clots in lungs?
blood clots. lowered blood pressure. lack of oxygen reaching the body's organs such as the heart, brain, lungs and kidneys. organ failure.
Can pneumonia cause septic emboli?
Patients with septic pulmonary embolism who require critical care, especially those with pneumonia and liver abscess, are associated with high mortality. Early diagnosis, appropriate antibiotic therapy, surgical intervention and respiratory support are essential.
Is septic embolism fatal?
A septic embolism is a type of embolism that is infected with bacteria, resulting in the formation of pus. These may become dangerous if dislodged from their original location. Like other emboli, a septic embolism may be fatal.
What bacteria causes pulmonary embolism?
Background. Septic pulmonary embolism (SPE) is an uncommon but serious complication resulting from infection of the blood. Gram-positive cocci, including methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, are the most common causative organisms of SPE.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is a type 2 exclude note?
A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I26) and the excluded code together. chronic pulmonary embolism (.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
damage to other organs in your body from not getting enough oxygen. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
The ICD code I26 is used to code Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of the lung's main artery or one of its branches by a substance that has traveled from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). PE results from a deep vein thrombosis (commonly a blood clot in a leg) that breaks off and migrates to the lung, a process termed venous thromboembolism (VTE).
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'I26.90 - Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code I26.90. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code I26.90 and a single ICD9 code, 415.12 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the ICd 10 code for pulmonary embolism?
I26.01 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Septic pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically.
What is the code for septic pulmonary emboli?
The attending documents staphylococcal septicemia due to bacterial endocarditis and septic pulmonary emboli. Code Assignment: A41.01 for the staphylococcal septicemia as the primary diagnosis (pdx)
What is a septic embolus?
A septic embolus is a type of bacterial infection inside a blood vessel due to a thrombus or fat globule or air or foreign material.
What is the underlying infection of a septic embolism?
The physician diagnoses the patient with septic arterial embolism. His underlying infection is acute infective endocarditis. Also, according to the documentation, the patient has an embolism and thrombosis of the thoracic aorta.
Where does septic pulmonary embolus go?
The embolic material travels through the ve nous system to the right side of the heart and goes into the pulmonary arterial system where it lodges in small vessels.
Can a septic pulmonary embolic be treated with anticoagulants?
Depending on the cause of the septic pulmonary embolic, treatment with anticoagulants may be considered. Note: Do not Sequence Embolism as Primary Diagnosis (pdx) Whether reporting septic arterial or septic pulmonary embolisms, you should never report these codes as the primary diagnosis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for parkinsonism
- 2. icd 10 code for lamotrigine level
- 3. icd 10 code for personal history of tia
- 4. icd 10 code for insurance paperwork
- 5. icd 10 code for anti smooth muscle antibody
- 6. icd-10 code for cologuard screening
- 7. icd 9 code for bph without obstruction
- 8. icd 10 pcs code for nasogastric tube placement
- 9. icd 10 code for long term use of thyroid medication
- 10. icd 10 code for didunspecified