What are the common ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM CATEGORY CODE RANGE SPECIFIC CONDITION ICD-10 CODE Diseases of the Circulatory System I00 –I99 Essential hypertension I10 Unspecified atrial fibrillation I48.91 Diseases of the Respiratory System J00 –J99 Acute pharyngitis, NOS J02.9 Acute upper respiratory infection J06._ Acute bronchitis, *,unspecified J20.9 Vasomotor rhinitis J30.0
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is the ICD 10 code for impacted tooth?
- DRG 011 - TRACHEOSTOMY FOR FACE,MOUTH & NECK DIAGNOSES OR LARYNGECTOMY WITH MCC
- DRG 012 - TRACHEOSTOMY FOR FACE,MOUTH & NECK DIAGNOSES OR LARYNGECTOMY WITH CC
- DRG 013 - TRACHEOSTOMY FOR FACE,MOUTH & NECK DIAGNOSES OR LARYNGECTOMY WITHOUT CC/MCC
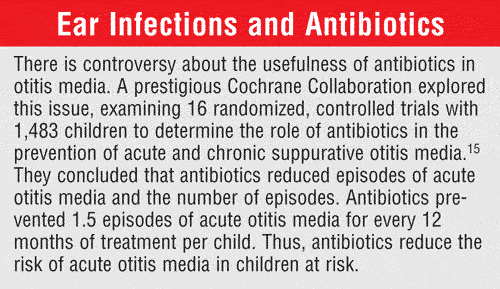
What is the ICD-10 code for acute serous otitis media right ear?
Acute serous otitis media, right ear H65. 01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H65. 01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for serous otitis media?
03.
What is serous otitis media?
Otitis media with effusion (OME (picture 1)), also called serous otitis media or "glue ear," is defined as the presence of middle ear fluid without signs of acute infection [1].
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R50 9?
ICD-10 | Fever, unspecified (R50. 9)
What is acute serous otitis media bilateral?
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear space. It is also called serous or secretory otitis media (SOM). This fluid may accumulate in the middle ear as a result of a cold, sore throat or upper respiratory infection.
What is the ICD 10 code for otitis media left ear?
ICD-10 Code for Otitis media, unspecified, left ear- H66. 92- Codify by AAPC.
What is serous otitis media in adults?
Serous otitis media (SOM), also known as otitis media with effusion (OME), fluid in the ear, middle ear effusion (MEE), or secretory otitis media, is a condition in which fluid resides in the middle ear. "Serous" refers to the type of fluid that is collecting inside the middle ear.
What is the difference between serous and suppurative otitis media?
Acute suppurative otitis media is distinguished from secretory (serous) otitis media by the presence of purulent fluid in the middle ear. Pathogenic bacteria may be cultured from the majority of needle aspirates of this purulent fluid.
How do you get serous otitis media?
Secretory otitis media is an effusion in the middle ear resulting from incomplete resolution of acute otitis media or obstruction of the eustachian tube without infection.
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is the ICD-10 code for R11 0?
ICD-10 code R11. 0 for Nausea is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What does the first letter in the alphanumeric ICD-10 code represent?
Code Structure: Comparing ICD-9 to ICD-10ICD-9-CMICD-10-CMFirst character is numeric or alpha ( E or V)First character is alphaSecond, Third, Fourth and Fifth digits are numericAll letters used except UAlways at least three digitsCharacter 2 always numeric; 3 through 7 can be alpha or numeric3 more rows•Aug 24, 2015
Is serous otitis media serious?
Chronic Serous Otitis Media Chronic otitis media may be irritating or painless, but ear pressure and popping of the ears is often constant. While chronic serous otitis media may not directly cause hearing damage, it can make a child vulnerable to recurrent ear infections, which place the child at risk of hearing loss.
How is serous otitis treated?
Etiologic treatment of serous otitis rests on restoration of satisfactory nasal ventilation (education to improve nose-blowing, adenoidectomy), improvement of eustachian tube patency (corticosteroids), and modification of the characteristics of middle ear secretions (mucolytic agents and mucomodifying agents).
How do you fix serous otitis media?
How is a middle ear infection treated?Antibiotics, taken by mouth or as ear drops.Medication for pain.Decongestants, antihistamines, or nasal steroids.For chronic otitis media with effusion, an ear tube (tympanostomy tube) may help (see below)
How is acute serous otitis media treated?
Management of acute otitis media should begin with adequate analgesia. Antibiotic therapy can be deferred in children two years or older with mild symptoms. High-dose amoxicillin (80 to 90 mg per kg per day) is the antibiotic of choice for treating acute otitis media in patients who are not allergic to penicillin.
Popular Posts:
- 1. billable icd 10 code for history of bronchitis
- 2. 2017 icd 10 code for plaque distal abdomonal aorta
- 3. icd-10-cm code for ercp with bile duct stone extraction ??
- 4. icd 10 code for mediterranean fever
- 5. what is icd 10 code for malignant adenofibroma
- 6. icd 9 code for traumatic wounds
- 7. icd 10 cm code for pain in upper extremity
- 8. icd 10 code for low appetite
- 9. icd 10 code for holosystolic
- 10. icd 10 code for hemorrhoids external