Full Answer
How do you cure short term memory loss?
- Be flexible and patient. Help the person try to remember what he or she can.
- Make it easier for the person to remember new information. ...
- Give verbal cues rather than ask questions. ...
- Keep a regular routine. ...
- Write down important pieces of information.
- Learn what to expect. ...
- Seek help from family and friends.
What are the reasons for short term memory loss?
- brain injuries and diseases
- chronic fatigue syndrome
- depression
- diabetes
- epilepsy
- hypertension
- menopause
- neurological disorders
- post-traumatic stress disorder
- schizophrenia
What is the best medicine for short term memory loss?
- Omega-3 fatty acid. Omega-3 fish oil supplements have piqued great interest. ...
- Huperzine A. Also known as Chinese club moss, this natural medicine works in a similar way as Alzheimer's drugs. ...
- Acetyl-L-carnitine. Some studies suggest that this amino acid might help Alzheimer's patients with memory problems. ...
- Vitamin E. ...
- Asian (or Panax) ginseng. ...
How many people suffer from short term memory loss?
The mildest form, age associated memory impairment, is characterised by self perception of memory loss and a standardised memory test score showing a decline in objective memory performance compared with younger adults.1About 40% of people aged 65 or older have age associated memory impairment—in the United States, about 16 million people.
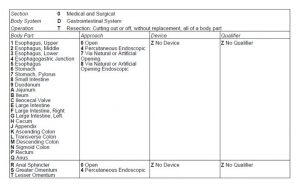
What is systemic and extensive loss of memory caused by?
Systematic and extensive loss of memory caused by organic or psychological factors. The loss may be temporary or permanent, and may involve old or recent memories.
When will the ICD-10-CM R41.3 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R41.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is memory loss permanent?
The loss may be temporary or permanent, and may involve old or recent memories. Compare forgetting and memory decay. Pathologic partial or complete loss of the ability to recall past experiences (amnesia, retrograde) or to form new memories (amnesia, anterograde). This condition may be of organic or psychologic origin.
What is the R41.1 code?
Valid for Submission. R41.1 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of anterograde amnesia. The code R41.1 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
Does memory always work?
Memory doesn't always work perfectly. As you grow older, it may take longer to remember things.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for child vaccination
- 2. icd 10 pcs code for extraperitoneal c-section, low transverse incision
- 3. icd 9 code for family history of diabetes
- 4. icd 10 code for exhaustion
- 5. icd 9 code for f 43 1
- 6. icd 9 code for vertebral fracture
- 7. icd-9-cm code for stenosis of the carotid artery
- 8. icd 10 code for blunt ocular trauma
- 9. icd 10 code for moderately distended urinary bladder
- 10. icd 10 code for ocular migraine without headache