What is the ICD 10 code for acute sialoadenitis?
Acute sialoadenitis. K11.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K11.21 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for sialolithiasis?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K11.5. Sialolithiasis. K11.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K11.5 became effective on October 1, 2018.
How is Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) diagnosed?
To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the four child codes of K11.2 that describes the diagnosis 'sialoadenitis' in more detail. Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of a salivary gland.
What is the ICD 10 code for excluded note?
K11.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K11.21 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K11.21 - other international versions of ICD-10 K11.21 may differ. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes.
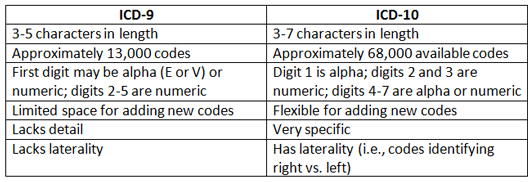
What is sialadenitis?
A salivary gland infection is also called sialadenitis and is caused by bacteria or viruses. A salivary stone or other blockage of the salivary gland duct can contribute to an acute infection. Chronic inflammation of a salivary gland can cause it to stop functioning.
What is the ICD-10 code for Sialolithiasis?
ICD-10 code K11. 5 for Sialolithiasis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is Sialoadenitis unspecified?
Sialadenitis is an infection of the salivary glands. It is usually caused by a virus or bacteria. The parotid (in front of the ear) and submandibular (under the chin) glands are most commonly affected. Sialadenitis may be associated with pain, tenderness, redness, and gradual, localized swelling of the affected area.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Acute recurrent Sialoadenitis?
22.
What is sialadenitis of submandibular gland?
Submandibular sialadenitis is inflammation of the submandibular gland, which is caused by salivary stasis that leads to retrograde seeding of bacteria from the oral cavity. Sialadenosis is a benign,non-inflammatory swelling of salivary glands usually associated with metabolic conditions.
What is submandibular Sialolithiasis?
Sialolithiasis is the formation of calcific concretions within the parenchyma or ductal system of the major or minor salivary glands, but it most commonly affects the submandibular salivary gland. Sialolithiasis usually occurs in adults aged 30 to 60 years and causes pathognomonic pain during meals.
Is sialadenitis and parotitis the same?
Sialadenitis in the pediatric population accounts for up to 10% of all salivary gland disease. Viral parotitis and juvenile recurrent parotitis are the two most common causes. Multiple factors, independently or in combination, can result in acute, chronic, or recurrent acute salivary gland inflammation.
Is sialadenitis bilateral?
Painless swellings (unless secondarily infected) classically occur in autoimmune sialadenitis (i.e., Sjogren syndrome) and may be unilateral or bilateral. Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Kuttner's tumor) is typically unilateral and may mimic a tumor.
How do you get sialadenitis?
What Causes Sialadenitis? Sialadenitis can be caused by a viral infection (such as mumps), bacterial infection, or an autoimmune disease such as Sjogren's syndrome (see below). Bacterial infections can happen when the flow of saliva is blocked due to stones in the salivary duct or a narrowing of the duct.
What is Acute parotitis?
Acute parotitis is recent swelling of one or both of the salivary glands. There are a number of causes, including viruses and bacteria. Acute viral parotitis is not a common symptom of influenza virus infection and is much more commonly seen following infection with the mumps virus.
What Are salivary glands?
The salivary glands are organs on each side of the face. They make saliva (spit), the lubricating fluid found in the mouth and throat. Saliva has enzymes that begin the process of digesting (breaking down) food. It also has antibodies and other substances that help prevent infections of the mouth and throat.
Where is the submandibular?
About the size of a walnut, the submandibular glands are located below the jaw. The saliva produced in these glands is secreted into the mouth from under the tongue. Like the parotid glands, the submandibular glands have two parts called the superficial lobe and the deep lobe.
What are the symptoms of sialoadenitis?
Depending on whether the condition is acute or chronic, symptoms of sialoadenitis will vary, and include: Abnormal or foul taste in the mouth. Dry mouth. Fever. Mouth or facial pain, especially when eating. Enlargement, firmness, and tenderness of the gland. Code selection for sialoadenitis is straightforward:
What is a Z72.0?
Tobacco dependence (F17.-) Tobacco use (Z72.0) Example: A 45-year-old woman presents with painful swelling on the left side of her face for the past four days. The pain was of sudden onset, continuous in nature, moderate in intensity, and radiating to the left ear when eating.
What is the name of the infection that causes saliva to stop flowing?
Sialoadenitis occurs when the flow of saliva is slowed or stopped, and is mainly caused by bacterial infection, such as Staphylococcus aureus.
Can parotidectomy be superficial?
Intractable cases may require superficial parotidectomy. Chronic sialoadenitis is often associated with a previous occurrence of acute inflammation with subsequent glandular destruction. Decreased salivary flow with stasis is a key factor for this condition.
Is sialoadenitis a bacterial infection?
Acute recurrent sialoadenitis is relatively uncommon, developing as a result of low-grade bacterial infection. It usually affects the parotid glands, and is characterized by recurrent, painful and swollen glands. Intractable cases may require superficial parotidectomy. Chronic sialoadenitis is often associated with a previous occurrence ...
The ICD code K112 is used to code Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of a salivary gland. It may be subdivided temporally into acute, chronic and recurrent forms.
Coding Notes for K11.2 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K11.2 - Sialoadenitis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K11.2. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
The ICD code K112 is used to code Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of a salivary gland. It may be subdivided temporally into acute, chronic and recurrent forms.
Coding Notes for K11.21 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Type-1 Excludes mean the conditions excluded are mutually exclusive and should never be coded together. Excludes 1 means "do not code here."
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K11.21 - Acute sialoadenitis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K11.21. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code K11.21 and a single ICD9 code, 527.2 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
The ICD code K112 is used to code Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of a salivary gland. It may be subdivided temporally into acute, chronic and recurrent forms.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K11.20 - Sialoadenitis, unspecified'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K11.20. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code K11.20 and a single ICD9 code, 527.2 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hydrops keratoconus
- 2. icd 10 code for occluded picc line
- 3. icd 10 code for acute on chronic anxiety
- 4. icd 10 code for alcoholic pancreatitis
- 5. icd 10 code for neoplasm right buttock
- 6. icd 10 code for hypoxemia
- 7. icd 10 code for acute otitis media externa serous with perforation
- 8. icd 10 cm code for light headed,
- 9. icd 10 code for neck injury closed posterior cord syndrome caused by a fracture
- 10. icd 9 code for nephrosclerosis