How do you code SIRS?
• SIRS (Systemic inflammatory response syndrome) – Identify the underlying trauma or infection then choose a code from 995.9x (Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)) depending on the information given. SIRS is defined as a clinical response to an insult, infection or trauma. The causative infection or trauma should be coded first.
How to code SIRS?
- Pulse greater than 90 beats per minute
- Respirations greater than 20/min or PaCO2 greater than 32 mm Hg
- Temperature less than 38 or greater than 36°C
- White blood cell count greater than 12,000 or less than 4,000 cells/mm3 or greater than 10% immature neutrophils (bands)
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
What is the longest ICD 10 code?
What is the ICD 10 code for long term use of anticoagulants? Z79.01. What is the ICD 10 code for medication monitoring? Z51.81. How do you code an eye exam with Plaquenil? Here’s the coding for a patient taking Plaquenil for RA:Report M06. 08 for RA, other, or M06. Report Z79. 899 for Plaquenil use for RA.Always report both.
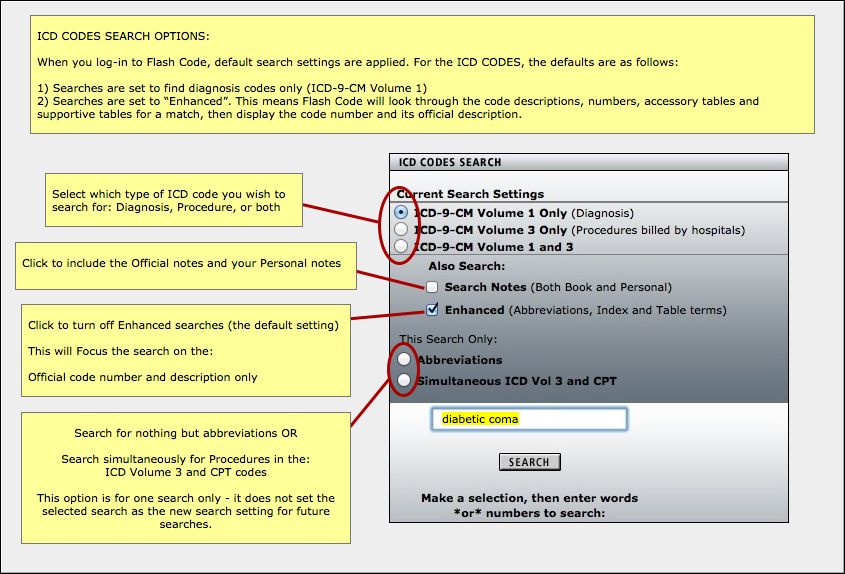
How do you code SIRS?
Coding sepsis requires a minimum of two codes: a code for the systemic infection (e.g., 038. xx) and the code 995.91, SIRS due to infectious process without organ dysfunction. If no causal organism is documented within the medical record, query the physician or assign code 038.9, Unspecified septicemia.
What is the difference between sepsis and SIRS?
Sepsis is a systemic response to infection. It is identical to SIRS, except that it must result specifically from infection rather than from any of the noninfectious insults that may also cause SIRS (see the image below).
Is SIRS the same as shock?
Although not universally accepted terminology, severe SIRS and SIRS shock are terms that some authors have proposed. These terms suggest organ dysfunction or refractory hypotension related to an ischemic or inflammatory process rather than to an infectious etiology.
What are the 4 SIRS criteria?
Four SIRS criteria were defined, namely tachycardia (heart rate >90 beats/min), tachypnea (respiratory rate >20 breaths/min), fever or hypothermia (temperature >38 or <36 °C), and leukocytosis, leukopenia, or bandemia (white blood cells >1,200/mm3, <4,000/mm3 or bandemia ≥10%).
What comes first SIRS or sepsis?
Sepsis is a clinical syndrome that complicates severe infection and is characterized by the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), immune dysregulation, microcirculatory derangements, and end-organ dysfunction.
When do we use SIRS criteria?
SIRS criteria are mostly used as a screening tool to identify patients that may need further workup for sepsis and severe sepsis. In the emergency department it is a triage tool that helps determine patient acuity and identify patients that are potentially septic and in need of further screening.
What is systemic inflammatory response syndrome SIRS?
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an exaggerated defense response of the body to a noxious stressor (infection, trauma, surgery, acute inflammation, ischemia or reperfusion, or malignancy, to name a few) to localize and then eliminate the endogenous or exogenous source of the insult.
What is SIRS in medical terms?
A serious condition in which there is inflammation throughout the whole body. It may be caused by a severe bacterial infection (sepsis), trauma, or pancreatitis. It is marked by fast heart rate, low blood pressure, low or high body temperature, and low or high white blood cell count.
What is SIRS with acute organ dysfunction?
SIRS is a serious condition related to systemic inflammation, organ dysfunction, and organ failure. It is a subset of cytokine storm, in which there is abnormal regulation of various cytokines. SIRS is also closely related to sepsis, in which patients satisfy criteria for SIRS and have a suspected or proven infection.
Is SIRS acute or chronic?
Excerpt. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) is an exaggerated defense response of the body to a noxious stressor (infection, trauma, surgery, acute inflammation, ischemia or reperfusion, or malignancy, to name a few) to localize and then eliminate the endogenous or exogenous source of the insult.
Can you code SIRS with pneumonia?
Documentation issues: When SIRS is documented with an inflammatory condition, such as pancreatitis, the inflammatory condition should be sequenced first, followed by the code for SIRS, R65. 1-. When SIRS is documented with an infectious source, for instance, “SIRS due to pneumonia,” only code pneumonia.
What is needed to qualify a patient who meets SIRS criteria as septic?
Temperature higher than 38°C (100.4°F) or lower than 36°C (96.8°F) Heart rate (HR) higher than 90 beats/min. Respiratory rate (RR) higher than 20 breaths/min or arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) lower than 32 mm Hg.
What is the ICd 10 code for systemic inflammatory response syndrome?
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) of non-infectious origin 1 underlying condition, such as: 2 heatstroke (#N#ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T67.0#N#Heatstroke and sunstroke#N#2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code#N#Use Additional#N#code (s) to identify any associated complications of heatstroke, such as:#N#coma and stupor ( R40.-)#N#rhabdomyolysis ( M62.82)#N#systemic inflammatory response syndrome ( R65.1-)#N#T67.0-) 3 injury and trauma ( S00-T88#N#ICD-10-CM Range S00-T88#N#Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes#N#S00-S09 Injuries to the head#N#S10-S19 Injuries to the neck#N#S20-S29 Injuries to the thorax#N#S30-S39 Injuries to the abdomen, lower back, lum...#N#S40-S49 Injuries to the shoulder and upper arm#N#S50-S59 Injuries to the elbow and forearm#N#S60-S69 Injuries to the wrist, hand and fingers#N#S70-S79 Injuries to the hip and thigh#N#S80-S89 Injuries to the knee and lower leg#N#S90-S99 Injuries to the ankle and foot#N#T07-T07 Injuries involving multiple body regions#N#T14-T14 Injury of unspecified body region#N#T15-T19 Effects of foreign body entering through...#N#T20-T25 Burns and corrosions of external body su...#N#T26-T28 Burns and corrosions confined to eye and...#N#T30-T32 Burns and corrosions of multiple and uns...#N#T33-T34 Frostbite#N#T36-T50 Poisoning by, adverse effect of and unde...#N#T51-T65 Toxic effects of substances chiefly nonm...#N#T66-T78 Other and unspecified effects of externa...#N#T79-T79 Certain early complications of trauma#N#T80-T88 Complications of surgical and medical ca...#N#)
When is ICD-10 R65.1 effective?
Short description: SIRS of non-infectious origin. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM R65.1 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What are the symptoms of SIRS?
SIRS is manifested by two or more of the following symptoms: fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, leukocytosis, or leukopenia. Documentation issues: When SIRS is documented on the chart, determine if it’s due to an infectious or non-infectious cause. SIRS due to a localized infection can no longer be coded as sepsis in.
When to add R65.2-?
If the patient has severe sepsis, add R65.2- with the codes for specific organ dysfunctions.
What is the A41.51?
A41.51 Sepsis due to Escherichia coli [E. coli] N39.0. SIR S. SIRS is the body’s clinical cascading response to infection or trauma that triggers an acute inflammatory reaction and progresses to coagulation of the blood, impaired fibrinolysis, and organ failure.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if severe sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
What is the P36 code?
Codes from category P36 include the organism; an additional code for the infectious organism is not assigned. If the P36 code does not describe the specific organism, an additional code for the organism can be assigned. Urosepsis. The term “urosepsis” is not coded in ICD-10-CM.
What is post-procedural sepsis?
Post-procedural Sepsis and Sepsis Due to a Device, Implant, or Graft. A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to wound infection, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.
When to query a physician for sepsis?
You must query the physician when the term “sepsis syndrome” is documented as a final diagnosis. Know when to Query. Sepsis is a complicated condition to code, and it is often necessary to query the physician to code the case correctly.
When SIRS is due to a noninfectious process, what is the code?
When SIRS is due to a noninfectious process, code first the noninfectious process, followed by the code for SIRS. If organ dysfunction is documented, code also R65.11 and the code (s) for the specific organ dysfunction.
What is SIRS in the body?
SIRS is an inflammatory state affecting the whole body. It is an exaggerated defense response of the body to a noxious stressor, such as infection or trauma, that triggers an acute inflammatory reaction, which may progress and result in the formation of blood clots, impaired fibrinolysis, and organ failure.
Why is severe sepsis not assigned?
For instance, if sepsis, pneumonia, and acute renal failure due to dehydration are documented, the code for severe sepsis may not be assigned because the acute renal failure is not stated as due to or associated with sepsis. If the documentation is unclear, query the physician.
When is a localized infection coded?
If the patient is admitted with a localized infection and the patient does not develop sepsis or severe sepsis until after the admission, the localized infection is coded first, followed by the appropriate codes for sepsis or severe sepsis, if applicable .
What are the symptoms of a localized infection?
Documentation issues: A patient with a localized infection usually presents with tachycardia, leukocytosis, tachypnea, and/or fever. These are typical symptoms of any infection. It is up to the clinical judgment of the physician to decide whether the patient has sepsis.
What is systemic infection?
A systemic infection can occur as a complication of a procedure or due to a device, implant, or graft. This includes systemic infections due to postoperative wound infections, infusions, transfusions, therapeutic injections, implanted devices, and transplants.
Is septicemia difficult to code?
Sepsis, systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), and septicemia have historically been difficult to code. Changing terminology, evolving definitions, and guideline updates over the past 20 years have created confusion with coding sepsis.
What is systemic scleroderma?
Systemic sclerosis [scleroderma] M34- 1 A chronic disorder, possibly autoimmune, marked by excessive production of collagen which results in hardening and thickening of body tissues. The two types of systemic scleroderma, limited cutaneous and diffuse cutaneous are classified with focus on the extent of affected skin. A relationship exists between the extent of skin area affected and degree of internal organ/system involvement. Systemic scleroderma can manifest itself in pulmonary fibrosis, raynaud's syndrome, digestive system telangiectasias, renal hypertension and/or pulmonary hypertension. 2 A chronic multi-system disorder of connective tissue. It is characterized by sclerosis in the skin, the lungs, the heart, the gastrointestinal tract, the kidneys, and the musculoskeletal system. Other important features include diseased small blood vessels and autoantibodies. The disorder is named for its most prominent feature (hard skin), and classified into subsets by the extent of skin thickening: limited scleroderma and diffuse scleroderma. 3 A disease that is marked by hardening and thickening of skin, connective tissue that surrounds other tissues and organs, and blood vessels. 4 A rare, chronic disease characterized by excessive deposits of collagen in the skin or other organs 5 Systemic disorder of the connective tissue; manifested by hardening and thickening of the skin, by abnormalities involving the microvasculature and larger vessels, and by fibrotic degenerative changes in various body organs including the heart, lungs, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A chronic disorder, possibly autoimmune, marked by excessive production of collagen which results in hardening and thickening of body tissues.

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2015 icd 10 code for hydronephrosis
- 2. icd 9 code for chest xray
- 3. icd 10 code for terminal ileum thickening
- 4. icd 10 code for normal postpartum
- 5. icd 10 code for compression fracture of t6 vertebra
- 6. icd 10 code for neurogenic orthostatic hypotension
- 7. icd 10 code for printed material for diet
- 8. icd 10 code for r intertrochanteric femur fracture
- 9. icd-10-cm code for ten hour old neonate who is having convulsions
- 10. icd 10 code for elavated estrogen