What does ICD - 10 stand for?
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Edition (ICD-10), is a clinical cataloging system that went into effect for the U.S. healthcare industry on Oct. 1, 2015, after a series of lengthy delays.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Disclosures: Kuwahara reports serving as a CMS fellow and previously served as a fellow at the Association of Asian Pacific Community Health Organizations. Disclosures: Kuwahara reports serving as a CMS fellow and previously served as a fellow at the Association of Asian Pacific Community Health Organizations.
What is ICD 10 code for?
What is ICD-10. The ICD tenth revision (ICD-10) is a code system that contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, circumstances and external causes of diseases or injury. The need for ICD-10. Created in 1992, ICD-10 code system is the successor of the previous version (ICD-9) and addresses several concerns.
Can ultrasound diagnose spina bifida?
Ultrasound is the gold standard diagnostic tool for spina bifida. Three-dimensional ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are also beginning to play a role in the characterisation of the open spina bifida spinal lesion.
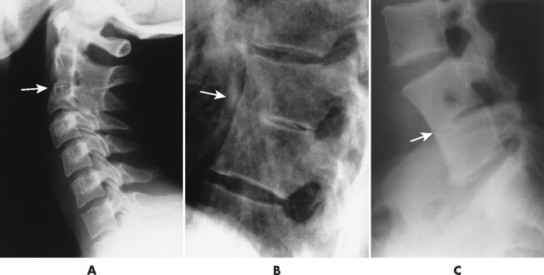
What is the ICD-10-CM code for spina bifida occulta?
ICD-10 code Q76. 0 for Spina bifida occulta is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
What is spina bifida unspecified?
It is a type of neural tube defect, which is a problem with the spinal cord or its coverings. It happens if the fetal spinal column doesn't close completely during the first month of pregnancy. There is usually nerve damage that causes at least some paralysis of the legs.
What is spina bifida myelomeningocele?
Myelomeningocele is the most severe form of spina bifida. A portion of the spinal cord or nerves is exposed in a sac through an opening in the spine that may or may not be covered by the meninges. The opening can be closed by surgeons while the baby is in utero or shortly after the baby is born.
Are Myelomeningocele and Meningomyelocele the same?
Meningomyelocele, also commonly known as myelomeningocele, is a type of spina bifida. Spina bifida is a birth defect in which the spinal canal and the backbone don't close before the baby is born. This type of birth defect is also called a neural tube defect.
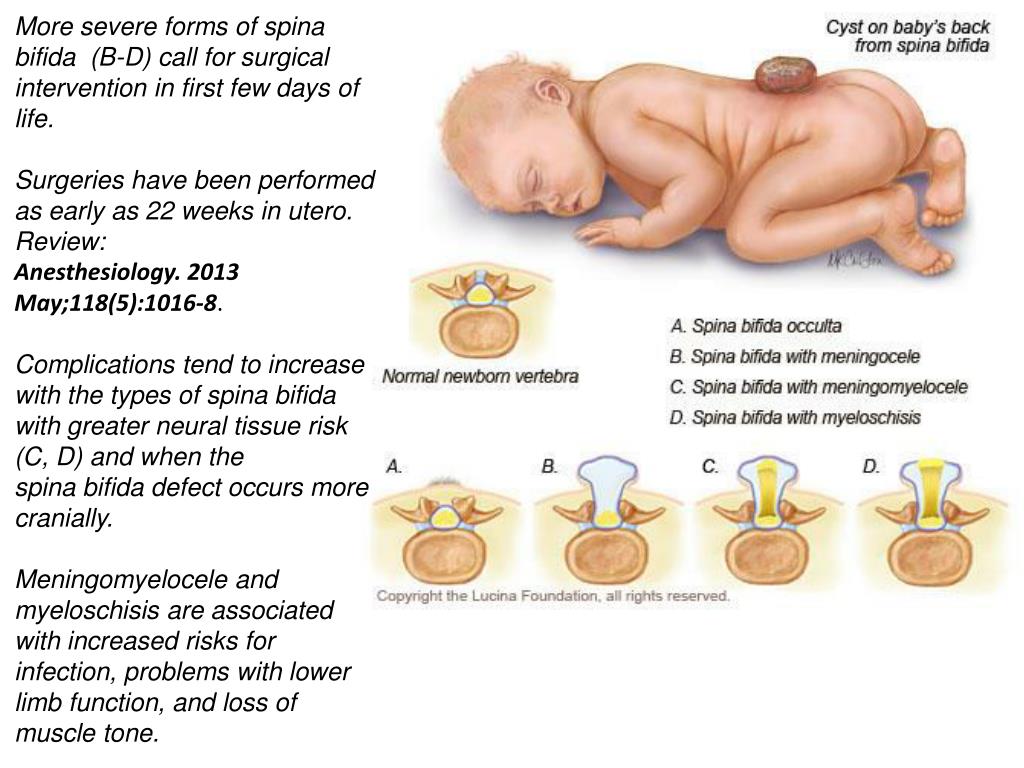
What are the 3 types of spina bifida?
The three most common types of spina bifida are:Myelomeningocele (sounds like: my-low-ma-nin-jo-seal; hear how “myelomeningocele” sounds ) ... Meningocele (sounds like: ma-nin-jo-seal; hear how “meningocele” sounds ) ... Spina Bifida Occulta (sounds like: o-cult-tuh; hear how “occulta” sounds )
Is spina bifida considered a spinal cord injury?
Congenital defects are problems that result from abnormal growth or development of the spine and spinal cord, and include spina bifida (incomplete closure of the spinal cord or myelomeningocele), scoliosis (bending or twisting of bony spine), tethered spinal cord and diastematomyelia (abnormal division of the spinal ...
What is the difference between spina bifida and myelomeningocele?
Myelomeningocele is a type of spina bifida — a birth defect in which your baby's spine and spinal canal don't close before birth. Healthcare providers can usually diagnose myelomeningocele during pregnancy and perform surgery during pregnancy or after birth to repair the opening in your baby's spine.
What is lumbosacral myelomeningocele?
A myelomeningocele (pronounced my-elo-men-IN-go-seal) is a defect of the backbone (spine) and spinal cord. Before birth, the baby's spine, the spinal cord and the spinal canal do not form or close normally. A myelomeningocele is the most serious form of spina bifida.
What is the difference between meningocele and myelomeningocele?
With meningoceles, the spinal cord has developed normally and is undamaged. The child has no neurological problems. Myelomeningocele is the most severe form of spina bifida, occurring nearly once for every 1,000 live births.
What is the difference between spina bifida and spina bifida occulta?
Spina bifida is a condition present at birth (a congenital birth defect) caused by your spine forming incorrectly during fetal development. The word “occulta” means “hidden.” Spina bifida occulta is also known as hidden spina bifida because a small layer of skin covers the opening of your spinal vertebrae.
What is meningocele lumbar?
A meningocele is a birth defect where there is a sac protruding from the spinal column. The sac includes spinal fluid, but does not contain neural tissue. It may be covered with skin or with meninges (the membranes that cover the central nervous system). The sac often is visible from the outside of the back.
What are the two characteristics of spina bifida?
Symptoms of spina bifida weakness or total paralysis of the legs. bowel incontinence and urinary incontinence. loss of skin sensation in the legs and around the bottom – the child is unable to feel hot or cold, which can lead to accidental injury.
How long can a person live with spina bifida?
The prognosis for survival was strikingly poor in those with the most extensive neurological deficit. Only 17% (7/42) of those born with a high sensory level (above T11) survived to the mean age of 40 years, compared with 61% (23/38) of those with a low sensory level (below L3; p=0.001).
Is spina bifida a disability?
If your family has limited income and resources, your child with spina bifida will likely qualify for SSI disability benefits. Spina bifida is a disease that affects children and can be very disabling. If your child has spina bifida, he or she may qualify for SSI disability benefits by applying through Social Security.
Can a child with spina bifida lead a normal life?
About 1,500 to 2,000 babies of the 4 million born in the U.S. every year have spina bifida. Thanks to advances in medicine, 90% of babies who have this defect live to be adults, and most go on to lead full lives.
What is the main cause of spina bifida?
Doctors aren't certain what causes spina bifida. It's thought to result from a combination of genetic, nutritional and environmental risk factors, such as a family history of neural tube defects and folate (vitamin B-9) deficiency.
What is the open form of spina bifida?
The open form is called spina bifida cystica and the closed form is spina bifida occulta. (from Joynt, Clinical Neurology, 1992, ch55, p34) Developmental anomaly characterized by defective closure of the bony encasement of the spinal cord, through which the cord and meninges may protrude.
What is Spina Bifida Aperta?
Spina bifida aperta. Spina bifida without hydrocephalus. Clinical Information. Birth defect involving inadequate closure of the bony casement of the spinal cord, through which the spinal membranes, with or without spinal cord tissue, may protrude.
Can Spina Bifida be cured?
They may have learning difficulties, urinary and bowel problems or hydrocephalus, a buildup of fluid in the brain. There is no cure.
The ICD code Q05 is used to code Rachischisis
Rachischisis (Greek: "rhachis - ῥάχις" - spine, and "schisis - σχίσις" - split) is a developmental birth defect involving the neural tube. This anomaly occurs in utero, when the posterior neuropore of the neural tube fails to close by the 27th intrauterine day.
Coding Notes for Q05.7 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'Q05.7 - Lumbar spina bifida without hydrocephalus'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code Q05.7. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 741.93 was previously used, Q05.7 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is Spina Bifida?
Vol. 23 No. 8 P. 27. Spina bifida is a congenital anomaly that results in spinal cord and vertebrae defects during pregnancy because the neural tube did not develop properly or failed to close. There are three main forms of spina bifida: occulta, meningocele, and myelomeningocele.
What is Spina bifida occulta?
Spina bifida occulta is the mildest form and results in a small separation or gap in one or more vertebrae. Typically, spina bifida occulta does not cause any signs or symptoms nor does the patient experience any neurological problems because the spinal nerves are not involved.
What is the procedure to put the meninges back in place?
For patients with meningocele, surgery may be performed to put the meninges back in place and close the opening. In myelomeningocele, surgery is performed to put the spinal cord and exposed tissue inside the body and cover with muscle and skin.
What is the name of the condition where the meninges push through the vertebrae?
A patch of hair, a birthmark, or a dimple may be present on the skin over the lower spine. Meningocele, which causes the meninges to push through the opening in the vertebrae, is a more severe form of spina bifida.
What is the ICd 10 code for spina bifida?
741.03 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of spina bifida with hydrocephalus, lumbar region. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What is the term for the buildup of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain?
Hydrocephalus is the buildup of too much cerebrospinal fluid in the brain. Normally, this fluid cushions your brain. When you have too much, though, it puts harmful pressure on your brain.
What is the ICd-9 GEM?
The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for gestational edema
- 2. icd 10 code for pancreatic disease wit diabetes
- 3. icd 10 code for depression unspecified depression type
- 4. icd 10 code for de quervain's tenosynovitis right wrist
- 5. icd 10 code for osteoarthritis of left knee
- 6. icd 10 pcs code for artificial rupture of membranes
- 7. icd 10 code for diabetic nonketotic hyperosmolar hyperglycemia
- 8. icd 10 code for spider bite nonvenomous
- 9. icd 10 code for enuresis unspecified
- 10. icd 10 code for infected breast tissue expander