Ulnar collateral ligament sprain of unspecified elbow, initial encounter. S53.449A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM S53.449A became effective on October 1, 2018.
Does ulnar nerve entrapment go away by itself?
Ulnar nerve injuries happen all the time. Sometimes, it may go away on its own, but if the problems persist for several weeks, treatment is very important: ulnar entrapment could wear away or stiffen the muscles in severe cases, sometimes even causing the hand to atrophy into a claw
What is the average settlement for ulnar nerve injury?
The average workers compensation settlement for hand injury claims is from $15,000 to $35,000 if you are released to full duty work when you reach maximum medical improvement. And from $55,000 to $85,000, or more, if you are unable to return to your pre-injury job or suffer additional injuries in the accident.
What are the symptoms of a lateral collateral injury?
What are the symptoms of a lateral collateral ligament injury?
- swelling of the knee (especially the outer aspect)
- stiffness of the knee joint that can cause locking of the knee.
- pain or soreness on the outside of the knee.
- instability of the knee joint (feeling like it’s going to give out)
How to diagnose a medial collateral ligament injury?
Your healthcare provider may use one or more of the following tests to diagnose an MCL tear:
- Physical exam: Your provider will examine your knee to see if you have pain with palpation on the inside of your knee. ...
- MRI: An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer to make detailed images of your organs and bones. ...
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures inside your body. ...
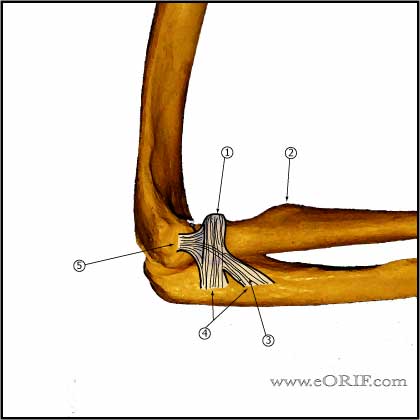
What is the ICD 10 code for right thumb ulnar collateral ligament tear?
Traumatic rupture of ulnar collateral ligament ICD-10-CM S53. 32XA is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v39.0):
What is ulnar collateral ligament sprain?
A ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) sprain is a tear to one of the ligaments on the inner side of your elbow. A UCL sprain usually occurs due to a throwing motion – that typically occurs during sports – or after elbow dislocation or surgery.
Is the ulnar collateral ligament the same as the lateral collateral ligament?
Ligaments keep joints stable. In the elbow, two of the major stabilizing ligaments are the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) and the lateral ulnar collateral ligament (LUCL). The UCL is also known as the medial collateral ligament or “Tommy John Ligament”. The LUCL is located on the lateral or outside part of the elbow.
Is the ulnar collateral ligament medial or lateral?
The medial (ulnar) collateral ligament (MCL) supports the ulnohumeral and radiohumeral joints medially, and is a fan-shaped structure. The lateral (radial) collateral ligament (LCL) also supports the ulnohumeral and radiohumeral joints, but laterally. It is more of a cord-like structure.
Where is the ulnar collateral ligament located?
The ulnar collateral ligament complex is located on the inside of the elbow (pinky or medial side). It is attached on one side to the humerus (the bone of the upper arm) and on the other side to the ulna (a bone in the forearm).
What is a Grade 1 UCL sprain?
A UCL injury is classified as a sprain and graded from grade 1 to 3. Grade 1 sprains — There is not a tear, but the ligament is stretched. Grade 2 sprains — The ligament is stretched, and it could be partially torn. Grade 3 sprains — Complete ligament tear.
What are the two collateral ligaments of the elbow joint?
The anterior band of the ulnar or medial collateral ligament (MCL) complex is the main static stabilizer of the elbow against valgus and internal rotation stress. The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) complex resists excessive varus and external rotational stress.
Is UCL a Tommy John?
Tommy John Surgery, more formally known as ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) reconstruction, is used to repair a torn ulnar collateral ligament inside the elbow. A UCL is a ligament on the inner side of your elbow that helps secure your elbow joint.
Are there two ulnar collateral ligaments?
The thumb metacarpophalangeal joint contains two important ligaments: the ulnar collateral ligament, which is on the pinky side of the thumb, and the radial collateral ligament, which is on the free side of the thumb.
What are the classifications for sprains of the elbow?
Elbow sprains are graded depending upon the severity of the symptoms as grade I (mild), grade II (moderate) and grade III (severe). Severe elbow sprains of grade III can lead to elbow dislocation or joint instability.
How do you treat a sprained UCL?
How Do You Treat UCL Sprains? First and second grade UCL sprains are treated by resting the elbow, ice application, medication and splinting. Third degree UCL sprains are first treated conservatively to reduce pain and swelling. This is followed by surgery to repair or reconstruct the ligament.
Why is it called medial collateral ligament?
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), or tibial collateral ligament (TCL), is one of the four major ligaments of the knee. It is on the medial (inner) side of the knee joint in humans and other primates. Its primary function is to resist outward turning forces on the knee.
Which ligament connects the ulna to the olecranon?
The transverse ligament connects to the inferior medial coronoid process of the ulna to the medial tip of the olecranon. Since it is connected to the same bone and not across the elbow joint, the transverse ligament has no contribution to the joint’s stability.
What ligament is responsible for dislocating the elbow?
The ulnar collateral ligament distributes over fifty percent of the medial support of the elbow. This can result in an ulnar collateral ligament injury or a dislocated elbow causing severe damage to the elbow and the radioulnar joints.
What are the symptoms of a left elbow injury?
Signs and symptoms. Ligaments of the left elbow. Red arrows mark the location of the UCL. Anatomy of the ulnar collateral ligament in the pitcher's elbow. Pain along the inside of the elbow is the main symptom of this condition. Throwing athletes report it occurs most often during the acceleration phase of throwing.
What is the risk of a UCL injury?
Specific overhead movements like those that occur during baseball pitching, tennis serving or volleyball spiking increase the risk of UCL injury. During the cocking phase of pitching, the shoulder is horizontally abducted, externally rotated and the elbow is flexed.
What causes a ruptured UCL?
Injuries to the ulnar collateral ligament are believed to result from poor throwing mechanics, overuse, high throwing velocities, and throwing certain types of pitches, such as curveballs. Poor mechanics along with high repetition of these overhead movements can cause irritation, micro-tears or ruptures of the UCL.
How to heal a torn UCL?
First a course of RICE (Rest, ice, compression, elevation) is typically coupled with NSAIDS (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) to help alleviate pain and swelling. When the swelling has subsided, individual exercises or physical therapy may be prescribed to strengthen muscles around the elbow joint to compensate for tearing in the UCL. These may include biceps curls (non resistance and resistance), pronating and supinating the forearm, and grip strengthening exercises , performed with low resistance and moderate repetitions no more than three times a week.
Can ulna rupture be painful?
At first, pain can be bearable and can worsen to an extent where it can terminate an athlete’s career. The repetitive stress placed on the ulna causes micro tears in the ligament resulting in the loss of structural integrity over time. The acute rupture is less common compared to the slow deterioration injury.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for quadriplegia secondary to myasthenia gravis
- 2. icd 10 code for osteoarthropathy
- 3. 2019 icd 10 code for premature baby pneumatocele
- 4. icd 9 code for critical ostial left main disease
- 5. icd 9 code for knee hemathroib
- 6. icd 9 code for rotator cuff injury
- 7. 2017 icd 10 code for gunshot wound to the right lower leg
- 8. icd-10 code for rib pain from fall
- 9. icd 10 code for other encounter
- 10. icd 10 cm code for fall. (while skateboarding