What is the ICD 10 code for staghorn calculus?
Calculus (stone), bladder; Calculus in diverticulum of bladder; Diverticulum of bladder, with calculus; Urinary bladder stone; staghorn calculus (N20.0); Calculus in diverticulum of bladder; Urinary bladder stone ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N20.2 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Calculus of kidney with calculus of ureter
What is the ICD 10 calculus of kidney 2019?
Calculus of kidney. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM N20.0 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N20.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 N20.0 may differ.
What is a staghorn calculus in kidney disease?
A staghorn calculus, a type of kidney stone with branches, happens in some cases because of repeated infections. The branches can block urine from leaving the kidney, causing kidney failure. What is a staghorn calculus? A staghorn calculus is a type of kidney stone. (Calculus in this case means a stone. The plural is calculi or stones.)
What is the ICD 10 code for kidney cancer?
Calculus of kidney. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code. N20.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM N20.0 became effective on October 1, 2019.
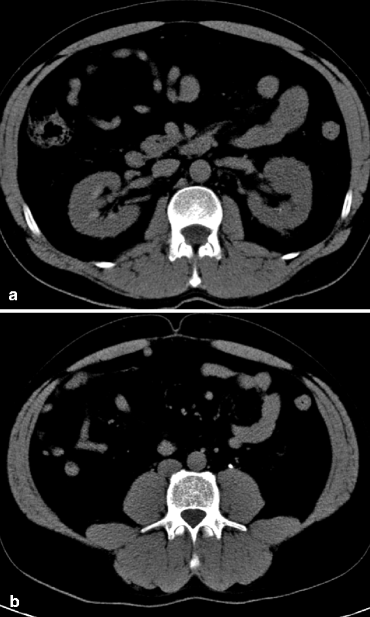
What is the ICD-10 code for staghorn calculus?
Calculus of kidney with calculus of ureter The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N20. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N20.
What is staghorn calculus?
A staghorn calculus is a type of kidney stone. (Calculus in this case means a stone. The plural is calculi or stones.) A staghorn calculus is the name given to a branching kidney stone, and may form if you have repeated urinary tract infections (UTIs).
What is the ICD-10 code for renal calculi?
ICD-10 code N20. 0 for Calculus of kidney is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the code for nephrolithotomy?
CPT 50081A commonly encountered scenario for urologists is the performance of percutaneous nephrolithotomy for a stone > 2 cm (CPT 50081) in a patient with a nephrostomy tube already in place.
Are struvite and staghorn stones the same?
Staghorn stones are large and branching stones that fill part or all of the pelvicalyceal system. They are usually unilateral and less common in men. They are linked to urease-producing bacterial infections and, hence, known as struvite infection stones.
What is the most common cause of staghorn renal calculi?
Staghorn calculi are most frequently composed of mixtures of magnesium ammonium phosphate (struvite) and calcium carbonate apatite; they are strongly associated with UTIs caused by organisms that produce the enzyme urease, which promotes the generation of ammonia and hydroxide from urea.
What is the diagnosis code N20 0?
0: Calculus of kidney.
What is ICD-10 code N20?
"N20. 0 - Calculus of Kidney." ICD-10-CM, 10th ed., Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the National Center for Health Statistics, 2018.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of renal stones?
ICD-10 code Z87. 442 for Personal history of urinary calculi is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the CPT code for PCNL?
However, the creation of these codes also has created some confusion for proper coding of percutaneous endourologic procedures with PCNL (CPT codes 50080 Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy or pyelostolithotomy, with or without dilation, endoscopy, lithotripsy, stenting, or basket extraction < 2 cm and 50081 > 2 cm).
What is a PCNL procedure?
PCNL is a technique used to remove certain stones in the kidney or upper ureter (the tube that drains urine from the kidney to the bladder) that are too large for other forms of stone treatment such as shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopy.
What is procedure code 52332?
In contrast, insertion of an indwelling or non-temporary stent (CPT® code 52332) involves the placement of a specialized self-retaining stent (e.g. J stent) into the ureter to relieve obstruction or treat ureteral injury. This requires a guidewire to position the stent within the kidney.
How serious is a staghorn kidney stone?
Staghorn calculi are complex renal stones that occupy the majority of the renal collecting system. These stones are associated with high morbidity and can lead to recurrent urinary tract infections, urosepsis, renal deterioration, and death if left untreated. Managing patients with staghorn calculi can be challenging.
What foods cause staghorn kidney stones?
Lower water intake, high levels of urine calcium, and excessive consumption of oxalate-rich foods like tomatoes, chocolates, eggplants, peanuts, beets, and spinach are responsible for calcium stones. Struvite Stones: These stones develop from urinary tract infections and are most commonly found in women.
How big is a staghorn calculus?
Urinary tract calculi (i.e., “liths” or stones) may vary in size from less than 1 mm to several centimeters (“staghorn” calculi) and are typically seen as round, oval, or polygonal foci of high radiodensity within the renal parenchyma (Fig.
What are the 4 types of kidney stones?
Types of kidney stones include:Calcium stones. Most kidney stones are calcium stones, usually in the form of calcium oxalate. ... Struvite stones. Struvite stones form in response to a urinary tract infection. ... Uric acid stones. ... Cystine stones.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for ttn
- 2. icd 9 code for overdue pregnancy
- 3. icd 10 code for pericardial window
- 4. icd 10 code for car accident in ditch
- 5. icd 10 code for contusion of clavile
- 6. icd-10 code for upper inner aspect of the posterior right breast
- 7. icd 9 code for massive tense ascites
- 8. icd 10 code for elevated dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate
- 9. icd 10 code for history o right tha
- 10. icd 10 code for myeldyplasia