Is pulmonary embolism a deadly disease?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and potentially deadly form of venous thromboembolic disease. It is the third most common cause of cardiovascular death and is associated with multiple inherited and acquired risk factors as well as advanced age.
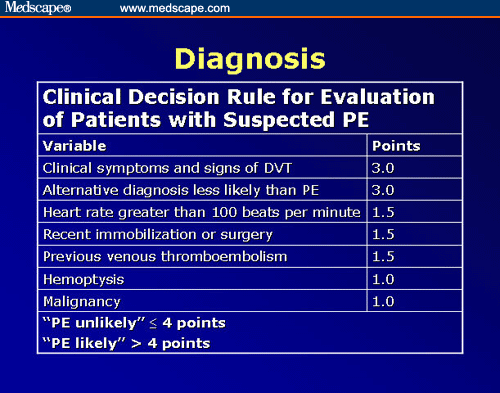
Which findings suggest pulmonary embolism?
transthoracic or transesophageal echocardiography may directly visualize embolized thrombi (right heart chambers or central pulmonary arteries) or show right heart hemodynamic changes that indirectly suggest pulmonary embolism.99indirect parameters such as unexplained right ventricular dilatation/dysfunction and marked tricuspid regurgitation, …
How do you prevent a pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism
- Diagnosis. Pulmonary embolism can be difficult to diagnose, especially in people who have underlying heart or lung disease.
- Treatment. Treatment of pulmonary embolism is aimed at keeping the blood clot from getting bigger and preventing new clots from forming.
- Clinical trials. ...
- Preparing for your appointment. ...
How do doctors diagnose a pulmonary embolism?
How is pulmonary embolism diagnosed?
- Chest X-ray. This imaging test is used to assess the lungs and heart. ...
- Pulmonary angiogram. This X-ray image of the blood vessels is used to evaluate various conditions, such as aneurysm (bulging of a blood vessel), stenosis (narrowing of a blood vessel), or ...
- Lab tests. ...
- Electrocardiogram (EKG). ...

What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for history of pulmonary embolism?
ICD-10 code Z86. 711 for Personal history of pulmonary embolism is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for pulmonary embolism right?
ICD-10 code I26. 9 for Pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
How do you code a history of a pulmonary embolism?
Z86. 711 - Personal history of pulmonary embolism. ICD-10-CM.
What is sequelae of pulmonary embolism?
Main sequelae of pulmonary embolism is difficulty to breath or pulmonary arterial hypertension. The emboli reaching the lung are progressively disappearing and healing due to the effect of anticoagulant drugs.
What is the ICD code for pulmonary embolism?
We used ICD-10 codes (I26. 9: pulmonary embolism without cor pulmonale, and I26. 0: pulmonary embolism with cor pulmonale) to identify patients diagnosed with PE; we refer to these identified patients as the coded PE group (Fig.
What is the ICD 10 code for pulmonary embolism and infarction?
415.19 - Other Pulmonary Embolism and Infarction [Internet]. In: ICD-10-CM.
What is personal HX of PE DVT?
Personal history of pulmonary embolism Z86. 711 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for long term use of anticoagulants?
Z79. 01 Long term (current) use of anticoagulants - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is the ICD-10 code for long term anticoagulation?
ICD-10 code Z79. 01 for Long term (current) use of anticoagulants is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is chronic pulmonary embolism?
A chronic pulmonary embolism is a blockage of the pulmonary arteries that occurs when prior clots in these vessels don't dissolve over time despite treatment of an acute PE, or the result of an undetected or untreated acute PE.
What is the difference between a thrombus and an embolism?
A thrombus is a blood clot that forms in a vein. An embolus is anything that moves through the blood vessels until it reaches a vessel that is too small to let it pass. When this happens, the blood flow is stopped by the embolus. An embolus is often a small piece of a blood clot that breaks off (thromboembolus).
When a pulmonary embolism occurs Which of the following are the results?
Rationale: When a PE occurs, the patient will have a VP mismatch due to the loss of blood flow to the affected area(s) of the lungs. The loss of blood flow also results in a decrease in surfactant production, leading to further lung injury and possibly atelectasis.
How long is a PE considered acute?
I have asked this question myself and gotten a variety of answers, from the initial stay only being the acute phase, all the way up to and including the entire first three months of management being the acute phase.
How do you code recurrent DVT?
DVT on chronic anticoagulation therapy. I82. 891 – Chronic embolism and thrombosis of other unspecified vein.
What is the ICD-10 code for deep vein thrombosis?
ICD-10 Code for Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of lower extremity- I82. 40- Codify by AAPC.
Is anticoagulation indicated in chronic DVT?
Anticoagulation should be initiated if DVT extends into the proximal veins. In patients with acute VTE, surgery should be delayed until 3 months of treatment have elapsed, if possible.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is a type 2 exclude note?
A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I26) and the excluded code together. chronic pulmonary embolism (.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
damage to other organs in your body from not getting enough oxygen. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
What is the meaning of "embolism" in medical terms?
The closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung. The obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung. Code History.
What is a type 2 exclude note?
A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I26) and the excluded code together. chronic pulmonary embolism (.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is the term for the closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches?
The closure of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung. The obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by an embolus, sometimes associated with infarction of the lung.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for nerve stimulator device status
- 2. icd code for weakness in left leg
- 3. icd 10 pcs code for debridement
- 4. icd 10 code for lapidus bunionectomy
- 5. icd 10 code for screening for cerebral aneurysm
- 6. 2016 icd 10 code for cerrvical pseudoarthrosis
- 7. icd 10 code for cardipovascular screening
- 8. icd 10 code for left foot ulcer stage 2
- 9. icd 10 code for excision of bilateral axillary redundant skin
- 10. icd 10 code for cyst on left foot