| ICD-10 Code | Definition |
|---|---|
| T81.4 | Infection following a procedure, not elsewhere classified (includes: intra-abdominal post procedural, stitch post procedural, subphrenic post procedural, wound post procedural, sepsis post procedural) |
What is the ICD 10 code for infection following surgery?
T81.49XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Infection following a procedure, other surgical site, init. ICD-10-CM T81.49XA is a new 2019 ICD-10-CM code that became effective on October 1, 2018.
Does the ICD-10 algorithm predict sternal wound infection following bypass grafting?
Validity of the ICD-10 Algorithm for Prediction of Sternal Wound Infection Following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting, According to Specific ICD-10 Code ICD-10 Code Algorithm Prevalence among Charts Reviewed (N= 197) Positive Predictive Value (95% Confidence Interval) Negative Predictive Value (95% Confidence Interval)
What is the ICD 10 code for urinary tract infection?
T81.49XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Infection following a procedure, other surgical site, init.
What is the ICD 10 code for infection of gastrostomy site?
Infection of gastrostomy; Infection of gastrostomy site; code to specify type of infection, such as:; cellulitis of abdominal wall (L03.311); sepsis (A40.-, A41.-) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S42.013 Anterior displaced fracture of sternal end of unspecified clavicle

What is the ICD-10 code for sternal wound?
Unspecified open wound of unspecified front wall of thorax without penetration into thoracic cavity, initial encounter. S21. 109A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM S21.
What is the ICD-10 code for post surgical infection?
ICD-10 code T81. 4 for Infection following a procedure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is the ICD-10 code for infection of wound?
ICD-10-CM Code for Local infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified L08. 9.
What are the different infections arises from sternotomy?
Type I infections occur within the first week after sternotomy and typically have serosanguineous drainage but no cellulitis, osteomyelitis, or costochondritis. They are typically treated with antibiotics and a single-stage operation.
What is surgical site infection?
A surgical site infection (SSI) is an infection that occurs after surgery in the part of the body where the surgery took place. Surgical site infections can sometimes be superficial infections involving the skin only.
What is the ICD 10 code for non healing surgical wound?
998.83 - Non-healing surgical wound is a topic covered in the ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified infection?
ICD-10 code B99. 9 for Unspecified infectious disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is L08 9?
9: Local infection of skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified.
What causes sternal infection?
Staphylococcus species are responsible for the majority of sternal infections, but environmental sources can cause infections by other organisms. The common signs and symptoms of mediastinitis are fever, leukocytosis, sternal instability, drainage, and pain.
What is sternotomy wound infection?
Sternal Wound Infection sternotomy wound infection is one of the most common surgical site infections following cardiac surgery; typically diagnosed within 30 days of surgery (early), but can be diagnosed well beyond initial postoperative period, sometimes months or even years after surgery (late) 4.
What is sternal osteomyelitis?
Sternal osteomyelitis refers to an infection of the marrow of the sternal bone, which may be primary or secondary in nature. In secondary osteomyelitis, there is an adjacent focus of infection, which usually develops in cardiac surgeries, intravenous drug users, and immunocompromised patients.
What is sternal wound infection?
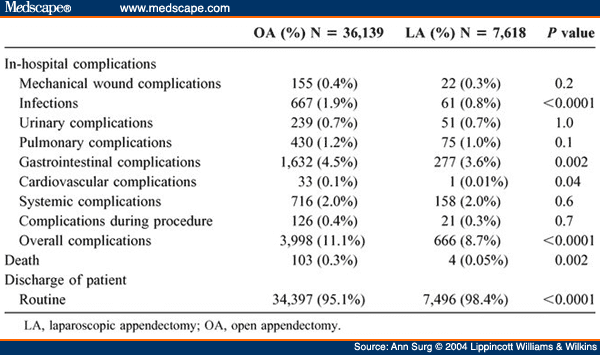
Sternal wound infection (SWI) following coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a challenging complication of the median sternotomy surgical approach. A comprehensive definition of SWI is described by El Oakley and Wright.1They describe mediastinal wound infection as “clinical or microbiological evidence of infected presternal tissue and sternal osteomyelitis with or without mediastinal sepsis and with or without unstable sternum.”2The incidence of SWI reported in the literature varies, generally ranging from 0.4 to 4 percent.3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13Despite being a relatively infrequent event, SWI following median sternotomy carries a significant risk of morbidity and mortality and is a potentially important indicator of care quality and patient safety. Defining which ICD codes accurately identify SWI cases in large administrative databases is helpful for tracking quality of care and monitoring interventions aimed at improving complication rates and patient safety.
When was the ICD-10 code used?
ICD-10 codes were used to identify cases of SWI within one year of CABG between April 2002 and November 2009. We randomly chose 200 charts for detailed chart review (100 from each of the groups coded as having SWI and not having SWI) to determine the utility of the ICD-10 coding algorithm.
When will the ICd 10 T81.32 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T81.32 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can you use T81.32 for reimbursement?
T81.32 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is sternal wound infection?
Sternal wound infection (SWI) following coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a challenging complication of the median sternotomy surgical approach. A comprehensive definition of SWI is described by El Oakley and Wright. 1 They describe mediastinal wound infection as “clinical or microbiological evidence of infected presternal tissue and sternal osteomyelitis with or without mediastinal sepsis and with or without unstable sternum.” 2 The incidence of SWI reported in the literature varies, generally ranging from 0.4 to 4 percent. 3-13 Despite being a relatively infrequent event, SWI following median sternotomy carries a significant risk of morbidity and mortality and is a potentially important indicator of care quality and patient safety. Defining which ICD codes accurately identify SWI cases in large administrative databases is helpful for tracking quality of care and monitoring interventions aimed at improving complication rates and patient safety.
What is the ICd 9 code for a SWI?
Hebden describes using ICD-9-CM coding for the identification of SWI cases. 32 The ICD-9-CM code 998.59 was used to identify deep SWI cases, and the authors report 100 percent sensitivity and 98 percent specificity using this code. Huang et al. used ICD-9-CM codes through Medicare claims to track surgical site infections following CABG. 33 They report that a post-CABG surgical site infection was confirmed with chart review 40 percent of the time when cases were identified as having an infection using ICD-9-CM codes. This finding is comparable to the PPV we report using ICD-10 codes (35.7 percent using T81.3 or T81.4). We acknowledge that the lower PPV in the study by Huang et al. was due to the inclusion of a much larger set of diagnosis codes than used in this study. We feel the results described in our work serve as an update to these studies for the ICD-10 coding system. As coding practices may vary, the use of ICD-10 codes to identify SWI cases should not be used as a safety indicator unless the definition is validated with chart review. However, monitoring the incidence of SWI in the same hospital is still a useful exercise because it can identify trends and can be important in patient safety. The proposed definition also offers clinicians and researchers a method of identifying possible cases of SWI (and subtype deep SWI) with reasonable accuracy that is comparable to methods previously described for ICD-9 coding (above).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for intractable menstrual migraine
- 2. icd 10 code for open wound left index finger
- 3. icd 10 code for rectal bleeding due to rectal ca
- 4. icd 10 code for warthin tumor of parotid
- 5. icd 10 code for rtka
- 6. icd 10 code for abdominal distention newborn
- 7. icd-10 code for left groin pain
- 8. icd 10 code for belly button discharge
- 9. icd 10 code for melanosis colon
- 10. icd 10 code for rt calf pain