How do you get rid of salivary gland stones?
Method 2 Method 2 of 3: Clearing the Blocked Salivary Duct at Home
- Drink a lot of water to keep the mouth hydrated. ...
- Take over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and swelling. If you’re experiencing intense pain from a blocked salivary gland, relieve your symptoms with an over-the-counter pain reliever.
- Suck on citrus fruits or hard candies to dislodge a stone. ...
- Massage the salivary gland with your fingers. ...
How do you remove a salivary gland stone?
- Stay hydrated.
- Massage the areas where salivary glands are located several times a day.
- Suck on hard candy or lollipops. To avoid cavities, try a sugar-free candy, like lemon heads.
- Take medications that increase saliva flow.
What is the treatment for salivary stone?
- Gender (being male)
- Age (30-60 years old)
- Dehydration
- Malnutrition
- Smoking
- Gum disease
- Anticholinergic medicine
- Trauma to the inside of the mouth
What happens when a salivary gland is removed?
Removal of a salivary gland doesn’t affect overall saliva production, but radiation therapy often causes dry mouth, which can increase your risk for cavities and mouth infections. Here are some tips to keep your mouth moist: Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day and take a water bottle with you wherever you go.
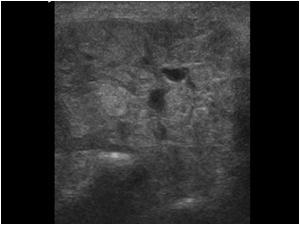
What is the ICD-10 code for Sialolithiasis?
K11.5ICD-10 code K11. 5 for Sialolithiasis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
Where is the Whartons duct?
major duct of each (Wharton's duct) opens into the floor of the mouth at the junction where the front of the tongue meets the mouth's floor. A capsule of tissue also surrounds each of these glands, which give off mixed secretions mostly serous in nature.
What is the ICD-10 code for sialadenitis?
K11. 20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is sialadenitis?
A salivary gland infection is also called sialadenitis and is caused by bacteria or viruses. A salivary stone or other blockage of the salivary gland duct can contribute to an acute infection. Chronic inflammation of a salivary gland can cause it to stop functioning.
What are the ducts of the salivary glands?
The ducts of the salivary glands allow the passage of salivary juice from the glands to the oral cavity:parotid duct (Stenson duct): connects the parotid gland to the buccal mucosa, adjacent to maxillary second molar.submandibular duct (Wharton duct): connects the submandibular gland to the floor of the mouth.More items...•
What is salivary duct?
We call the major salivary glands the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. They all secrete saliva into your mouth, the parotid through tubes that drain saliva, called salivary ducts, near your upper teeth, submandibular under your tongue, and the sublingual through many ducts in the floor of your mouth.
Is parotitis the same as sialadenitis?
Classically, HIV parotitis is either asymptomatic or a non-painful swelling, which is not characteristic of sialadenitis. Some common bacterial causes are S. aureus, S. pyogenes, viridans streptococci and H.
What is sialadenitis of submandibular gland?
Submandibular sialadenitis is inflammation of the submandibular gland, which is caused by salivary stasis that leads to retrograde seeding of bacteria from the oral cavity. Sialadenosis is a benign,non-inflammatory swelling of salivary glands usually associated with metabolic conditions.
What is submandibular Sialolithiasis?
Sialolithiasis is the formation of calcific concretions within the parenchyma or ductal system of the major or minor salivary glands, but it most commonly affects the submandibular salivary gland. Sialolithiasis usually occurs in adults aged 30 to 60 years and causes pathognomonic pain during meals.
What is a blocked salivary gland?
Parotid duct obstruction is when part of your parotid duct becomes blocked. Saliva then can't flow normally from the parotid gland into your mouth. Salivary gland stones are the most common cause of this condition. Symptoms can include pain and swelling in the area around the back of your jaw.
What causes salivary gland stones?
The underlying cause of salivary gland stones is unknown. No foods or drinks have been shown to cause salivary gland stones. The only known risk factors are dry mouth and dehydration. Therefore, staying well-hydrated is the only preventative measure to date.
How can you tell the difference between a lymph node and a submandibular gland?
0:542:37Parotid Gland and Submandibular Triangle - Lymph Nodes - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOne is typically anterior to the submandibular gland. Which you can see here. And then you will haveMoreOne is typically anterior to the submandibular gland. Which you can see here. And then you will have and note that the lymph node is typically darker than and separate from the gland.
What is a benign lesion of the salivary glands?
A benign, inflammatory, variably ulcerated, occasionally bilateral, self-healing lesion of the minor salivary glands that is often confused clinically and histologically with carcinoma. A chronic, benign, and usually painless inflammatory swelling of the lacrimal and salivary glands.
What is tobacco dependence?
tobacco dependence ( F17.-) A benign, inflammatory, variably ulcerated, occasionally bilateral, self-healing lesion of the minor salivary glands that is often confused clinically and histologically with carcinoma. A chronic, benign, and usually painless inflammatory swelling of the lacrimal and salivary glands.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. sicca syndrome [Sjögren] (.
The ICD code K115 is used to code Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis (also termed salivary calculi, or salivary stones), is a condition where a calcified mass or sialolith forms within a salivary gland, usually in the duct of the submandibular gland (also termed "Wharton's duct"). Less commonly the parotid gland or rarely the sublingual gland or a minor salivary gland may develop salivary stones.
Coding Notes for K11.5 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K11.5 - Sialolithiasis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K11.5. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 527.5 was previously used, K11.5 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for morbid obesity with bmi of 50.0-59.9
- 2. icd 10 code for pulmonary embolism right lung
- 3. icd 10 diagnosis code for copd exacerbation
- 4. icd 10 code for liable mood
- 5. icd 10 code for unspecified diagnosis
- 6. icd 10 code for diabetes with peripheral circulatory disorders
- 7. icd 10 code for cbd dilation
- 8. icd 10 code for post menopausal vaginal bleeding
- 9. 2015 icd 10 code for abscess mouth
- 10. icd-10 code for av fistula creation