What is the ICD 10 code for feces?
Positive culture findings in specimens from digestive organs and abdominal cavity ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Y92.25 Cultural building as the place of occurrence of the external cause ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R86.5 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Abnormal microbiological findings in specimens from male genital organs
What are the indications for stool culture?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R86.5 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Abnormal microbiological findings in specimens from male genital organs. Abn microbiolog findings in specmn from male genital organs; Abnormal microbiological finding in male genital organ specimen; Abnormal microbiological finding in specimen from male genital organ; colonization status (Z22.-); …
What is the ICD 10 code for abdominal microbiology?
Oct 01, 2021 · R19.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R19.5 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R19.5 - other international versions of ICD-10 R19.5 may differ. Applicable To Abnormal stool color Bulky stools
What is the ICD 10 code for abnormal microbiological findings in specimens from female genital organs?
Feb 06, 2021 · What is the ICD 10 code for stool culture? Other fecal abnormalities. R19.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM R19.5 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R19.5 – other international versions of ICD-10 R19.5 …
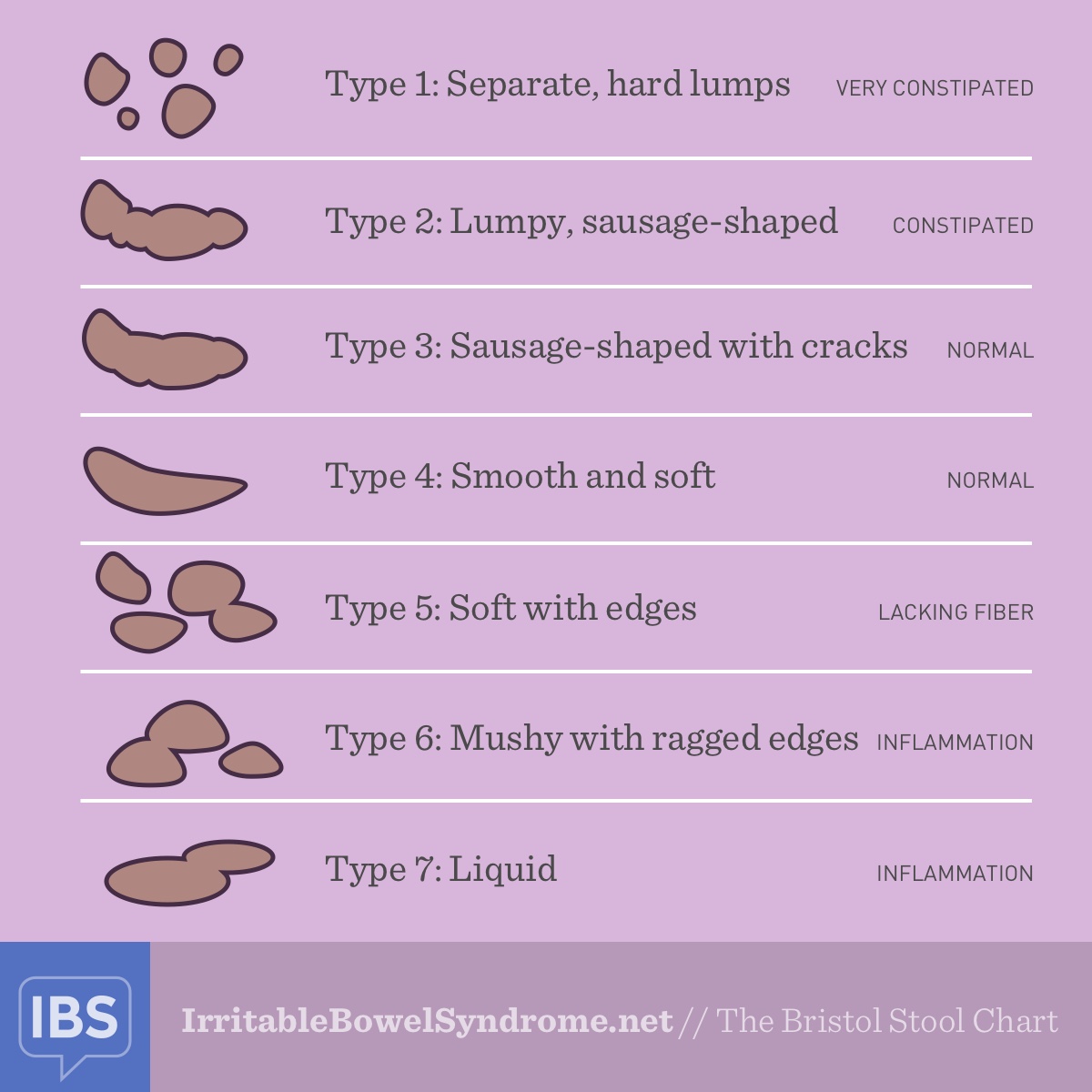
What is the ICD-10 code for occult blood in stool?
R19. 5 - Other fecal abnormalities | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 for loose stools?
ICD-10 | Diarrhea, unspecified (R19. 7)
What is k921?
Abnormally dark tarry feces containing blood (usually from gastrointestinal bleeding).
What is the ICD-10 code for black stool?
K92.1K92. 1 - Melena. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for fecal retention?
K56.41ICD-10 | Fecal impaction (K56. 41)
What is the ICD-10 code for constipation?
K59.00ICD-10 | Constipation, unspecified (K59. 00)
What is occult stool?
The fecal occult blood test (FOBT) is a lab test used to check stool samples for hidden (occult) blood. Occult blood in the stool may indicate colon cancer or polyps in the colon or rectum — though not all cancers or polyps bleed.May 12, 2020
What is Melaena stool?
Melena refers to black tarry stools, which usually occurs as a result of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. It has a characteristic tarry colour and offensive smell, and is often difficult to flush away, which is due to the alteration and degradation of blood by intestinal enzymes.
What is Melanotic stool?
Thus, a melenic stool is indicative of recent hemorrhage but does not indicate the presence or rapidity of bleeding at the time of passage. Administration of blood into the small intestine or cecum can cause melena if the blood remains in the intestine long enough.
What is a stool burden?
Visible stool burden is a common finding on plain film abdominal x-ray (AXR). The AXR is a relatively inexpensive, noninvasive imaging modality that poses a minimal radiation risk to patients and can serve as an objective measure of assessment of constipation among symptomatic patients (1).
What is the diagnosis code for blood in stool?
578.1 - Blood in stool. ICD-10-CM.
What is a rectal swab?
Rectal swabs are useful for the diagnosis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia infections. AIDS patients are also subject to cytomegalovirus, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shigella, C difficile, herpes, and Treponema pallidum gastrointestinal tract involvement. Diarrhea Syndromes Classified by Predominant Features.
What causes diarrhea in AIDS patients?
It is frequently caused by the classic bacterial pathogens as well as unusual opportunistic bacterial pathogens and parasitic infestation. ( Giardia, Cryptosporidium, and Entamoeba histolytica frequently reported.)
Can a stool specimen be used to rule out bacteria?
A single stool specimen cannot be used to rule out bacteria as a cause of diarrhea. It is recommended that two or three stool specimens, collected on separate days, be submitted to increase the probability of isolating a bacterial pathogen.
Can Yersinia sp be isolated?
Yersinia sp and Vibrio parahaemolyticus will not be isolated unless specifically requested; these will each be done with an additional charge. These organisms are fastidious and have very specific requirements for growth.
Can you culture genital bacterial culture?
Specimens from sources, such as genital, stool, urine, and upper and lower respiratory specimens, cannot be cultured under the aerobic bacterial culture test number. If specimens are incorrectly submitted with an order for aerobic bacterial culture, the laboratory will process the specimen for the test based on the source listed on the request form.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
Type 1 Excludes. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!". An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code R85.5 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lumbar myofascial pain syndrome
- 2. icd 10 code for left fractured hip
- 3. icd 10 code for salpingo-oophorectomy
- 4. icd 10 code for cardiac defibrillator firing
- 5. icd 10 pcs code for transfusion of 2 units of fresh rbcs via peripheral vein
- 6. icd 10 code for elevated white cell count
- 7. icd-10 code for place of occurrence passenger in car
- 8. icd 10 code for renal artery thrombosis
- 9. icd-9 code for 362.03
- 10. icd 10 diagnosis code for