What is the ICD 10 code for subclavian occlusion?
ICD-10-PCS Code 03L43ZZ 1: Section 0 Medical and Surgical 2: Body System 3 Upper Arteries 3: Root Operation L Occlusion 4: Body Part 4 Subclavian Artery, Left 5: Approach 3 Percutaneous 2 more rows ...
What is the ICD 10 code for left subclavian artery injury?
Unspecified injury of left innominate or subclavian artery, initial encounter Unsp injury of left innominate or subclavian artery, init; Left brachiocephalic artery injury; Left subclavian artery injury ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H34.13 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Central retinal artery occlusion, bilateral
What is the ICD 10 code for subclavian vein stenosis?
Subclavian vein stenosis Superior vena cava compression syndrome Superior vena cava syndrome ICD-10-CM I87.1 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0):
What is stenosis of the left subclavian artery?
Stenosis of left subclavian artery. Stenosis of right subclavian artery. Clinical Information. Narrowing or stricture of the vessels carrying blood away from the heart. ICD-10-CM I77.1 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 299 Peripheral vascular disorders with mcc.
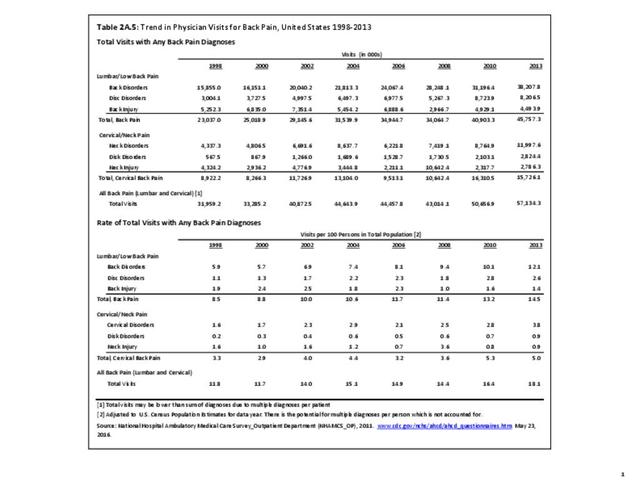
What is the ICD-10 code for subclavian artery occlusion?
I82. B - Embolism and thrombosis of subclavian vein | ICD-10-CM.
What is a subclavian blockage?
Subclavian Steal Syndrome is a blockage of the subclavian artery which sits under the collarbone. It delivers blood to the arm and brain. The blockage causes the blood to flow in reverse. The arm "steals" blood flow from the blood which was intended for the posterior (back side) of the brain.
What is the code for subclavian artery stenosis?
I77. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I77. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the subclavian artery?
The subclavian arteries lie just below the clavicles, providing blood supply to the bilateral upper extremities with contributions to the head and neck. The right subclavian artery derives from the brachiocephalic trunk, while the left subclavian artery originates directly from the aortic arch.
Is the subclavian artery an extremity artery?
The subclavian arteries provide blood flow to the upper extremities. On the left, the subclavian artery originates directly from the aorta distal to the left common carotid artery.
Is the subclavian artery a peripheral artery?
Subclavian artery disease is a form of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), which involves blockages in arteries outside of your heart. However, the blood vessels of the upper body are affected less often.
What is the CPT code for subclavian artery stent?
37239 (each additional venous stent placement for the subclavian vein).
What are the branches of the subclavian artery?
The main branches of the subclavian artery are the vertebral arteries, the thyrocervical trunk, the internal thoracic (mammary) artery and the costocervical trunk. The axillary artery runs from the lateral border of the first rib to the outer, inferior margin of the pectoralis major muscle.
What happens if the subclavian vein is blocked?
A condition caused by repetitive arm motion This tissue causes the vein to narrow and restrict blood flow, leading to the formation of blood clots. Left untreated, axillo-subclavian vein thrombosis can cause: Arm pain and fatigue. Arm swelling.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for sequelae
- 2. icd 10 code for history of mitoxantrone
- 3. icd-10-cm code for bilateral patellofemoral syndrome.pain
- 4. icd 10 code for hypertrophic turbinate
- 5. icd 10 cm code for blood in mucus
- 6. icd 10 code for cellulitus to arm
- 7. icd 10 cm code for onychomycosis
- 8. icd 10 code for concerns for neglect
- 9. icd 10 code for baby delivery at home
- 10. icd 9 code for h pylori infection