Retinal hemorrhage, unspecified eye. H35.60 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H35.60 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for subdural hemorrhage?
Nontraumatic subdural hemorrhage, unspecified. I62.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I62.00 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is the ICD 10 code for retinal hemorrhage?
Retinal hemorrhage, left eye. H35.62 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for haemorrhage?
Hemorrhage, not elsewhere classified. R58 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM R58 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R58 - other international versions of ICD-10 R58 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for subretinal hemorrhage of left eye?
Subretinal hemorrhage of left eye ICD-10-CM H35.62 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 124 Other disorders of the eye with mcc 125 Other disorders of the eye without mcc
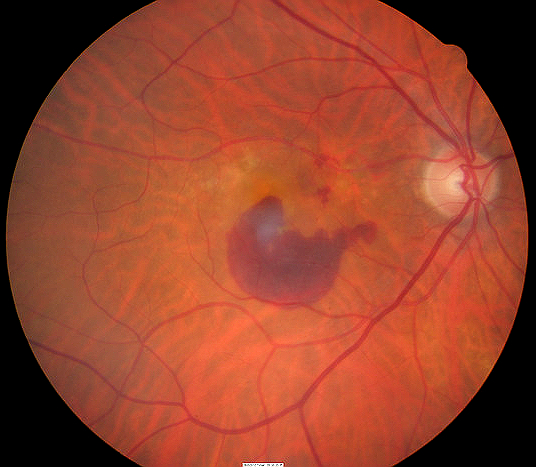
What is subretinal hemorrhage?
Subretinal hemorrhage is an accumulation of blood between the neurosensory retina and the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) arising from the choroidal or retinal circulation.
What is the ICD-10 code for macular hemorrhage?
H35. 62 - Retinal hemorrhage, left eye. ICD-10-CM.
What is a dot hemorrhage?
Dot and blot hemorrhages occur as microaneurysms rupture in the deeper layers of the retina, such as the inner nuclear and outer plexiform layers. These appear similar to microaneurysms if they are small; fluorescein angiography may be needed to distinguish between the two.
What is macular hemorrhage?
Caused by alterations to retinal or choroidal circulation, macular hemorrhage is an accumulation of blood in the macular area. Subretinal hemorrhages have a worse prognosis, due to the toxicity of the blood on the photoreceptors and the retinal cells.
What causes retinal hemorrhage?
The Most Common Causes of Retinal Hemorrhage Retinal hemorrhaging often occurs as a result of car accidents, sports accidents, falls from high locations, trip or slip and fall accidents, violent attacks, and similar traumatic events.
What is the ICD 10 code for subconjunctival hemorrhage?
31-33 Subconjunctival Hemorrhage. A subconjunctival hemorrhage is bleeding underneath the conjunctiva.
What is superficial retinal hemorrhages?
Flame shaped hemorrhages: These hemorrhages are diffuse, found in the posterior pole, and last approximately 6 to 12 weeks. They occur typically in diseases affecting superficial retinal capillary plexus secondary to arterial diseases like hypertension, blood dyscrasias, and anemias.
What is a pre retinal hemorrhage?
Preretinal hemorrhage is a known complication of diabetic retinopathy. 1 Typically patients present with painless loss of vision due to the blood accumulation in the premacular area between the retina and posterior hyaloid face, or under the internal limiting membrane.
What is the difference between vitreous hemorrhage and retinal hemorrhage?
Vitreous hemorrhage is usually less dense and will fade as the gain is decreased. It usually layers inferiorly with gravity. Ocular movements produce a rapid, staccato motion of the hemorrhage, unlike a retinal detachment that is stiffer and slower in movements.
What causes subretinal fluid?
Subretinal fluid (SRF) from the choroid enters the subretinal space through damaged pigment epithelium caused by inflammation or tumour. In the 'uveal effusion syndrome' shifting subretinal fluid is the typical feature.
How is subretinal hemorrhage treated?
Subretinal hemorrhages may be amenable to tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) and pneumatic displacement while sub-RPE hemorrhages may only benefit from pneumatic displacement alone.
What does a retinal hemorrhage look like?
Seeing haze or shadows. Distorted vision. Rapid flashes of light in peripheral vision. Red tint to vision.
What are 3 types of hemorrhage?
There are three main types of bleeding: arterial, venous, and capillary bleeding. These get their names from the blood vessel that the blood comes from.
Do retinal hemorrhages go away?
Retinal hemorrhages, especially mild ones not associated with chronic disease, will normally reabsorb without treatment. Laser surgery is a treatment option which uses a laser beam to seal off damaged blood vessels in the retina.
How long does it take for a retinal hemorrhage to heal?
In many cases, they resolve spontaneously in 2-3 months, although if the bleeding is not reabsorbed, it may require a surgery called vitrectomy.
Is retinal hemorrhage an emergency?
Assessing and documenting the patient's vision prior to symptoms of hemorrhage is crucial. Underlying eye disease often provides clues to the cause of hemorrhage. Patients with acute vitreous hemorrhage frequently seek emergency care because the loss of vision is dramatic.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for gastrocnemius strain
- 2. icd 10 code for grade 1 ulceration right toe
- 3. icd 10 cm code for end-stage renal disease
- 4. icd-10-cm code for muscle spasms, right thigh
- 5. icd 10 code for acute duodenal ulcer with bleeding
- 6. icd code for left arm pain
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for pancreatic insufficiency
- 8. icd-10 code for uterine mass
- 9. icd 10 code for pulmonary hypertension
- 10. icd 10 code for periaortic mass