What is a partial thickness burn?
Second-degree (partial-thickness) burns — Second-degree burns (also called partial-thickness burns) involve the top two layers of skin. These burns form blisters, are very painful, may seep fluid, and blanch when pressed (picture 2). Second-degree burns typically heal within 7 to 21 days.
What is a t30 0 burn?
0 - Burn of unspecified body region, unspecified degree.
What is the ICD 10 code for 2nd degree sunburn?
L55.1ICD-10-CM Code for Sunburn of second degree L55. 1.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
How do you code burn in ICD-10?
Burns involving less than 10% of body surface T31. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM T31. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Why are superficial partial thickness burns more painful?
Superficial dermal burns are initially the most painful. Even the slightest change in the air currents moving past the exposed superficial dermis causes a patient to experience excruciating pain. Without the protective covering of the epidermis, nerve endings are sensitized and exposed to stimulation.
What is the ICD-10 code for first degree sunburn?
L55.0ICD-10-CM Code for Sunburn of first degree L55. 0.
What is the main term for initial encounter for second degree burn of the left foot?
Burn of second degree of left foot, initial encounter T25. 222A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How do you know if you have a first or second degree burn?
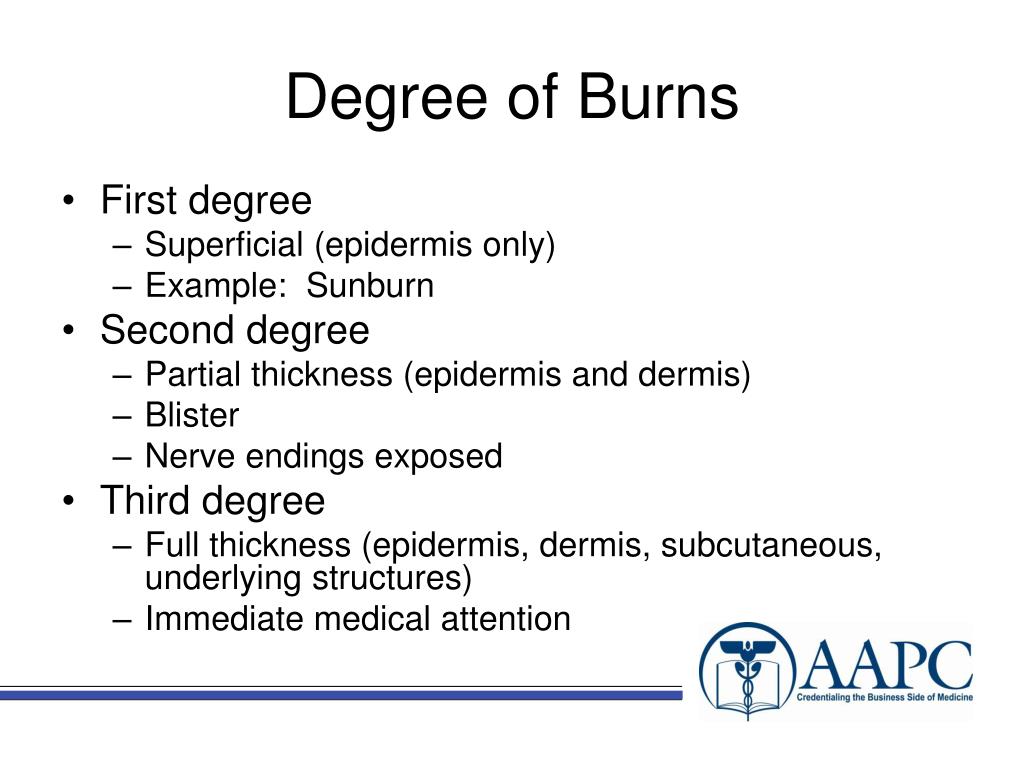
BurnsFirst-degree burns affect only the outer layer of the skin. They cause pain, redness, and swelling.Second-degree burns affect both the outer and underlying layer of skin. They cause pain, redness, swelling, and blistering. ... Third-degree burns affect the deep layers of skin.
What is the ICD-10 code for R11 0?
ICD-10 code R11. 0 for Nausea is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is ICD-10 code R51?
Code R51 is the diagnosis code used for Headache. It is the most common form of pain.
What are the different types of burns?
Burn of unspecified degree of multiple sites of head, face, and neck, initial encounter 1 Burn injury of face head or neck multiple sites 2 Superficial burn of multiple sites of face, head or neck
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code.
What is the difference between a first degree burn and a second degree burn?
first-degree burns damage only the outer layer of skin. second-degree burns damage the outer layer and the layer underneath. third-degree burns damage or destroy the deepest layer of skin and tissues underneath. burns can cause swelling, blistering, scarring and, in serious cases, shock and even death.
What is the first degree of burn?
Injury to tissues caused by contact with dry heat, moist heat, flames, chemicals, electricity, friction or radiant and electromagnetic energy. A first degree burn is associated with redness, a second degree burn with vesication and a third degree burn with necrosis through the entire skin.
What is generic burn injury?
Generic burn injury, including that due to excessive heat, as well as cauterization, friction, electricity, radiation, sunlight, and other causes. Injuries to tissues caused by contact with heat, steam, chemicals (burns, chemical), electricity (burns, electric), or the like.
What causes burns on the skin?
Scalds from hot liquids and steam, building fires and flammable liquids and gases are the most common causes of burns. Another kind is an inhalation injury, caused by breathing smoke.there are three types of burns: first-degree burns damage only the outer layer of skin.
What is a Z18 code?
code to identify any retained foreign body, if applicable ( Z18.-) A burn is damage to your body's tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight or radiation. Scalds from hot liquids and steam, building fires and flammable liquids and gases are the most common causes of burns.
Can antibiotic creams be used for burns?
Antibiotic creams can prevent or treat infections. After a third-degree burn, you need skin or synthetic grafts to cover exposed tissue and encourage new skin to grow. First- and second-degree burns usually heal without grafts. nih: national institute of general medical sciences.
What is the ICd code for burns?
The ICD code T31 is used to code Burn. A burn is a type of injury to skin , or other tissues, caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, friction, or radiation. Burns that affect only the superficial skin layers are known as superficial or first-degree burns.
What is the primary code for a burn?
Use as primary code only if site of burn unspecified, otherwise use as a supplementary code with categories t20-t29 (burns) Use as primary code only if site of burn unspecified, otherwise use as a supplementary code with categories t20-t25 (burns)
What is a third degree burn?
In a full-thickness or third-degree burn, the injury extends to all layers of the skin. A fourth-degree burn additionally involves injury to deeper tissues, such as muscle, tendons, or bone. Specialty: Critical Care Medicine.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code T31.0 and a single ICD9 code, 948.00 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What does it mean when you have a second degree burn?
Second-degree burns indicate blistering with damage extending beyond the epidermis partially into the layer beneath it (dermis) Third-degree burns indicate full-thickness tissue loss with damage or complete destruction of both layers of skin (including hair follicles, oil glands, & sweat glands)
What is a burn?
Burn Types. A burn is tissue damage with partial or complete destruction of the skin caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, sunlight, or nuclear radiation. Proper selection of burn codes requires consideration of the location of the burn, severity, extent, and external cause in addition to laterality and encounter.
What is the difference between a burn and a corrosion?
ICD-10 makes a distinction between burns and corrosions: Burn codes apply to thermal burns (except sunburns) that come from a heat source, such as fire, hot appliance, electricity, and radiation. Corrosions are burns due to chemicals.
What is a T20 T28 code?
The descriptions of codes in the T20-T28 range are first defined by an anatomical location of the body affected by burn or corrosion.
How many hospital admissions are there for burns?
According to the American Burn Association, an estimated 486,000 hospital admissions and visits to hospital emergency departments occur annually for burn evaluation and treatment in the United States.
What happens if you burn your skin with partial thickness?
With superficial partial-thickness burns, the skin will be extremely red, appear wet and/or shiny, painful to the touch, and will form blisters. Once again, blanching may occur, but color will return quickly after pressure is removed.
What is a second degree burn?
Burns, Superficial Partial-Thickness (Second-Degree) A burn is an injury to the tissue of the body, typically the skin. Burns can vary in severity from mild to life-threatening. Most burns only affect the uppermost layers of skin, but depending on the depth of the burn, underlying tissues can also be affected.
What is a circumferential burn?
Circumferential burns: In cases where a full thickness burn affects the entire circumference of a digit, extremity, or even the torso, this is called a circumferential burn.
What is the uppermost layer of the dermis?
The dermis itself is divided into two regions, the uppermost being the papillary region . This area is composed mostly of connective tissue and serves only to strengthen the connection between the epidermis and the dermis. Partial-thickness burns that only extend down to this layer of the skin are considered superficial.
Can you put ice on a burn?
Do not apply ice to the affected area. Doing so can cause further damage to the wound and increase the risk of hypothermia. Do not apply butter, ointment, petroleum jelly, oil, or grease on the burn. Not only do wounds need air to heal, but these also trap heat at the burn site and can further damage deeper tissues.
Can a partial thickness burn turn into a full thickness burn?
Wound progression: Swelling and decreased blood flow to the affected tissue at burn sites can result in partial thickness burns developing into full thickness burns. Tetanus: Burn sites are specifically susceptible to tetanus. If the patient hasn't been immunized in the past 5 years, generally a booster shot is recommended.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for bilateral equinus
- 2. icd 9 code for chronic benzodiazepine dependence
- 3. icd 10 code for acute dvt left femoral vein
- 4. icd 10 cm code for activities involving snow skiing
- 5. icd 10 code for personal history of emotional and sexual abuse
- 6. icd 10 code for blind spot
- 7. icd 10 code for uti prophylaxis
- 8. icd 10 code for right intertrochanteric fracture
- 9. icd 10 code for ureterolithiasis
- 10. what is the icd-10-cm code for admission for adjustment of artificial eye