Punctate keratitis, unspecified eye. H16.149 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H16.149 became effective on October 1, 2018.
| ICD-10: | H16.149 |
|---|---|
| Short Description: | Punctate keratitis, unspecified eye |
| Long Description: | Punctate keratitis, unspecified eye |
What is the ICD 10 code for bilateral punctate keratitis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H16.149 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Punctate keratitis, unspecified eye. Punctate epithelial keratopathy (pek); Punctate keratitis; Punctate keratitis (eye condition); Punctate keratopathy. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H16.149.
What is the ICD 10 code for keratitis of the right eye?
Oct 01, 2021 · Punctate keratitis, unspecified eye. H16.149 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H16.149 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the different H16 numbers for keratitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H16.14 Punctate keratitis 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code H16.14 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H16.14 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for trauma to the eye?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H16.141 Punctate keratitis, right eye 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code H16.141 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H16.141 became effective on October 1, 2021.
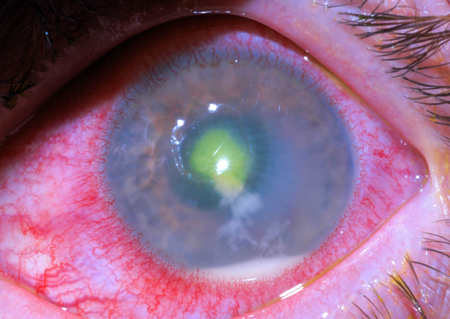
What is superficial punctate keratitis?
Superficial punctate keratitis is corneal inflammation of diverse causes characterized by scattered, fine, punctate corneal epithelial loss or damage. Symptoms are redness, lacrimation, photophobia, and slightly decreased vision. Diagnosis is by slit-lamp examination. Treatment depends on the cause.
What is the ICD 10 code for keratitis?
H16.109Unspecified superficial keratitis, unspecified eye H16. 109 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is punctate epithelial keratitis?
The punctate epithelial keratitis (PEK) is a distinct clinical entity characterized by coarse, raised intraepithelial lesions surrounded by focal inflammatory cells, with punctate staining as well as areas of negative staining on fluorescein. PEK is often a clinical picture common to various cornea pathologies.
What is mild superficial punctate keratitis?
Superficial punctate keratitis is an eye disorder caused by death of small groups of cells on the surface of the cornea (the clear layer in front of the iris and pupil). The eyes become red, watery, and sensitive to light, and vision may decrease somewhat.
What means keratitis?
Overview. Keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea — the clear, dome-shaped tissue on the front of your eye that covers the pupil and iris. Keratitis may or may not be associated with an infection.28 Aug 2020
What is unspecified keratitis?
Diseases of the eye and adnexa A disorder characterized by inflammation to the cornea of the eye. Inflammation of the cornea. Inflammation of the cornea.
How is superficial punctate keratitis treated?
The treatment considerations for superficial punctate keratitis and UV keratitis are the same as with corneal abrasion (because both entail an injury to the corneal epithelium and superficial cornea, seeCorneal Abrasions) and include limited use of topical anesthetics and topical antibiotics administered for 3 to 5 ...
What are punctate epithelial erosions?
Punctate epithelial erosions (PEE) are evidence of ocular surface dryness. They represent areas of epithelial cell loss and therefore stain positively with fluorescein. The distribution of the PEE can provide information regarding the underlying etiology.
What is punctate opacity?
Punctate keratitis (snowflake opacities) is sometimes visible to the naked eye, but it is best seen by slitlamp examination. These lesions are comprised of cellular infiltrates around dead or dying microfilariae and they are the corneal equivalent of the discrete papular lesions seen in the skin.
Is thygeson's an autoimmune disease?
Abstract. Thygeson's superficial punctate keratitis (TSPK) is a chronic, bilateral epithelial keratitis. Dr Philips Thygeson first reported TSPK in 1950. Although the etiology of TSPK remains unknown, it has been reported to be associated with viral and autoimmune pathologies.
What is the difference between SPK and pee?
One must differentiate PEE from punctate epithelial keratitis (PEK) and superficial punctate keratopathy (SPK). PEK will have corneal infiltrates associated with the negative staining pattern and is thought to be a progression of the PEE to becoming subepithelial infiltrates (SEIs).9 Jun 2016
What is PUK in eyes?
Peripheral ulcerative keratitis (PUK) is a form of unilateral crescent-shaped stromal inflammation, which involves the juxtalimbal cornea and is characterized by sectorial thinning of the affected area. It is always associated with an overlying epithelial defect and progressive loss of the corneal stroma (Figure 1A).14 May 2012
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for pain in unspecified ankle
- 2. icd 10 code for strep bovis endocarditis
- 3. icd 10 code for respiratory failure on ventilator
- 4. icd 10 cm code for drug use. methamphetamine.
- 5. icd 9 code for fatal and nonfatal
- 6. icd 10 code for increased oral secretions
- 7. icd 10 code for personal history of duodenal ulcer
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for nonsustained ventricular tachycardia
- 9. icd 10 code for cellulitis of both feet
- 10. icd-9 code for blunting of costophrenic