What does ICD - 10 stand for?
The ICD-10-CM (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification) is a system used by physicians and other healthcare providers to classify and code all diagnoses, symptoms and procedures recorded in conjunction with hospital care in the United States.
What is the purpose of ICD 10?
Why ICD-10 codes are important
- The ICD-10 code system offers accurate and up-to-date procedure codes to improve health care cost and ensure fair reimbursement policies. ...
- ICD-10-CM has been adopted internationally to facilitate implementation of quality health care as well as its comparison on a global scale.
- Compared to the previous version (i.e. ...
Is chronic kidney disease stage 5 ICD 10 curable?
N18.5 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Chronic kidney disease, stage 5 . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 . ICD-10 code N18.5 is based on the following Tabular structure:
What is ICD 10 used for?
Used for medical claim reporting in all healthcare settings, ICD-10-CM is a standardized classification system of diagnosis codes that represent conditions and diseases, related health problems, abnormal findings, signs and symptoms, injuries, external causes of injuries and diseases, and social circumstances.

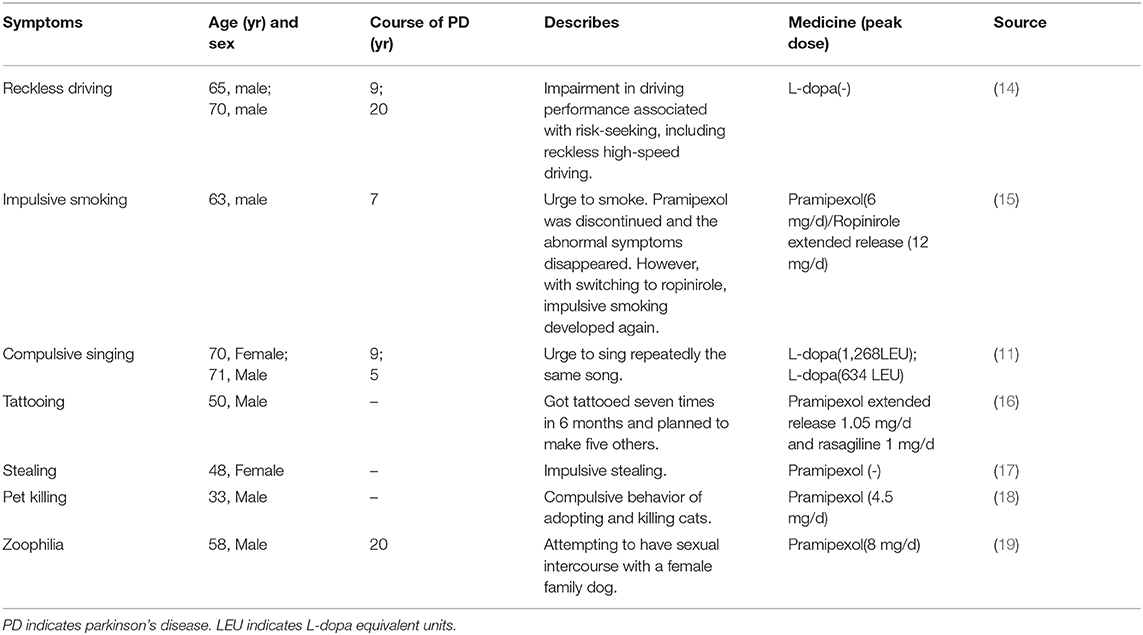
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for Parkinson's disease?
ICD-10 code G20 for Parkinson's disease is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
How do you confirm a diagnosis of Parkinsons?
No specific test exists to diagnose Parkinson's disease. Your doctor trained in nervous system conditions (neurologist) will diagnose Parkinson's disease based on your medical history, a review of your signs and symptoms, and a neurological and physical examination.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Parkinson's disease with dementia?
Disease, Parkinson: You will see Parkinsonism dementia listed with the codes G31. 83 and F02. 80.
What is Parkinson's disease G20?
Progressive, degenerative disorder of the nervous system characterized by tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, and gait abnormalities; caused by a loss of neurons and a decrease of dopamine in the basal ganglia.
What are the four cardinal signs of Parkinson's disease?
One of the most prevalent neurological disorders is Parkinson's disease (PD), characterized by four cardinal signs: tremor, bradykinesia, rigor and postural instability.
What can be mistaken for Parkinson's?
Movement Disorders Similar to Parkinson'sProgressive supranuclear palsy. ... Multiple system atrophy. ... Viral parkinsonism. ... Essential tremor. ... Drug- and toxin-induced parkinsonism. ... Post-traumatic parkinsonism. ... Arteriosclerotic parkinsonism. ... Parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam.More items...•
What is I10 diagnosis?
ICD-Code I10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Essential (Primary) Hypertension.
What is the ICD-10 code for F02 80?
80 for Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere without behavioral disturbance is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders .
Can F02 81 be primary diagnosis?
Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with behavioral disturbance. F02. 81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is Parkinson disease HCC?
Trouble with balance and. possible falls, also. called postural instability. Parkinson's disease is a HCC diagnosis, whether the condition is idiopathic, drug induced or a result of infectious or other external agents. G20.
What is the ICD-10 code for ASHD?
ICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for Bradykinesia?
8X5, and consistent nonfluctuating bradykinesia could be coded with T42. 8X6. There is currently an ICD-10-CM code for dystonia (G24) and subcodes for different types of dystonia (G24. 0–G24.
What is usually the first symptom of Parkinson disease?
Symptoms start gradually, sometimes starting with a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. Tremors are common, but the disorder also commonly causes stiffness or slowing of movement. In the early stages of Parkinson's disease, your face may show little or no expression. Your arms may not swing when you walk.
Does Parkinson's show up on an MRI?
MRI in Parkinson's Testing It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people (less than 55 years) or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinson's.
How is early onset Parkinson's diagnosed?
Diagnosing early onset Parkinson's disease The condition is usually diagnosed by a neurologist based on a review of your symptoms and a physical exam. A DaTscan to visualize your brain's dopamine system may help confirm diagnosis. Blood tests and other imaging tests, such as an MRI scan, don't diagnose Parkinson's.
Can blood tests show Parkinson's?
Researchers found the blood test was just as accurate as a spinal fluid test at diagnosing whether someone had Parkinson's or an APD, in both early stages of disease and in those who had been living with the diseases longer.
What is Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson's disease is a disorder that affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. In parkinson's, neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements.
How old do you have to be to get Parkinson's?
They may also have problems such as depression, sleep problems or trouble chewing, swallowing or speaking. Parkinson's usually begins around age 60, but it can start earlier.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What does a type 1 excludes note mean?
They must be used in conjunction with an underlying condition code and they must be listed following the underlying condition. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as G20.
What are the symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
The early stages of PD include the following signs and symptoms: Slight shaking of a finger, hand, leg, chin, or lip. Stiffness or difficulty walking. Difficulty getting out of a chair.
How many people are affected by Parkinson's disease?
As a neurodegenerative disease of the brain, which impacts an individual’s motor function, Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is the most common neurological disorder, affecting approximately one million people in the United Status. It is estimated that approximately 60,000 Americans are diagnosed with PD each year, and this number does not reflect ...
What is the PD G20 code?
With PD G20 code, you will be coding associated signs and symptoms or those complications not necessarily inherent to the disease. Most of these complications will be found in Chapter 18, as signs and/or symptoms.
What are the most common drugs for PD?
The first category includes drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain. The most common drugs for PD are dopamine pre cursors—substances such as levodopa that cross the blood-brain barrier and are then changed into dopamine.
What is the third category of medication for PD?
The third category of drugs prescribed for PD includes medications that help control the non-motor symptoms of the disease ; that is, the symptoms that don't affect movement. For example, people with PD-related depression may be prescribed antidepressants.
What is the second category of PD drugs?
The second category of PD drugs affects other neurotransmitters in the body in order to ease some of the symptoms of the disease. For example, anticholinergic drugs interfere with production or uptake of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. These can be effective in reducing tremors.
How many people have PD?
Worldwide up to 14 million people have a diagnosis of PD. Most individuals with PD are diagnosed when they are 60 years old or older, but early-onset PD also occurs, like that of actor Michael J. Fox and deceased professional boxer Muhammad Ali.
PD Progression & Motor Complications
PD is a chronic, progressive disorder affecting approximately 1 million people in the US. 3-5 Disease progression causes greater morbidities and disabilities because of advancing fluctuations in motor and nonmotor symptoms.
Limitations of Current ICD-10-CM Coding for PD
Unlike other neurologic disorders (eg, migraine and epilepsy), there is only a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, namely G20. 22 The single, nonspecific code for PD cannot accurately capture motor fluctuations and dyskinesia that emerge with PD progression.
Recommendations for PD ICD-10-CM Coding
Based on this review, the panel recommends the ICD-10-CM coding structure for PD be expanded to provide specificity to distinguish motor complications of dyskinesia and/or “OFF” episodes (Table 2; Figure 1).
Revising PD ICD-10-CM Coding May Improve Care
The current, single, nonspecific ICD-10-CM code for PD does not accurately specify patients with motor complications, including “OFF” episodes and dyskinesia.
Support for Revision of ICD-10-CM Codes for PD
The American Academy of Neurology supports the need to update the ICD-10-CM coding to better reflect the progression of PD. Patient advocacy groups also support this need, including the Michael J.
Summary
Revision of the ICD-10-CM coding structure for PD is a major unmet need for a population that is expected to continue to increase over the next decade. The treatment paradigm for PD continues to evolve with specific medications now available for PD dyskinesia and for the on-demand management of “OFF” episodes in PD.
What is the ICd 10 code for Parkinson's disease?
G20 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Parkinson's disease . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
When an excludes2 note appears under a code, is it acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code
When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
What are some examples of Parkinson's disease?
Examples include parkinsonism caused by vascular injury, drugs, trauma, toxin exposure, neoplasms, infections and degenerative or hereditary conditions.
Is G21 a reimbursement code?
G21 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM G21 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G21 - other international versions of ICD-10 G21 may differ. Type 1 Excludes.
PD Progression & Motor Complications
Limitations of Current ICD-10-CM Coding For PD
- Unlike other neurologic disorders (eg, migraine and epilepsy), there is only a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, namely G20.22 The single, nonspecific code for PD cannot accurately capture motor fluctuations and dyskinesia that emerge with PD progression. Based on the limitations of a single ICD-10-CM code for PD, a 7-member panel (6 movement disorder ...
Recommendations For PD ICD-10-CM Coding
- Based on this review, the panel recommends the ICD-10-CMcoding structure for PD be expanded to provide specificity to distinguish motor complications of dyskinesia and/or “OFF” episodes (Table 2; Figure 1). The proposed changes include delineating between individuals without dyskinesia or fluctuations (G20.01), without dyskinesia but with fluctuations (G20.02), with dyski…
Revising PD ICD-10-CM Coding May Improve Care
- The current, single, nonspecific ICD-10-CM code for PD does not accurately specify patients with motor complications, including “OFF” episodes and dyskinesia. Consequently, the prevalence of these symptoms and their effect on patients, caregivers, and the overall health care system is extremely difficult to screen, document, and track in a systematic fashion. There is a pressing n…
Support For Revision of ICD-10-CM Codes For PD
- The American Academy of Neurology supports the need to update the ICD-10-CMcoding to better reflect the progression of PD. Patient advocacy groups also support this need, including the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research (MJFF) and the Unified Parkinson’s Advocacy Council (UPAC), which is a group of national, regional, and state organizations including the Par…
Summary
- Revision of the ICD-10-CM coding structure for PD is a major unmet need for a population that is expected to continue to increase over the next decade. The treatment paradigm for PD continues to evolve with specific medications now available for PD dyskinesia and for the on-demand management of “OFF” episodes in PD. The recommended changes to the ICD-10-CMcoding stru…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for i48.81
- 2. icd 10 code for personal history of pe
- 3. icd 10 code for dental infection unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for rigidity
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for stiff back
- 6. icd 10 code for peripheral neuropathy of foot
- 7. icd 10 code for chronic facial rash
- 8. icd 9 code for rhinosinusitis acute
- 9. icd 10 pcs code for code for repair of torn tracheostomy
- 10. icd 9 code for aortic aneurysm unspecified