What are ICD-10 diagnostic codes?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes
| A00.0 | B99.9 | 1. Certain infectious and parasitic dise ... |
| C00.0 | D49.9 | 2. Neoplasms (C00-D49) |
| D50.0 | D89.9 | 3. Diseases of the blood and blood-formi ... |
| E00.0 | E89.89 | 4. Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic ... |
| F01.50 | F99 | 5. Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopme ... |
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is diagnosis code I10?
I10 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of essential (primary) hypertension. The code I10 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is amyloidosis?
What organs does amyloidosis affect?
What happens when amyloid deposits enlarge?
When will the ICd 10 E85.9 be released?
Is amyloidosis a hereditary disease?
About this website
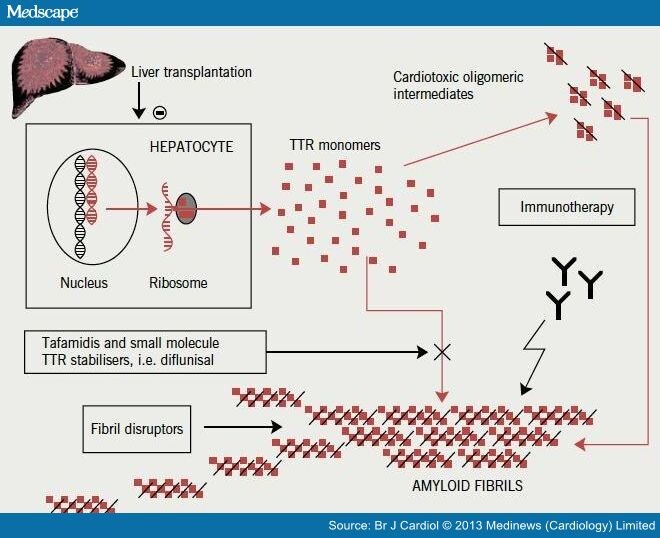
What is systemic amyloidosis?
Systemic amyloidosis is an uncommon disorder in which misfolded protein becomes resistant to the body's catabolic processes and fibrils deposit extracellularly within tissues, leading to organ dysfunction and death.
Is amyloid the same as amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis is the name for a group of rare, serious conditions caused by a build-up of an abnormal protein called amyloid in organs and tissues throughout the body. The build-up of amyloid proteins (deposits) can make it difficult for the organs and tissues to work properly.
What is a amyloid tumor?
Amyloid tumor of the breast, first reported in 1973 [1], is a rare disease, with only six cases [2–7] reported in Japan to date. Amyloidosis is defined as a disease that causes abnormalities in organs due to extracellular deposition of fibrous abnormal proteins called amyloid [8].
What can cause systemic amyloidosis?
The exact cause of secondary systemic amyloidosis is unknown. You are more likely to develop secondary systemic amyloidosis if you have a long-term infection or inflammation. This condition may occur with: Ankylosing spondylitis -- a form of arthritis that mostly affects the bones and joints in the spine.
What is the difference between localized and systemic amyloidosis?
In systemic amyloidosis, the heart, kidneys, and nerves are most commonly affected, resulting in congestive heart failure, arrhythmia, nephrotic syndrome, renal failure, and peripheral and autonomic neuropathies. In localized amyloidosis, amyloid deposits at the site of production, so only one organ is disrupted.
What's the meaning of amyloid?
Definition of amyloid : a waxy translucent substance consisting primarily of protein that is deposited in some animal organs and tissues under abnormal conditions (such as Alzheimer's disease) — compare beta-amyloid.
What is amyloidosis diagnosis?
The diagnosis of amyloidosis is suspected following a detailed patient history and clinical evaluation but requires aspiration of abdominal fat pad and/or biopsy of the involved organ. If the disease is suspected on clinical grounds, a biopsy of the involved organ will give the highest yield.
What is amyloid pathology?
Amyloid-β (Aβ) misfolding is one of the hallmark pathological features of Alzheimer's disease (AD). AD can manifest with diverse symptomatology including variable rates of cognitive decline, duration of clinical disease, and other detrimental changes.
What is the function of amyloid?
The amyloid-beta precursor protein is an important example. It is a large membrane protein that normally plays an essential role in neural growth and repair. However, later in life, a corrupted form can destroy nerve cells, leading to the loss of thought and memory in Alzheimer's disease.
What are the 3 types of amyloidosis?
The most common types of amyloidosis are: AL (Primary) Amyloidosis. AA (Secondary) Amyloidosis. Familial ATTR Amyloidosis.
What are the 4 types of amyloidosis?
Subtypes of amyloidosis include:AL amyloidosis (immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis). The most common type of amyloidosis in developed countries, AL amyloidosis is also called primary amyloidosis. ... AA amyloidosis. ... Hereditary amyloidosis (familial amyloidosis). ... Wild-type amyloidosis. ... Localized amyloidosis.
Is amyloid an autoimmune disease?
Additional Testing for AA Amyloidosis An underlying condition is one medical condition that causes another one. With AA amyloidosis, the underlying condition is an autoimmune disease or chronic infection.
What organs does amyloidosis affect?
Generally, primary amyloidosis affects the nerves, skin, tongue, joints, heart, and liver; secondary amyloidosis often affects the spleen, kidneys, liver, and adrenal glands. A group of diseases in which protein is deposited in specific organs or throughout the body.
When will the ICd 10 E85 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E85 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is metabolic disorder?
Metabolic disorders. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by the localized or diffuse accumulation of amyloid protein in various anatomic sites. It may be primary, due to clonal plasma cell proliferations; secondary, due to long standing infections, chronic inflammatory disorders, or malignancies; or familial.
What is the ICd code for amyloidosis?
The ICD code E85 is used to code AL amyloidosis. Amyloid Light-chain (AL) amyloidosis, primary systemic amyloidosis (PSA) or just primary amyloidosis is the most common form of systemic amyloidosis in the US. The disease is caused when a person's antibody-producing cells do not function properly and produce abnormal protein fibers made ...
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code E85 is a non-billable code.
What is the cause of a person's antibody-producing cells not functioning properly?
The disease is caused when a person's antibody-producing cells do not function properly and produce abnormal protein fibers made of components of antibodies called light chains. These light chains come together to form amyloid deposits in different organs which can cause serious damage to these organs.
What is the ICd code for secondary amyloidosis?
E85.3 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of secondary systemic amyloidosis. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is hemodialysis associated amyloidosis?
Haemodialysis-associated amyloidosis is a form of amyloidosis associated with chronic kidney failure.
What is amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by the localized or diffuse accumulation of amyloid protein in various anatomic sites. It may be primary, due to clonal plasma cell proliferations; secondary, due to long standing infections, chronic inflammatory disorders, or malignancies; or familial.
What organs does amyloidosis affect?
Generally, primary amyloidosis affects the nerves, skin, tongue, joints, heart, and liver; secondary amyloidosis often affects the spleen, kidneys, liver, and adrenal glands. A group of diseases in which protein is deposited in specific organs or throughout the body.
What happens when amyloid deposits enlarge?
As the amyloid deposits enlarge they displace normal tissue structures, causing disruption of function. Various signs and symptoms depend on the location and size of the deposits. Amyloidosis occurs when abnormal proteins build up and form deposits. The deposits can collect in organs such as the kidney and heart.
When will the ICd 10 E85.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E85.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is amyloidosis a hereditary disease?
Amyloidosis may be either primary (with no known cause), secondary (caused by another disease, including some types of cancer, such as multiple myeloma), or hereditary (passed down from parents to children). Many organs are affected by amyloidosis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for swelling left elbow
- 2. icd-10 code for status post right ankle surgery
- 3. icd 10 code for right humerus fracture
- 4. icd 10 code for total shoulder replacement
- 5. icd 10 code for sternoclavicular osteomyelitis
- 6. icd 10 code for unspecified behavioral disorder
- 7. icd 9 code list for rheumatology
- 8. icd 10 code for hormone regulation with hyperlipidemia
- 9. icd 10 code for cystic ovarian disorder
- 10. icd-10 code for bone graft