What is the latest version of the ICD 10 for Fallot?
Oct 01, 2021 · Tetralogy of Fallot. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt. Q21.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10 …
What is the tetralogy of Fallot?
The ICD code Q213 is used to code Tetralogy of Fallot. Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect which is classically understood to involve four anatomical abnormalities of the heart (although only three of them are always present). It is the most common cyanotic heart defect and the most common cause of blue baby syndrome.
What is the ICD 10 code for Z code?
ICD-10 code Q21.3 for Tetralogy of Fallot is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
Which ICD 10 code should not be used for reimbursement purposes?
Oct 01, 2021 · ICD-10-CM Code. Q21.3. Q21.3 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Tetralogy of Fallot . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . Q21.3 is exempt from POA reporting ( Present On Admission).
What is the meaning of tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy of Fallot (pronounced te-tral-uh-jee of Fal-oh) is a birth defect that affects normal blood flow through the heart. It happens when a baby's heart does not form correctly as the baby grows and develops in the mother's womb during pregnancy.
Why is it called tetralogy of Fallot?
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects....Tetralogy of FallotSpecialtyCardiac surgery, pediatricsSymptomsEpisodes of bluish color to the skin, difficulty breathing, heart murmur, finger clubbing11 more rows
Are there different types of tetralogy of Fallot?
The following 4 diagnostic subgroups of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) are described [1, 2] : (1) tetralogy of Fallot with absent pulmonary valve syndrome; (2) tetralogy of Fallot with common atrioventricular (AV) canal; (3) tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia; and (4) tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary stenosis.Mar 30, 2017
Is tetralogy of Fallot a disease?
Tetralogy of Fallot is the most common form of cyanotic congenital heart disease. Cyanosis is the abnormal bluish discoloration of the skin that occurs because of low levels of circulating oxygen in the blood.
What are the 4 components of tetralogy of Fallot?
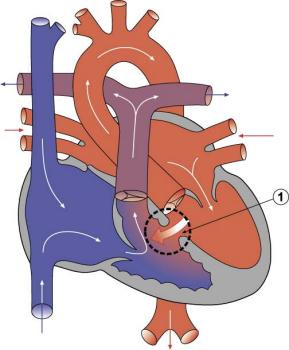
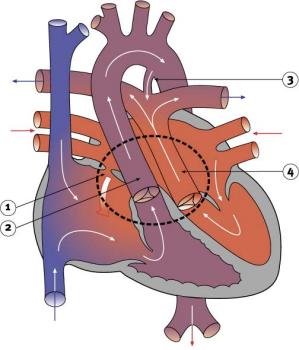
Tetralogy of Fallot is a combination of four congenital heart defects. The four defects are a ventricular septal defect (VSD), pulmonary stenosis, a misplaced aorta and a thickened right ventricular wall (right ventricular hypertrophy).Aug 17, 2021
How do you remember tetralogy of Fallot?
MnemonicP: pulmonary stenosis.R: right ventricular hypertrophy.O: overriding aorta.V: ventricular septal defect.Apr 26, 2020
When is tetralogy of Fallot diagnosed?
Usually, tetralogy of Fallot is diagnosed soon after birth. Your baby's skin may appear blue. A doctor might hear an abnormal whooshing sound (heart murmur) when listening to the baby's heart with a stethoscope.Aug 17, 2021
How is tetralogy of Fallot diagnosed?
How Is Tetralogy of Fallot Diagnosed? Sometimes, a doctor will diagnose TOF while the baby is still in the mother's uterus when a fetal ultrasound displays a heart abnormality. Your doctor can also diagnose it shortly after birth if they hear a murmur during a heart exam or if the baby's skin color is bluish.
How do you say Fallot?
0:371:02How To Say Fallot - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFalam ou falam falam ou falam.MoreFalam ou falam falam ou falam.
Which laboratory finding is consistent with a diagnosis of tetralogy of Fallot?
Laboratory findings consistent with the diagnosis of tetralogy of fallot include diminished oxygen saturation, hematocrit between 65% to 70%, and low platelet count and coagulation factors.Apr 14, 2020
Why is tetralogy of Fallot cyanotic?
The cause of cyanosis is a lower than normal blood oxygen level. Patients with tetralogy of Fallot are at risk for cyanosis because the narrowing of blood flow to the lungs in combination with a VSD or hole allows blood in many instances to bypass the lungs and go directly up to the body.
Why morphine is given in tetralogy of Fallot?
Conclusions: Morphine-induced postconditioning may provide enhanced cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury in children undergoing corrections of TOF.Apr 11, 2013
What is the tetralogy of fallot?
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT-. a combination of congenital heart defects consisting of four key features including ventricular septal defects; pulmonary stenosis; right ventricular hypertrophy; and a dextro positioned aorta. in this condition blood from both ventricles oxygen rich and oxygen poor is pumped into the body often causing cyanosis.
What is the Q21.3 code?
Q21.3 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of tetralogy of fallot. The code Q21.3 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the medical term for heart murmurs?
Heart murmurs and other sounds (Medical Encyclopedia) Patent ductus arteriosus (Medical Encyclopedia) Ventricular septal defect (Medical Encyclopedia) Critical congenital heart disease Critical congenital heart disease ( CCHD) is a term that refers to a group of serious heart defects that are present from birth.
What are the most common birth defects?
A congenital heart defect is a problem with the structure of the heart. It is present at birth. Congenital heart defects are the most common type of birth defect. The defects can involve the walls of the heart, the valves of the heart, and the arteries and veins near the heart. They can disrupt the normal flow of blood through the heart. The blood flow can slow down, go in the wrong direction or to the wrong place, or be blocked completely.
What are the risks of heart defects?
Adults with these heart defects have an increased risk of abnormal heart rhythms, heart failure, sudden cardiac arrest, stroke, and premature death.Each of the heart defects associated with CCHD affects the flow of blood into, out of, or through the heart.
What are the two chambers of the heart?
Some of the heart defects involve structures within the heart itself, such as the two lower chambers of the heart (the ventricles) or the valves that control blood flow through the heart. Others affect the structure of the large blood vessels leading into and out of the heart (including the aorta and pulmonary artery).
What causes a purple tint on the skin?
These can include an abnormal heart sound during a heartbeat (heart murmur), rapid breathing (tachypnea), low blood pressure (hypotension), low levels of oxygen in the blood (hypoxemia), and a blue or purple tint to the skin caused by a shortage of oxygen ( cyanosis).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for status post loss of eye
- 2. icd 10 code for status post mva in pregnancy
- 3. icd 10 code for difficulty losing weight
- 4. icd 10 code for abnormal metabolic screening
- 5. icd 10 code for back acne
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for status post 1 kidney
- 7. icd 10 code for cyclic citrullinated peptide
- 8. what is icd 9 code for diabetic orthostatic hypotension
- 9. icd 10 code for history of hcv
- 10. 2016 icd 10 code for fracture orbital floor