What is the diagnosis and treatment for an aortic aneurysm?
Oct 01, 2021 · Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I71.6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I71.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD10 code for family history of aneurysm?
ICD-10 code I71.6 for Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now Official Long Descriptor Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture I71
What is the diagnosis code for abdominal aortic aneurysm?
Oct 01, 2021 · I71.6 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
Is an aortic aneurysm considered heart disease?
Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture BILLABLE Adult Only | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 I71.6 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code I71 is used to code Aortic aneurysm
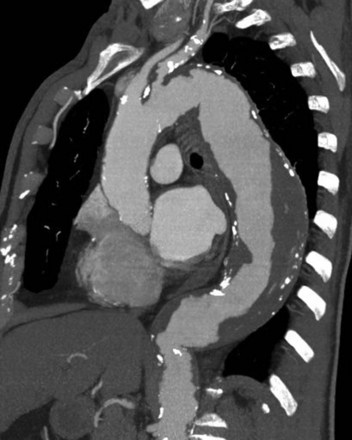
What is a thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm?
A thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm is a bulging in the aorta that extends from the chest to the abdomen. Thoracoabdominal aneurysms are often one of the most complex aortic aneurysms to treat due to the complexity of their location.
What is dissection of thoracoabdominal aorta?
Thoracoabdominal aortic dissection (TAAD) is defined as separation of the layers of the tunica media by ingress of the blood, producing a false lumen (FL) with variable proximal or distal extension. It is not an infrequent clinical entity and constitute 40% of all dissections.
What is thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm repair?
TAAA repair is an extensive surgery done to fix aneurysms (ballooning) of the aorta that extend from the chest into the abdomen. A catheter, inserted at the start of the procedure to drain spinal fluid, relieves pressure created during surgery and reduces the risk of post-surgical paralysis.
Is ascending aorta thoracic?
The ascending aorta, along with the aortic arch and the descending aorta, makes up the thoracic aorta. The ascending aorta begins right after the left ventricle of the heart and contains the aortic heart valve, which is a flap that opens and closes to allow blood to enter the aorta from the left ventricle.Oct 20, 2021
What is the difference between Type A and B aortic dissection?
Type A which is the more common and dangerous of the two and involves a tear in the part of the aorta where it exits the heart or a tear in the upper, or ascending aorta, which may extend into the abdomen. Type B which involves a tear in the lower, or descending, aorta only, which may also extend into the abdomen.
How can you tell the difference between a Type A and B aortic dissection?
Aortic dissections are classified into two types: type B dissection involves a tear in the descending part of the aorta and may extend into the abdomen, whereas type A dissection develops in the ascending part of the aorta just as it branches off the heart.May 10, 2014
What is thoracoabdominal incision?
ABSTRACT The left thoracoabdominal incision is ap- proaching its first century of use. Its history is reviewed. The incision provides wide exposure of the spleen, stomach, left hemidiaphragm, aorta, and esophagus; expo- sure is not limited to the distal esophagus.
How do you say Thoracoabdominal?
Phonetic spelling of thoracoabdominaltho-ra-coab-dom-i-nal.tho-ra-coab-dom-i-nal.thor-a-coab-dom-inal.
What is TAA medical term?
When a weak area of your thoracic aorta expands or bulges, it is called a thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA). Approximately 25 percent of aortic aneurysms occur in the chest and the rest occur in the abdomen. Thoracic aneurysms affect approximately 15,000 people in the United States each year.
What is the most common cause of thoracic aortic aneurysm?
The most common cause of a thoracic aortic aneurysm is hardening of the arteries. This condition is more common in people with high cholesterol, long-term high blood pressure, or who smoke. Other risk factors for a thoracic aneurysm include: Changes caused by age.Jun 16, 2020
What is the difference between an ascending and descending aortic aneurysm?
Ascending aorta, which emerges from the top of the aortic root. Aortic arch, the part of the aorta that arches and turns downward before it becomes the descending aorta. Descending aorta, which branches into the thoracic and abdominal aorta.
Is thoracic aorta the same as ascending aorta?
The upward part of the arch, which is the section closest to the heart, is called the ascending aorta. The part of the aorta in the chest is called the thoracic aorta. The portion further down in your trunk is called the abdominal aorta.
The ICD code I71 is used to code Aortic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is enlargement (dilation) of the aorta to greater than 1.5 times normal size. They usually cause no symptoms except when ruptured. Occasionally there may be abdominal, back or leg pain.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'I71.6 - Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code I71.6. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 441.7 was previously used, I71.6 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for c diff sepsis
- 2. icd 10 code for status post laparoscopic surgery for lysis of adhesions
- 3. icd 9 code for left femoral syndrum
- 4. what is the icd 10 code for history of tobacco dependence
- 5. icd 9 code for parkinson
- 6. icd 10 code for encounter for port check
- 7. icd 9 cm code for nuclear sclerotic cataract
- 8. icd-9 code for bubonic plaque
- 9. code for rsv bronclitiasis of a newborn in icd 10
- 10. icd 10 code for diazepam use and abuse