What is the ICD 10 code for hyperthyroidism?
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperthyroid? E05. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM E05. 90 became effective on October 1, 2019. Click to see full answer. Similarly, it is asked, what is a overactive thyroid?
What is the ICD 10 code for TSH?
recommend reference from the official guide as it pertains to the use of ICD-10 coding. M102.001 ICD-10 Diagnosis Codes CPT CODE: 84436 THYROXINE; TOTAL CPT CODE: 84439 THYROXINE; FREE CPT CODE: 84443 THYROID STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) CPT CODE: 84479 THYROID HORMONE (T3 or T4) UPTAKE or thyroid hormone binding ratio (THBR)
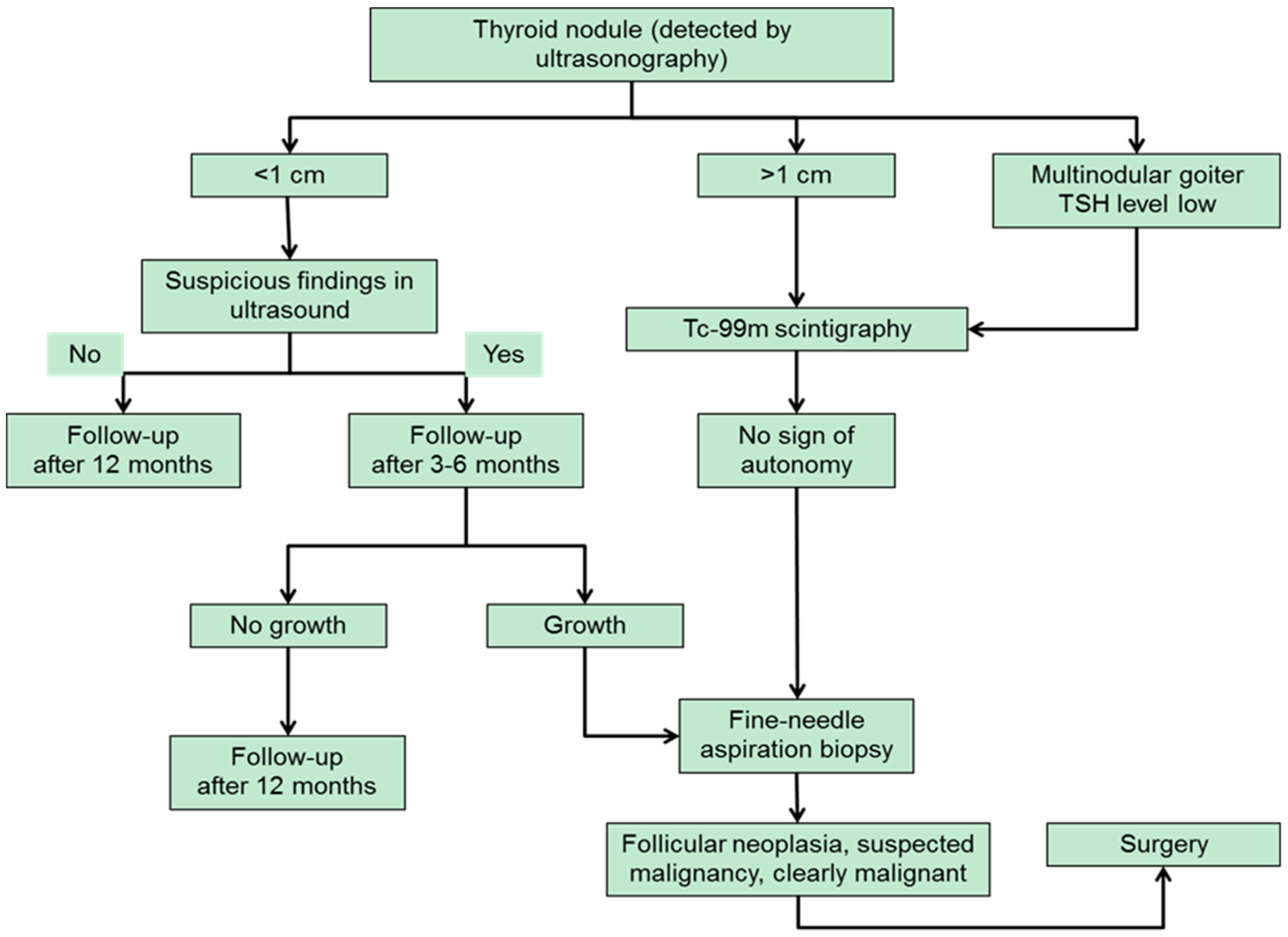
What is the ICD 10 code for thyroid nodule?
ICD-10 code E04.1 for Nontoxic single thyroid nodule is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What are the differential diagnoses for hypothyroidism?
The differential diagnosis of hypothyroidism can be divided into two major groups based on laboratory tests and clinical symptoms. The hallmark of hypothyroidism is high THS and this can be found in variety of other conditions in addition to hypothyroidism, which include the following.
What is the ICD-10 code for autoimmune thyroiditis?
ICD-10 code E06. 3 for Autoimmune thyroiditis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What thyroiditis means?
Thyroiditis is the swelling, or inflammation, of the thyroid gland and can lead to over- or under-production of thyroid hormone. There are three phases to thyroiditis: Thyrotoxic phase. Thyrotoxicosis means that the thyroid is inflamed and releases too many hormones. Hypothyroid phase.
What is the difference between thyroiditis and hyperthyroidism?
If you have hyperthyroidism, you may experience a fast heartbeat, increased appetite, anxiety, sensitivity to heat, or sudden weight loss. In hyperthyroidism, an irritation of your thyroid known as thyroiditis allows too much thyroid hormone to enter your blood. This can lead to pain and discomfort.
What are the different types of thyroiditis?
There are several different types of thyroiditis.Hashimoto's thyroiditis. ... De Quervain's (subacute) thyroiditis. ... Postpartum thyroiditis. ... Silent (painless) thyroiditis. ... Drug-induced thyroiditis. ... Radiation-induced thyroiditis. ... Acute or infectious thyroiditis.
Is thyroiditis the same as hypothyroidism?
Thyroiditis literally means inflammation of the thyroid. Over time, thyroiditis results in the thyroid not being able to make enough hormone, so many people develop hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is named after the doctor who initially described the condition in the early 1900s.
What is another name for thyroiditis?
Hashimoto's disease is also called Hashimoto's thyroiditis, chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, or autoimmune thyroiditis.
Is thyroiditis the same as Hashimoto's?
Hashimoto's disease affects the thyroid gland. It's also called Hashimoto's thyroiditis, chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis or autoimmune thyroiditis. The thyroid gland makes hormones that control virtually all of the body's metabolic functions (how the body turns food into energy) and keep it working normally.
What is the most common cause of thyroiditis?
Thyroiditis is caused by an attack on the thyroid, causing inflammation and damage to the thyroid cells. Antibodies that attack the thyroid cause most types of thyroiditis. As such, thyroiditis is often an autoimmune disease, like juvenile (type 1) diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis.
How can you tell the difference between Graves and thyroiditis?
Hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease is caused by thyroid-stimulating autoantibodies to the TSH receptor (TSHR), whereas hypothyroidism in Hashimoto's thyroiditis is associated with thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin autoantibodies.
What is Hashimoto's thyroiditis diagnosis?
The diagnosis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis may be made when patients present with symptoms of hypothyroidism, often accompanied by a goiter (an enlarged thyroid gland) on physical examination, and laboratory testing of hypothyroidism, which is an elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) with or without a low thyroid ...
What are 2 types of thyroid disorders?
The two main types of thyroid disease are hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Both conditions can be caused by other diseases that impact the way the thyroid gland works. Conditions that can cause hypothyroidism include: Thyroiditis: This condition is an inflammation (swelling) of the thyroid gland.
What is the difference between acute and subacute thyroiditis?
Subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis (silent thyroiditis) is considered autoimmune in origin and commonly occurs in the postpartum period. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism and depressed RAIU predominate. Acute (suppurative) thyroiditis is a rare, infectious thyroid disorder caused by bacteria and other microbes.
What is thyroiditis?
Inflammation of the thyroid gland. Inflammation of the thyroid gland. Thyroiditis may be an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland over time, causing hypothyroidism (too little thyroid hormone).
Is thyroiditis a subacute disease?
Thyroiditis can be classified into acute (thyroiditis, suppurative), subacute (granulomatous and lymphocytic), chronic fibrous (riedel's), chronic lymphocytic (hashimoto disease), transient (postpartum thyroiditis), and other autoimmune thyroiditis subtypes. Code History.
What is thyroiditis autoimmune?
Thyroiditis, autoimmune. Thyroiditis, fibrous autoimmune. Clinical Information. An autoimmune condition of the thyroid gland (a gland located beneath the larynx). It is caused by the formation of antibodies that attack the thyroid gland and it usually causes hypothyroidism (too little thyroid hormone).
What are the symptoms of thyroid disease?
Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, depression, and the inability to exercise. It is more common in females and can run in families. An autoimmune disorder caused by the production of autoantibodies against thyroid tissue.
What is the term for the destruction of the thyroid gland?
There is progressive destruction of the thyroid follicles leading to hypothyroidism. An inflammatory disorder that affects the thyroid gland. It is characterized by the infiltration of the thyroid parenchyma by lymphocytes. It includes hashimoto thyroiditis and subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis.
What is postpartum thyroid?
Postpartum (after childbirth) thyroid disease . Postpartum thyroid disease. Thyroid disease in childbirth. Thyroid disease in pregnancy. Thyroid disorder. Thyroid mass. Clinical Information. Condition in which there is a deviation from or interruption of the normal structure or function of the thyroid gland, which is a highly vascular endocrine ...
How does the thyroid help your metabolism?
The thyroid helps set your metabolism - how your body gets energy from the foods you eat.millions of people in the United States Have thyroid diseases. Most of them are women. If you have a thyroid disease, your body uses energy more slowly or quickly than it should.

Popular Posts:
- 1. what is the icd 10 code for rt tmj
- 2. icd 10 code for dog bite injury
- 3. icd 10 code for open wound to right lower leg
- 4. icd 10 code for oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- 5. 2017 icd 10 code for swelling nasal bone
- 6. icd 10 code for a uti
- 7. icd 10 code for post op open heart surgery
- 8. icd 10 code for personal history of abdominal aortic aneurysm
- 9. icd 10 code for tendon release
- 10. icd 9 code for shoulder trauma