What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
What is the T33-T34?
effects of foreign body on external eye ( T15.-) frostbite ( T33-T34) insect bite or sting, venomous ( T63.4) Injuries to the head. Clinical Information. A traumatic injury to the head. Chances are you've bumped your head before. Usually, the injury is minor because your skull is hard and it protects your brain.
What is a frostbite?
frostbite ( T33-T34) insect bite or sting, venomous ( T63.4) Injuries to the head. Clinical Information. A traumatic injury to the head. Chances are you've bumped your head before. Usually, the injury is minor because your skull is hard and it protects your brain.
What is a venomous insect bite?
insect bite or sting, venomous ( T63.4) Injuries to the head. Clinical Information. A traumatic injury to the head. Chances are you've bumped your head before. Usually, the injury is minor because your skull is hard and it protects your brain.
Can you bump your head?
Chances are you've bumped your head before. Usually, the injury is minor because your skull is hard and it protects your brain. But other head injuries can be more severe, such as a skull fracture, concussion, or traumatic brain injury.head injuries can be open or closed. A closed injury does not break through the skull.
Can a skull fracture break through the skull?
A closed injury does not break through the skull.
Can a head injury be open or closed?
But other head injuries can be more severe, such as a skull fracture, concussion, or traumatic brain injury.head injuries can be open or closed. A closed injury does not break through the skull. With an open, or penetrating, injury, an object pierces the skull and enters brain tissue.
What is the ICd 10 code for fracture of skull?
Fracture of skull and facial bones 1 S02 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S02 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S02 - other international versions of ICD-10 S02 may differ.
When is the ICd 10 code for fracture of skull and facial bones effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S02 became effective on October 1, 2020.
Is a fracture not indicated as open or closed?
A fracture not indicated as open or closed should be coded to closed. Code Also. Code Also Help. A code also note instructs that 2 codes may be required to fully describe a condition but the sequencing of the two codes is discretionary, depending on the severity of the conditions and the reason for the encounter.
What is the ICd 10 code for injury?
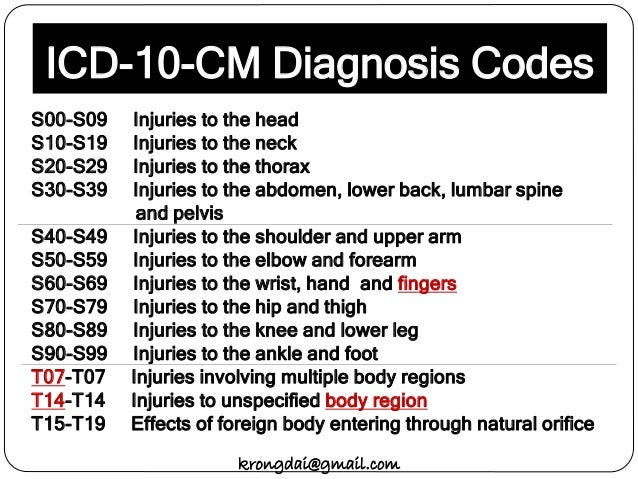
Injury, unspecified, initial encounter 1 S00-T88#N#2021 ICD-10-CM Range S00-T88#N#Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes#N#Note#N#Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code#N#Type 1 Excludes#N#birth trauma ( P10-P15)#N#obstetric trauma ( O70 - O71)#N#Use Additional#N#code to identify any retained foreign body, if applicable ( Z18.-)#N#Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes 2 T14#N#ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T14#N#Injury of unspecified body region#N#2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code#N#Type 1 Excludes#N#multiple unspecified injuries ( T07)#N#Injury of unspecified body region 3 T14.90#N#ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T14.90#N#Injury, unspecified#N#2016 2017 2018 - Converted to Parent Code 2019 2020 2021 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code#N#Applicable To#N#Injury NOS#N#Injury, unspecified
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code.
What is the S09.93XA code?
S09.93XA is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of unspecified injury of face, initial encounter. The code S09.93XA is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. S09.93XA is an initial encounter code, ...
When is S09.93XA valid?
The code S09.93XA is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. S09.93XA is an initial encounter code, includes a 7th character and should be used while the patient is receiving active treatment for a condition like unspecified injury of face.
When to use S09.93XA?
Unspecified diagnosis codes like S09.93XA are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code S09.93XA its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
Can facial injuries cause pain?
In severe cases, they can affect sight, speech, breathing and your ability to swallow. Broken bones, especially the bones of your nose, cheekbone and jaw, are common facial injuries.
Can broken bones affect your speech?
In severe cases, they can affect sight, speech, breathing and your ability to swallow. Broken bones, especially the bones of your nose, cheekbone and jaw, are common facial injuries. Certain diseases also lead to facial disorders.
What causes facial pain?
Certain diseases also lead to facial disorders. For example, nerve diseases like trigeminal neuralgia or Bell's palsy sometimes cause facial pain, spasms and trouble with eye or facial movement.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for above knee amputation
- 2. icd 10 code for breast cancer female
- 3. what is the correct icd 10 code for aki
- 4. icd 10 code for history of coronary stents
- 5. icd-10-cm diagnosis code for septic shock ??
- 6. icd-10 code for tracheostomy infection
- 7. icd 10 code for right leg below knee amputation
- 8. icd code for virtual reality treatment
- 9. icd 10 code for hpvd
- 10. icd 10 code for intractable abdominal pain