What is the ICD 10 code for trichotillomania?
Trichotillomania. F63.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM F63.3 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of F63.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 F63.3 may differ.
What is the pathophysiology of trichilemmoma?
Trichilemmoma is a benign follicular tumor with differentiation toward the outer root sheath of the hair follicle. Patients may present with an individual papule or they may have multiple skin-colored papules that tend to localize to the central face. Although most commonly found on this location, any nonglabrous site may be affected.
When should multiple trichilemmomas be considered in the diagnosis of Cowden syndrome?
If multiple trichilemmomas are present in context of other cutaneous findings and certain malignancies, then the diagnosis of Cowden syndrome should be considered. Cowden syndrome, or multiple hamartoma syndrome, is an autosomal dominant disease resulting from mutations in the PTEN gene.
What is the treatment for trichilemmoma?
Trichilemmoma is a benign follicular tumour that requires no treatment. Occasionally lesion (s) may be removed for cosmetic reasons or if they occur in functionally sensitive areas. The main reason for surgery is to establish the correct diagnosis and to ensure that a potential malignancy, such as trichilemmal carcinoma, is not left untreated.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
Can multiple neoplasms be coded?
About this website
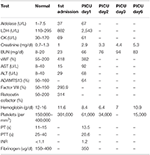
How do you code a dysplastic nevus?
ICD20 Dysplastic Nevi I would use D48. 5 for the dx of dysplastic nevi. Also, if the patient also has a hx of dysplastic nevi, don't forget to include Z86. 03 (Personal hx of neoplasm of uncertain behavior).
What is the ICD-10 code for benign skin lesion?
D23. 9 - Other benign neoplasm of skin, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for atypical mole?
D22. 9 - Melanocytic nevi, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for skin tags?
8: Other hypertrophic disorders of the skin.
What is benign neoplasm of skin?
A non-cancerous (benign) tumour of the skin is a growth or abnormal area on the skin that does not spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Non-cancerous tumours are not usually life-threatening. They usually don't need any treatment but may be removed with surgery in some cases.
What is other benign neoplasm of skin?
Types of benign skin neoplasms include: skin tags. cherry angioma. dermatofibroma.
What is an atypical mole?
(ay-TIH-pih-kul mole) A type of mole that looks different from a common mole. Several different types of moles are called atypical. Atypical moles are often larger than common moles and have regular or ragged or blurred borders that are not easy to see.
What is nevus non neoplastic?
A abnormal, congenital formation or mark on the skin or neighboring mucosa that does not show neoplastic growth. [
What is dysplastic nevus of skin?
A specific type of nevus (mole) that looks different from a common mole. Dysplastic nevi are mostly flat and often larger than common moles and have borders that are irregular. A dysplastic nevus can contain different colors, which can range from pink to dark brown.
How do you bill for skin tags?
Skin tags. For removal of skin tags by any method, use codes 11200 and 11201. For the first 15 skin tags removed, use code 11200. For each additional 10 skin tags removed, also report code 11201. For example, if you removed 35 skin tags, then you would submit codes 11200, 11201 and 11201.
What is the ICD-10 code for removal of skin tags?
For skin tag removal, you code 11200 for removing the first 15 lesions, and then you add code 11201 for removal of each additional 10 lesions.
What is the CPT 4 code for removal of 25 skin tags?
CPT® 11200, Under Removal of Skin Tags Procedures The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) code 11200 as maintained by American Medical Association, is a medical procedural code under the range - Removal of Skin Tags Procedures.
2022 ICD-10-CM Code D23.9 - Other benign neoplasm of skin, unspecified
D23.9 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other benign neoplasm of skin, unspecified. The code D23.9 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D23.4: Other benign neoplasm of skin of ...
Free, official coding info for 2022 ICD-10-CM D23.4 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD-9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping and more.
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D23.39: Other benign neoplasm of skin of ...
Free, official coding info for 2022 ICD-10-CM D23.39 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD-9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping and more.
ICD-10-CM Poroma, eccrine
ICD-10-CM/PCS codes version 2016/2017/2018/2019/2020/2021, ICD10 data search engine
ICD-10-CM Code D48.5 Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of skin
D48.5 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of neoplasm of uncertain behavior of skin. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Can multiple neoplasms be coded?
For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, ...
What is the code for trichomonas?
infectious and parasitic diseases complicating pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium ( O98.-) code to identify resistance to antimicrobial drugs ( Z16.-) Infections in birds and mammals produced by various species of trichomonas. Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by a parasite.
What is Z16 code?
code to identify resistance to antimicrobial drugs ( Z16.-) Infections in birds and mammals produced by various species of trichomonas. Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by a parasite. It affects both women and men, but symptoms are more common in women.
Is trichomonas a parasite?
Infections in birds and mammals produced by various species of trichomonas. Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by a parasite. It affects both women and men, but symptoms are more common in women.
Can trichomoniasis cause urination?
Symptoms in women include a green or yellow discharge from the vagina, itching in or near the vagina and discomfort with urination. Most men with trichomoniasis don't have any symptoms, but it can cause irritation inside the penis.you can cure trichomoniasis with antibiotics.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the only definitive diagnosis for trichilemmoma?
A small biopsy (when a tiny piece of skin is removed under local anaesthetic) is the only definitive diagnosis for trichilemmoma. The histology of trichilemmoma will differentiate it from other skin tumours that have similar clinical presentations, such as trichoepithelioma, trichofolliculoma and basal cell carcinoma.
What is a desmoplastic trichilemmoma?
Desmoplastic trichilemmomas, a subtype of trichilemmoma, mainly occurs in white males around 50 years old. Lesions of this subtype are usually less than 1 cm in diameter and occur mainly on the face, neck and scalp, and sometimes on the chest and vulva. Trichilemmoma.
What is tricholemmoma?
What is trichilemmoma? Trichilemmoma, also called tricholemmoma is a benign tumour originating from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle. Diagnosis depends on careful histopathological examination of a skin biopsy. Trichilemmoma often occurs alongside other skin lesions such as trichoblastoma, sebaceous adenoma and sebaceous naevus. ...
How big is a trichilemmoma?
Trichilemmoma typically presents as a solitary papule or mass of small skin-coloured papules that are 1-5 cm in diameter . These lesions slowly grow over time and tend to form small plaques that may resemble a wart/verruca or a cutaneous horn.
Where do trichilemmomas occur?
They most commonly occur around the central part of the face, ears and neck, but also occur on the forearms and hands. Solitary trichilemmomas are relatively common benign follicular tumours and occur in both male and females usually between 20-80 years of age.
What is the histological variant of trichilemmoma?
Histological variants of trichilemmoma. Desmoplastic trichilemmoma: In this variant the tumour develops infiltrating cords predominantly at the base of the lesion. This is surrounded by a sclerotic stroma and a mild to moderate lymphocytic inflammatory response.
What is the name of the benign skin tumor that is thought to arise from the outer root sheath of the hair
274900003, 46199002, 403928006, 254691005. Trichilemmoma is a benign skin tumour thought to arise from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Can multiple neoplasms be coded?
For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for stenotrophomonas maltophilia
- 2. icd 10 code for pre ulcerative callus
- 3. icd 10 code for personal history of colon avm
- 4. 2017 icd 10 code for calcified plaque popliteal artery
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for b12 deficiency
- 6. icd 10 code for lump on leg
- 7. icd 10 code for pregnancy complicated by breech presentation 39 weeks gestations
- 8. icd 10 code for tick bite right popiteal
- 9. icd 10 code for b12 deficicy dementia
- 10. icd 10 cm code for bydureon pen