What N50 89?
N50. 89 - Other specified disorders of the male genital organs | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for testicular swelling?
Inflammatory disorders of scrotum The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N49. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for testicular Microlithiasis?
8.
What is the ICD-10 code for left epididymitis?
ICD-10 code: N45. 9 Orchitis, epididymitis and epididymo-orchitis without abscess.
What is the ICD-10 code for testicular pain?
ICD-10 code N50. 819 for Testicular pain, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
Why does a testicle swell?
Infection: The testicle and epididymis, the part of the testicle that stores sperm, can sometimes become infected, causing pain and swelling that starts quickly and gets worse. Fluid Buildup: An injury or infection can cause fluid to build up around the testicle, causing painful swelling. This is called a hydrocele.
What is Microlithiasis in the testes?
Gargollo, M.D. Testicular microlithiasis (tes-TIK-yoo-lur my-kroh-lih-THIE-uh-sis) is a condition in which small clusters of calcium form in the testicles. It can be detected on an ultrasound exam of the scrotum. Several studies show a relationship between testicular microlithiasis and testicular cancer.
What is the ICD 10 code for testicular torsion?
N44.0ICD-10 code N44. 0 for Torsion of testis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is the most common symptom of Orchialgia?
Chronic orchialgia, if we are looking at the base of the term, is chronic testicular pain. However, it is used more loosely clinically to include scrotal pain and scrotal content pain. Other frequently associated terms include testicular pain, epididymalgia, epididymal pain, and spermatic cord pain.
What is the ICD 10 code for epididymal cyst?
ICD-10-CM Code for Cyst of epididymis N50. 3.
What is orchitis and epididymitis?
Epididymitis is swelling or pain in the back of the testicle in the coiled tube (epididymis) that stores and carries sperm. Orchitis is swelling or pain in one or both testicles, usually from an infection or virus.
What is the ICD 10 code for left testicular pain?
ICD-10 code N50. 812 for Left testicular pain is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What is a genetic disorder of the kidney tubules?
A group of genetic disorders of the kidney tubules characterized by the accumulation of metabolically produced acids with elevated plasma chloride, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Defective renal acidification of urine (proximal tubules) or low renal acid excretion (distal tubules) can lead to complications such as hypokalemia, hypercalcinuria with nephrolithiasis and nephrocalcinosis, and rickets.
When will the ICd 10 N25.89 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N25.89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Presentation
It is usually found in men older than 55 years and is frequently found on bilateral testes but often asymmetrical.
Mechanism
The formation of cysts in the rete testis is associated with the obstruction of the efferent ducts, which connect the rete testis with the head of the epididymis. They are often bilateral.
Diagnosis
The condition can be detected with ultrasonography. Cystic lesions us usually found at the mediastinum testis with elongated shaped lesion displacing the mediastinum. It is commonly associated with epididymal abnormalities, such as spermatocele, epididymal cyst, and epididymitis.
Treatment
Typically none is required, but they can be treated surgically if symptomatic.
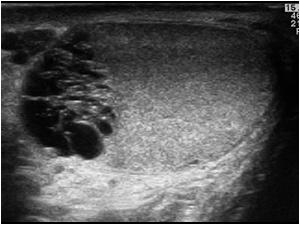
What is the sagittal sonogram of the right testis?
Sagittal sonogram of the right testis depicts an ovoid cluster of small anechoic structures (cursors), located in the region of the mediastinum, representing a typical form of dilatation of the rete testis. There is also a large spermatocele (asterisk) and a small ipsilateral hydrocele (arrow).
Is a rete testis a benign entity?
Dilatation or tubular ectasia of the rete testis (TERT) is a well-known benign intratesticular entity, for which the clinical, as well as the imaging findings may unable a correct diagnosis and the avoidance of invasive tests, as unnecessary biopsy or orchiectomy.
How is the rete testis formed?
The rete testis is formed by the confluence of the seminiferous tubules which fold to form a compact structure within the mediastinum testis and merge in the efferent ducts , which conform the epididymal head. 5 From an aetiological perspective, obliteration of the seminiferous tubules, due to either luminal obstruction or external compression, causes the formation of the cystic dilatations that characterise this condition. The tubules may contain spermatozoa and can be connected to the lumen of non-dilated ducts in cases of partial obstruction.
What causes extrinsic tubular compression?
Haematocoele has been described as a cause of extrinsic tubular compression. Other causes are cryptorchidism and vasectomy. From a systemic point of view, cirrhosis has been described as a possible triggering factor, giving rise to hormonal alterations that can lead to ischaemia of organs such as the testes.
How old is the youngest person diagnosed with tert?
According to the existing literature, TERT is a condition that affects middle-aged men and its prevalence increases with age; 6 in our series, the youngest patient was 47 years old. Nevertheless, most diagnoses correspond to patients in the sixth decade of their life and onwards.
What version of SPSS is used for statistical analysis?
Outcome Measurements and Statistical Analysis: SPSS ® version 20 (IBM, New York, USA) was used for the descriptive analysis of the data.
Is rete testis malignant?
Despite malignant transformation of the rete testis being rare, some past literature has referred to it, always acknowledging the rarity of this degeneration. 8 Since the bulk of the evidence suggests that TERT is a condition with benign behaviour, a correct differential diagnosis is the most important aspect of the disease. In the presence of a cystic image in the mediastinum testis, it is important to know the features that allow us to distinguish between the different possible diagnoses. Intratesticular varicocoele has ultrasound characteristics that are very similar in terms of morphology and location to those of TERT. However, the two conditions can be clearly distinguished using Doppler ultrasound sonography, which reveals a slow vascular flow in cases of varicocoele, a finding that is absent in tubular ectasia. This flow is more obvious during a Valsalva manoeuvre or in the standing position. Intratesticular varicosities usually appear in patients with extratesticular varicocoele. In addition, a hypotrophic ipsilateral testis may be observed, which can manifest as testicular asymmetry. 9,10
Where are tunica albuginea cysts located?
Cysts of the tunica albuginea are small anechoic nodules generally located within the superficial testicular layers , and show no flow signal in Doppler exploration. Furthermore, these lesions are palpable at physical examination and are commonly discovered by the patient; they are usually described as a painless nodule <5 mm. Detection of these cysts may follow a haemorrhage, trauma, or infection of the cyst. Most cases require no subsequent treatment measures. 14
Is tetra a clinical condition?
Conclusions: According to our experience, TERT is an incidental condition where detailed clinical history, adequate physical examination, and SU findings can lead to the diagnosis. Knowledge of this disease is therefore essential for urologists.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for obesity complicating childbirth
- 2. icd 10 code for allergies seasonal
- 3. icd 10 code for crps right lower extremity
- 4. icd 10 code for prostate pain
- 5. icd-10 code for motor vehicle accident
- 6. icd 9 code for nodular basal cell carcinoma exact code
- 7. icd 10 code for lead poisoning
- 8. icd 10 code for cpam
- 9. icd 10 code for total hysterectomy
- 10. icd 10 code for right lower leg cellulitis