How severe is Turner syndrome?
The heart defects associated with some cases of Turner syndrome can increase the risk of severe, life-threatening complications including high blood pressure of the arteries of the lungs (pulmonary hypertension) or aortic dissection, a condition in which there is a tear in the inner wall of the aorta.
Is Turner syndrome considered a disability?
Turner syndrome is not considered a disability, although it can cause certain learning challenges, including with learning mathematics and with memory. 7 Most girls and women with Turner syndrome lead normal, healthy, productive lives with proper medical care. My daughter has been diagnosed with Turner syndrome.
Who can get Turner syndrome?
They might include:
- Heart problems because of its physical structure
- Increased chance of diabetes and high blood pressure
- Hearing loss
- Kidney problems that can raise the chance of high blood pressure and urinary tract infections
Is Turner syndrome a rare disorder?
Turner syndrome is a rare chromosomal disorder that affects females. The disorder is characterized by partial or complete loss (monosomy) of one of the second sex chromosomes. Turner syndrome is highly variable and can differ dramatically from one person to another. Affected females can potentially develop a wide variety of symptoms, affecting ...
What is the ICD-10 code for Mosaic Turner syndrome?
Turner's syndrome, unspecified Q96. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q96. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Turner's syndrome Down syndrome?
Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome constitute the most common chromosomal abnormalities encountered by primary care physicians. Down syndrome typically is recognized at birth, Turner syndrome often is not recognized until adolescence,and many men with Klinefelter syndrome are never diagnosed.
What are the different types of Turner syndrome?
There are 2 types of Turner syndrome: monosomy X TS and mosaic TS. About half of all girls with Turner syndrome have a monosomy disorder. Monosomy means that a person is missing one chromosome in the pair. Instead of 46 chromosomes, the person has only 45 chromosomes.
What is Turner mosaic syndrome?
Mosaic Turner syndrome (TS) is a condition in which cells inside the same person have different chromosome packages. Mosaic TS can affect any cell in the body. Some cells have X chromosomes and some don't. Every 3 out of every 10 girls with TS will have some form of Mosaic TS.
Is Turner syndrome the same as Down syndrome?
In contrast to Down syndrome, there is no association between Turner syndrome and advanced maternal age [27]. Different karyotypes are associated with varying phenotypic expression. The most prevalent karyo- type in patients with Turner syndrome is 45,X monosomy.
What is the difference between Turner syndrome and mosaic Turner syndrome?
In classical Turner syndrome, an X chromosome is completely missing. This affects about half of all people with TS. Mosaic Turner syndrome, mosaicism, or Turner mosaicism is where the abnormalities occur only in the X chromosome of some of the body's cells.
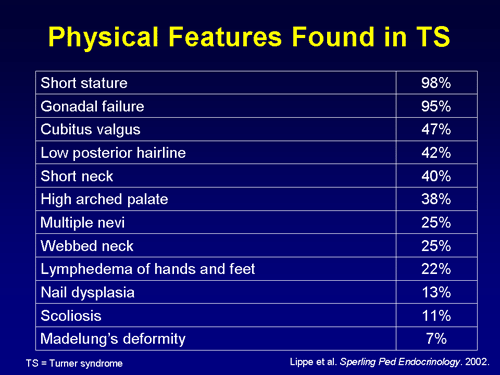
What are three symptoms of Turner syndrome?
Signs of Turner syndrome at birth or during infancy may include:Wide or weblike neck.Low-set ears.Broad chest with widely spaced nipples.High, narrow roof of the mouth (palate)Arms that turn outward at the elbows.Fingernails and toenails that are narrow and turned upward.More items...•
Which characteristic is commonly associated with Turner syndrome?
Turner syndrome is a chromosomal condition that affects development in females. The most common feature of Turner syndrome is short stature, which becomes evident by about age 5. An early loss of ovarian function (ovarian hypofunction or premature ovarian failure) is also very common.
Is Turner's syndrome monosomy or trisomy?
Monosomy X, or Turner syndrome, occurs when a baby is born with only one X sex chromosome, rather than the usual pair (either two Xs or one X and one Y sex chromosome).
Is Turner's syndrome a form of dwarfism?
Turner syndrome is a type of dwarfism that only affects females. In addition to being short in stature, girls with Turner syndrome often have heart defects and their ovaries do not develop normally.
Why is the butterfly the symbol for Turner syndrome?
As awareness and support for the TS community grew, the butterfly symbol came to represent the metamorphosis from a difficult beginning (the caterpillar) to its emergence as a strong, beautiful being (the butterfly). The butterfly has become a symbol of strength and perseverance for the TS community.
How is Turner's syndrome diagnosed?
If, based on signs and symptoms, the doctor suspects that your child has Turner syndrome, a lab test will be done to analyze your child's chromosomes. The test involves a blood sample. Occasionally, your doctor may also request a cheek scraping (buccal smear) or skin sample.
What is the phenotype of 45 xo?
The phenotype varies and not all abnormalities occur in all patients. A syndrome of defective gonadal development in phenotypic females associated with the karyotype 45,x (or 45,xo). Patients generally are of short stature with undifferentiated gonads (streak gonads), sexual infantilism, hypogonadism, webbing of the neck, cubitus valgus, ...
What is the name of the syndrome where the absence of a part of the sex chromosome is?
A gonadal dysgenesis syndrome occurring in phenotypic females, characterized by the absence of a part or all of one of the sex chromosomes. Signs and symptoms include short stature, webbing of neck, low-set ears, hypogonadism, and sterility. A gonadal dysgenesis syndrome occurring in phenotypic females, characterized by the complete absence ...
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A gonadal dysgenesis syndrome occurring in phenotypic females, characterized by the absence of a part or all of one of the sex chromosomes. Signs and symptoms include short stature, webbing ...
How many chromosomes are in a fetus with XO?
The syndrome occurs in 1/2500 female births and nearly 99% of xo fetuses are aborted. Gonadal agenesis and short stature are the main features in the surviving infants.
What is a short neck?
short, "webbed" neck with folds of skin from tops of shoulders to sides of neck
What are the physical features of turner syndrome?
They are at risk for health difficulties such as high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes, cataracts, osteoporosis and thyroid problems.other physical features typical of turner syndrome are. short, "webbed" neck with folds of skin from tops of shoulders to sides of neck. low hairline in the back. low-set ears.
What causes sterile females?
Genetic disease that produces sterile females due to the x chromosome defect. Turner syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects a girl's development. The cause is a missing or incomplete x chromosome. Girls who have it are short, and their ovaries don't work properly.
What is the syndrome of a fetus with 45 chromosomes?
A syndrome in which the affected patients have only 45 chromosomes, the loss of one of the x chromosomes producing an xo chromosome constitution. The syndrome occurs in 1/2500 female births and nearly 99% of xo fetuses are aborted. Gonadal agenesis and short stature are the main features in the surviving infants. Associated anomalies may included webbed neck, cubitus valgus, shield chest, short stature, lymphedema, coarctation of the aorta, pigmented nevi, and various renal, skeletal, dermatologic, neoplastic, and autoimmune complications. Mental retardation is attributed to ring chromosome x. The phenotype varies and not all abnormalities occur in all patients.
What does "exclude note" mean?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as Q96. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
When will the ICD-10-CM Q96 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q96 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD code for Turner's syndrome?
ICD Code Q96 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the seven child codes of Q96 that describes the diagnosis 'turner's syndrome' in more detail.
What is an abnormal number of chromosomes?
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example when having 45 or 47 chromosomes when 46 is expected in a human cell. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes, which is called euploidy. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of genetic disorders, including some human birth defects. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells.
What is the most common condition due to aneuploidy?
Chromosomes in Down syndrome, the most common condition due to aneuploidy. Notice the three copies of chromosome 21 in the last row.
What does "type 1 excludes" mean?
Type-1 Excludes mean the conditions excluded are mutually exclusive and should never be coded together. Excludes 1 means "do not code here."
What is the ICd code for an abnormal number of chromosomes?
The ICD code Q96 is used to code Aneuploidy. Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example when having 45 or 47 chromosomes when 46 is expected in a human cell. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes, which is called euploidy. An extra or missing chromosome is ...
What is DRG #742-743?
DRG Group #742-743 - Uterine and adnexa procedure for non-malignancy without CC or MCC.
Why do some cancer cells have extra chromosomes?
An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of genetic disorders, including some human birth defects. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells. Specialty:
What is the ICD code for turner syndrome?
Code is only used for female patients. Q96.9 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of turner's syndrome, unspecified. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Documentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) requires medical coders to indicate whether or not a condition was present at the time of admission, in order to properly assign MS-DRG codes.
What is the most common condition due to aneuploidy?
Chromosomes in Down syndrome, the most common condition due to aneuploidy. Notice the three copies of chromosome 21 in the last row.
What is the ICd 10 code for Turner's syndrome?
Q96.9 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Turner's syndrome, unspecified . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
What does "Excludes 2" mean?
A type 2 Excludes note represents 'Not included here'. An Excludes2 note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together.
What is a code also note?
A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
What does NEC not elsewhere mean?
NEC Not elsewhere classifiable#N#This abbreviation in the Tabular List represents “other specified”. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the “other specified” code.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes. It means 'NOT CODED HERE!' An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
Is Q96.9 a POA?
Q96.9 is exempt from POA reporting ( Present On Admission).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for personal history prostate cancer
- 2. icd 10 code for history of pulmonary fibrosis
- 3. icd 10 cm code for benzo withdrawal
- 4. icd 10 code for history of bypass surgery
- 5. icd 10 cm code for feeling foggy
- 6. icd 10 code for rotator cuff dysfunction
- 7. icd 10 code for copd with acute bronchitis
- 8. icd 10 cm code for s/p gastrectomy
- 9. icd 10 code for lumbar disc degeneration with radiculopathy
- 10. 2015 icd 10 code for prostate cancer