What are the ICD 10 codes for diabetes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code E11.621 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.621 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is ICD 10 for poorly controlled diabetes?
Oct 01, 2021 · E11.52 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w diabetic peripheral angiopathy w gangrene. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What is the diagnosis code for diabetic foot ulcer?
ICD-10-CM Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer E11.621. ICD-10 code E11.621 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the ICD 10 code for diabetic foot exam?
Oct 01, 2021 · E11.621. E11.621 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
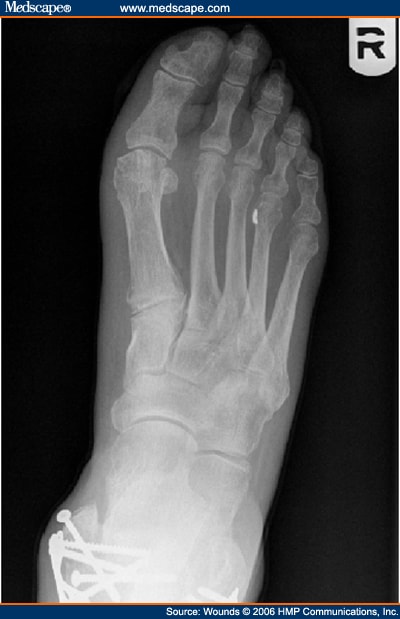
How do you code a diabetic with an ulcer?
ICD-10 Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer- E11. 621- Codify by AAPC.
When do you use E11 59?
ICD-10 code E11. 59 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other circulatory complications is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for foot ulcer?
ICD-10 code L97. 509 for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of unspecified foot with unspecified severity is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
Can diabetes 2 cause foot ulcers?
Closely linked with diabetes neuropathy, diabetic nerve pain and diabetes foot care, diabetic foot ulcers affect many people with diabetes. Experts suggest that around 10 per cent of people with diabetes develop a foot ulcer at some point. Foot ulcers can affect people with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes?
ICD-10 Code: E11* – Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 for CAD?
Code I25* is the diagnosis code used for Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease, also known as Coronary artery disease (CAD).
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes, and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, six percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication.
What ICD-10-CM code is reported for a diabetic foot ulcer on the right foot?
Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of right foot with unspecified severity. L97. 519 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L97.
What is an ulcer on the foot?
Foot ulcers are open sores or lesions that will not heal or that return over a long period of time. These sores result from the breakdown of the skin and tissues of the feet and ankles and can get infected. Symptoms of foot ulcers can include swelling, burning, and pain.
What is Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer?
High glucose levels can slow the healing process of an infected foot ulcer, so blood sugar management is critical. People with type 2 diabetes and other ailments often have a harder time fighting off infections from ulcers. Nerve damage is a long-term effect and can lead to a loss of feeling in your feet.
Is foot ulcer a complication of type 2 diabetes?
Diabetic foot ulceration is a serious limb-threatening complication of diabetes. It is the common cause of hospital admissions and amputations.Aug 6, 2018
Do you stage diabetic foot ulcers?
When treating diabetic foot ulcers it is important to be aware of the natural history of the diabetic foot, which can be divided into five stages: stage 1, a normal foot; stage 2, a high risk foot; stage 3, an ulcerated foot; stage 4, an infected foot; and stage 5, a necrotic foot.
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
Regarded as the most common reason for hospital stays among people with diabetes, a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is an open sore caused by neuropathic (nerve) and vascular (blood vessel) complications of the disease. Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot, these complex, ...
How many people with diabetes have foot ulcers?
According to the American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA), approximately 15 percent of people with diabetes suffer from foot ulcers. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, about 6 percent will be hospitalized due to serious infections or other ulcer-related complications.
Where are diabetic ulcers located?
Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot , these complex, chronic wounds can affect people with both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. If left untreated, diabetic foot ulcers can have a permanent, long-term impact on the morbidity, mortality and quality of a patients’ life.
How many amputations are there for diabetics?
The risk of foot ulceration and limb amputations increases with age and duration of diabetes. In the United States, about 82,000 amputations are performed each year on persons with diabetes; half of those ages 65 years or older. Treatment for diabetic foot ulcers varies depending on their causes.
Why is it important to remove dead skin?
This procedure is important because dead skin hampers the development of healthy new tissues, and also makes the affected area more vulnerable to infections. Removal of the dead skin will promote quick and easy healing. Debridement will be done surgically, enzymatically, biologically, or through autolysis.
What are the risk factors for ulcers?
The most common risk factors for ulcer formation include – diabetic neuropathy, structural foot deformity, kidney disease, obesity and peripheral arterial occlusive disease. The condition can be effectively prevented if the underlying conditions causing it are diagnosed early and treated correctly.
How are cannabinoids separated?
Cannabinoids are separated from hemp using supercritical CO2 extraction. Thanks to modern-day innovation, the resulting solution is tidy, devoid of unneeded waxes and heavy metals, naturally present in the plant, and the sucked liquid has a common, oily consistency.
What is insulin resistant diabetes?
insulin resistant diabetes (mellitus) Clinical Information. A disease in which the body does not control the amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in the blood and the kidneys make a large amount of urine. This disease occurs when the body does not make enough insulin or does not use it the way it should.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E11. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What does it mean when your blood sugar is too high?
diabetes means your blood glucose, or blood sugar, is too high. With type 2 diabetes , the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. Without insulin, too much glucose stays in your blood.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose comes from the foods you eat . Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well.
What is the difference between ICd 9 and ICd 10?
One of the greatest differences between ICD-9 and ICD-10, other than the obvious alphanumeric codes, is the organization of the diabetes mellitus coding. ICD-10 organizes diabetes mellitus diagno-ses, manifestations, and complica-tions into five categories (think of a category as a coding chapter):
What is codingline gold?
Gold is Codingline’s premium service that bundles a number of unique benefits to assist you in achieving coding accuracy, reimbursement effectiveness, practice efficiencies, and practice profitability. Codingline Gold is designed to provide coding and reimbursement information for today’s foot and ankle specialists. What does Gold offer? “Direct to Expert” Hotline (confidential interactive Q/A service); both Codingline#TAB#Silver#TAB#and#TAB#CodinglinePRINT#TAB#access#TAB#and#TAB#benefits;#TAB#discounts to Codingline seminars and workshops; access to#TAB#The#TAB#Library;#TAB#access#TAB#to#TAB#Reference#TAB#Desk;#TAB#and#TAB#access#TAB#to#TAB#the#TAB#Forum. Doctors, staff, and coders, go to www.codingline.com/gold.htm for more information. At $529/year, this is an ultimate value. If you have any questions, email [email protected] (Harry Goldsmith, DPM)

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for status post left tha
- 2. icd 10 code for bilobed placenta in pregnancy
- 3. icd 10 code for past history ofraynauds phenomenion
- 4. icd 10 code for replacement of gastrostomy tube
- 5. icd-10 code for hcg screening
- 6. icd 10 cm code for left ankle bimalleolar equivalent fracture
- 7. icd-9 code for hypoplastic kidney
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for congenital tricuspid regurgitation
- 9. icd 10 code for chronic tonsillitis
- 10. what is the correct icd 10 code for right bundle branch block