How many codes in ICD 10?
· Myocardial infarction type 2. 2018 - New Code 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. I21.A1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I21.A1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
· 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I21.4 Non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I21.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I21.4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are ICD 10 codes?
· Beginning FY2018 on October 1, 2017, a new code is available for MI Type 2 or MI due to demand ischemia I21.A1, Myocardial infarction type 2. In addition, other new codes are available for MI Types 3, 4a-c, and 5, I21.A9, Other myocardial infarction type.
What is ICD 10 used for?
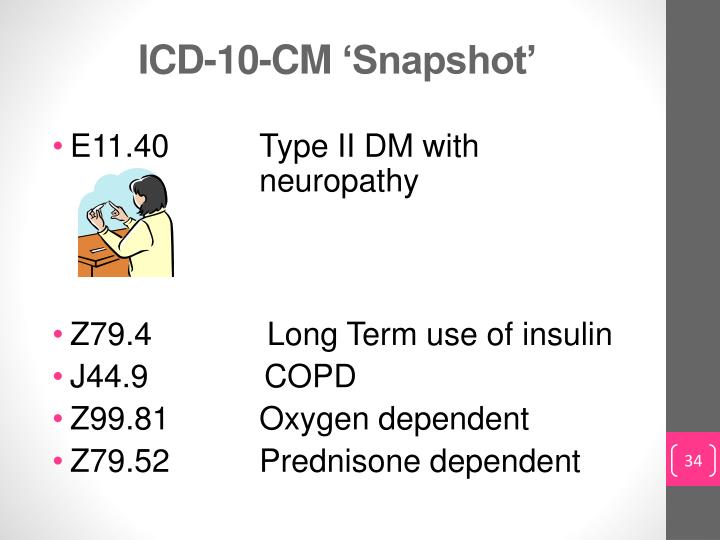
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia. Diabetes type 2 with hyperglycemia; Hyperglycemia due to type 2 diabetes mellitus. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E11.65. Type 2 diabetes mellitus with hyperglycemia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code.
How do you code a Type 2 NSTEMI?
Type 2 myocardial infarction (myocardial infarction due to demand ischemia or secondary to ischemic imbalance) is assigned to code I21.
What is a Type 2 NSTEMI?
Type 2 NSTEMI is defined as myocardial ischemia resulting from mismatched myocardial oxygen supply and demand that is not related to unstable coronary artery disease (CAD).
Is type 2 myocardial infarction NSTEMI?
Among MI patients, type 1 MI was identified in 137 patients (47.2%), with 20 (14.6%) ST segment elevation MI (STEMI) and 117 (85.4%) non-ST segment elevation MI (NSTEMI), type 2 MI was identified in 146 patients (50.3%), and type 3, type 4, or type 5 MI was identified in 7 patients (2.4%).
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 NSTEMI?
For patients with type 1 MI, the focus is on aggressive antithrombotic therapy and consideration of urgent coronary angiography and revascularization. For patients with type 2 MI, the focus is on treating the extracardiac stressor precipitating the myocardial oxygen supply and demand imbalance.
What is Type 1 and Type 2 MI?
Type 1 MI is a primary coronary arterial event attributable to atherothrombotic plaque rupture or erosion. Type 2 MI occurs secondary to an acute imbalance in myocardial oxygen supply and demand without atherothrombosis.
Is type 2 MI the same as demand ischemia?
Demand ischemia should be reserved for when there is evidence of supply-demand mismatch causing ischemia without an elevated troponin above the 99th percentile. If the troponin is > 99th percentile the diagnosis is a Type 2 MI.
What causes a type 2 myocardial infarction?
The main causes of type-II MI were anemia (31%), sepsis (24%), and arrhythmia (17%). Patients with type-II MI tended to be older (75.6±12 vs. 63.8±13, p<0.0001), female majority (43.3% vs. 22.3%, p<0.0001), had more frequently impaired functional level (45.7% vs.
Is myocarditis a Type 2 MI?
Type 2 MI is distinguished from myocardial injury without acute ischemia, for example, acute heart failure and myocarditis.
Is Type 1 or Type 2 MI worse?
The one-year mortality rate was significantly higher for type 2 MI: 27% of these patients died at the end of one year compared to 13% of type 1 patients (P<0.00001) (Figure 5).
What are the types of NSTEMI?
Types 1 and 2 MI are spontaneous events, while type 4 and type 5 are procedure-related; type 3 MI is identified only after death. Most type 1 and type 2 MI present as non-ST-elevation MI (NSTEMI), although both types can also present as ST-elevation MI.
What are the 5 types of NSTEMI?
MI Types by CausationType 1: Spontaneous Myocardial Infarction. ... Type 2: Myocardial Infarction Secondary to an Ischemic Imbalance. ... Type 3: Cardiac Death Due to Myocardial Infarction. ... Type 4: Myocardial Infarction Associated With Revascularization Procedure. ... Type 5: Myocardial Infarction Related to CABG Procedure.
How serious is NSTEMI?
A non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction, also called an NSTEMI or a non-STEMI, is a type of heart attack. While it's less damaging to your heart than a STEMI, it's still a serious condition that needs immediate diagnosis and treatment.
What is worse a STEMI or NSTEMI?
An NSTEMI is a less severe form of heart attack than the STEMI because it inflicts less damage to the heart. However, both are heart attacks and require immediate medical care.
How many types of NSTEMI are there?
Types 1 and 2 MI are spontaneous events, while type 4 and type 5 are procedure-related; type 3 MI is identified only after death. Most type 1 and type 2 MI present as non-ST-elevation MI (NSTEMI), although both types can also present as ST-elevation MI.
What happens to the heart during NSTEMI?
STEMI heart attacks are diagnosed when part of the wave, the ST segment, rises higher than normal. In most cases, a STEMI heart attack happens because of a total blockage of one of the main coronary arteries that provide blood flow to your heart muscle.
What is type 2 NSTEMI?
A type 2 NSTEMI is secondary to ischemia from a supply-and-demand mismatch. Something other than coronary artery disease is contributing to this supply-and-demand mismatch. This type of MI is typically marked by non ST elevation. Some of these causes may be respiratory failure, renal failure, COPD, heart failure, severe anemia, hypotension/shock, severe infection, extremely fast or slow heart rate, and hypertension. These are just a few examples.
What is the diagnosis of MI type 2?
In diagnosing a Type 2 MI, the patient will have an elevated troponin level (that changes), no clinical features of a typical MI (Type 1), and a clinical condition that is known to increase the oxygen demand or decrease the oxygen supply (see listed above). Treatment for a Type 2 MI consists of treating the underlying cause/condition. Once this is corrected the insult to the heart should improve/resolve.
When will ICD-10 PCS codes be released?
In June CMS released the final ICD-10-PCS codes for FY2022, which begins October 1, 2021. We are giving you a sneak peek at the changes. HIA will have a full educational module on these changes available later this summer.
What is the R40.2- scale?
The coma scale codes (R40.2-) can be used in conjunction with traumatic brain injury codes, acute cerebrovascular disease or sequelae of cerebrovascular disease codes. These codes are primarily for use by trauma registries, but they may be used in any setting where this information is collected. The coma scale may also be used to assess the status of the central nervous system for other non-trauma conditions, such as monitoring patients in the intensive care unit regardless of medical condition.
How many ICD-10 codes are there for FY2021?
In this part, the ICD-10-PCS procedure codes are presented. For FY2021 ICD-10-PCS there are 78,115 total codes (FY2020 total was 77,571); 556 new codes (734 new last year in FY2020)…
When will the CMS release the final rule for FY2022?
CMS released the IPPS proposed rule on 4/27/21 outlining the proposed changes to the Inpatient Prospective Payment System for FY2022, which begins October 1, 2021. Later this year, sometime in August, CMS will release the Final Rule.
What causes Type 2 MI?
There is always an underlying condition or disease process that causes the Type 2 MI. Ischemia means insufficient blood perfusion, and prolonged ischemia leads to infarction, i.e., cell death. When cells die and break down, they release their contents, including troponin, a heart-muscle protein.
What is type 1 MI?
Type 1 MI is myocardial necrosis, or cell death, caused by an anatomic blockage of blood flow for a prolonged period of time. This is usually due to atherosclerotic plaque and rupture or thrombosis, causing mechanical coronary artery obstruction. Type 2 MI is also cell death, but in a non-anatomic distribution due to generalized hypoperfusion, ...
Is type 2 MI the same as type 1 MI?
However, Type 2 MI does not have the same course, prognosis, or treatment as Type 1 MI. Once the underlying condition is brought under control, the Type 2 MI resolves. Healthcare providers were gun-shy about calling out Type 2 MIs initially because the inability to code and separate out the condition caused them to fall out of the AMI Core Measures. Most facilities bypassed this problem by using “not indicated due to Type 2 MI” as an exclusion in their order set.
Can a second MI be a type 1?
A second Type 1 MI can either be reinfarction in the same anatomic distribution, as an extension of the first MI, or a patient can have another Type 1 MI in a different vessel , with a different area of the heart being affected. Treatment of myocardial infarction has always been informed by the desire to prevent death, reinfarction, ...
Is a type 2 MI a sequitur?
It is a non sequitur to have a subsequent Type 2 MI. Type 2 MI is related to flogging a heart on the basis of some other condition, not a direct reflection of the heart’s intrinsic health (although Type 2 MIs are more likely to occur in older patients with underlying generalized heart disease), and it is limited to the index admission. If one survives septic shock with a Type 2 MI, one might follow up with a cardiologist to rule out coronary artery and heart disease – which might respond to chronic treatment, but not for long-term treatment of the Type 2 MI, per se.
What does a type 2 exclude note mean?
A type 2 excludes note represents "not included here". A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I21) and the excluded code together.
What is the code for myocardial infarction?
Codes. I21 Acute myocardial infarction.
What is the ICD-10 code for a type 2 MI?
One of the problems providers have had with diagnosing Type 2 MI was that there was no unique code for a Type 2 MI until October 2017. This meant that every time a Type 2 MI was diagnosed, the patient was marked as having atherosclerotic heart disease, and the core measures were initiated. Last October, the code I21.A1, Myocardial infarction, Type 2, was added to ICD-10-CM.
When to consider Type 2 MI?
If you note an abnormal troponin early and you are interacting with a provider verbally and concurrently, bring it to their attention. It is optimal to consider Type 2 MI early, and to diagnose or rule out subsequently. I would not formally query unless and until the condition declares itself.
Can you diagnose NSTEMI instead of MI?
If the patient has EKG changes or known CAD, it may be appropriate to diagnose NSTEMI or STEMI instead of Type 2 MI. If you do so, be sure to attend to core measures.
What is the implication of Type 2 MI?
There is always an underlying etiology. The implication of a Type 2 MI is that it portends a worse prognosis for the causative condition.
Can MI 2 be sequenced?
There is always an underlying condition, but a Type 2 MI may be sequenced first if it was the diagnosis that, after study, occasioned the admission. If this were the case, the DRG falls into the Acute Myocardial Infarction sets (MS-DRGs 280-285) with higher weights than MS-DRG 311. All myocardial infarctions are major CCs (MCCs).
What is type 3 MI?
Type 3 MI, which is cardiac death with symptoms of myocardial ischemia and suggestive EKG changes, but demise occurs before any biomarker trending can be demonstrated;
Is troponin a type 2 MI?
If troponins stay relatively constant and are not significantly elevated (by significantly, I mean exceeding the 99 th percentile URL), and your provider doesn’t remark on it, don’t query. It isn’t a Type 2 MI and you will just irritate.
What is the code for a type 2 myocardial infarction?
Type 2 myocardial infarction (myocardial infarction due to demand ischemia or secondary to ischemic imbalance) is assigned to code I21.A1, Myocardial infarction type 2 with a code for the underlying cause coded first. Do not assign code I24.8, Other forms of acute ischemic heart disease, for the demand ischemia. Sequencing of type 2 AMI or the underlying cause is dependent on the circumstances of admission. When If a type 2 AMI code is described as NSTEMI or STEMI, only assign code I21.A1. Codes I21.01-I21.4 should only be assigned for type 1 AMIs.
What is a type 2 MI?
Type 2 MI is frequently incorrectly diagnosed and inconsistently documented.
What to do if a type 2 MI is diagnosed?
Education for clinical providers is critical. When a Type 2 MI is diagnosed, the clinical provider should make it a habit to document the etiology of the MI. If the provider does not document the etiology, a query will need to be issued. Over time, linking the etiology will become a habit for clinicians, but in the meantime, expect more queries.
What is the ICd 10 code for MI?
MI due to demand ischemia or MI secondary to ischemic imbalance are equivalent to Type 2 MI from a coding perspective. These terms map to ICD-10-CM code, I21.A1, MI Type 2.
What is the mistake when considering a Type 2 MI diagnosis?
When considering a Type 2 MI diagnosis, a common mistake is to forget about the requirement of acute myocardial ischemia. If the patient does not meet one of the criteria for myocardial ischemia, the patient should not be diagnosed with a Type 2 MI.
What are the symptoms of myocardial ischemia?
Symptoms of myocardial ischemia (shortness of breath, etc.)

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2019 icd 10 code for right epididymitis cyst
- 2. icd 10 cm code for past smoker
- 3. icd-10 code for bacterial overgrowth syndrome
- 4. icd 10 cm code for laceration without foreign body of right elbow, initial encounter → poa yes
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for liver hemangioma
- 6. icd 10 code for mechanical fall
- 7. icd 10 code for kidney transplant cadidacy evaluation
- 8. cpt code and icd code for dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- 9. icd-10 code for visual hallucinations
- 10. icd-10 code for abdominal mri