Precautions
UBRELVY 50 mg is supplied as white to off-white, capsule-shaped, biconvex tablets debossed with “U50” on one side. UBRELVY 100 mg is supplied as white to off-white, capsule-shaped, biconvex tablets debossed with “U100” on one side.
What is the difference between ubrelvy 50 and 100 mg?
The recommended dose of UBRELVY is 50 mg or 100 mg taken orally with or without food. If needed, a second dose may be taken at least 2 hours after the initial dose. The maximum dose in a 24-hour period is 200 mg. The safety of treating more than 8 migraines in a 30-day period has not been established.
What is the maximum amount of ubrelvy I can take?
The inactive ingredients include colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone vinyl acetate copolymer, sodium chloride, sodium stearyl fumarate, and vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate. UBRELVY is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
What are the inactive ingredients in ubrelvy?
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Ubrelvy that is written for health professionals. What are the ingredients in Ubrelvy?
Where can I find information about ubrelvy for health professionals?
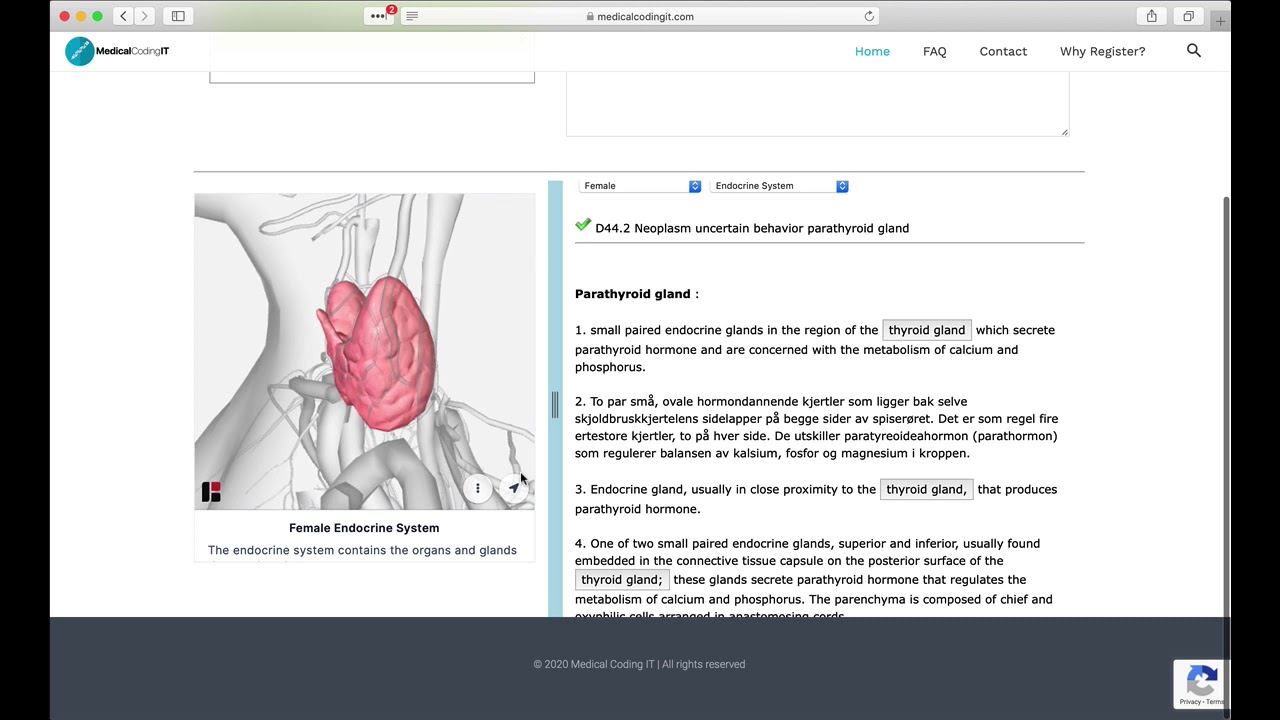
What is the ICD-10 code for medication?
ICD-10 Codes for Long-term TherapiesCodeLong-term (current) use ofZ79.899other drug therapyH – Not Valid for Claim SubmissionZ79drug therapy21 more rows•Aug 15, 2017
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic migraine?
ICD-10 code G43. 709 for Chronic migraine without aura, not intractable, without status migrainosus is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is the ICD-10 code for migraine headache?
909 – Migraine, Unspecified, not Intractable, without Status Migrainosus.
What is the ICD-10 code for intractable migraine?
Migraine, unspecified, intractable, without status migrainosus. G43. 919 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-9 code for migraine headaches?
ICD-9-CM Codes headache G43 (migraine) 346 (migraine) G43. 0 (migraine without aura) 346.1 (migraine without aura…) G43.
What is the ICD-10 code for episodic migraine?
Episodic tension-type headache, not intractable The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G44. 219 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G44. 219 - other international versions of ICD-10 G44.
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic migraine with aura?
ICD-10 Code for Migraine with aura- G43. 1- Codify by AAPC.
What does intractable migraine mean?
Published: June 27, 2016. Intractable headache is “doctor speak” for that headache that just doesn't seem to go away, no matter what you and your doctor do. The headache may be migraine or another kind of headache, or a combination of two or more different headache types.
What does not intractable migraine mean?
What is a not intractable migraine? An intractable migraine causes severe pain that extends beyond 72 hours and usually requires a hospital visit for treatment. Comparatively, a not intractable migraine typically lasts up to 72 hours and can be treated with migraine medications.
What is migraine with aura intractable without status migrainosus?
Status migrainosus, or intractable migraine, is a persistent, debilitating migraine without aura that significantly affects a person's ability to function. Even when affected individuals take steps to control triggers and make deliberate lifestyle changes, it still has a major impact on their quality of life.
What is an atypical migraine?
Atypical migraines generally skip the aura phase. This phase would typically include flashes of light, blind spots, or tingling in the extremities. Instead of aura signaling the start of a migraine, an atypical migraine abruptly begins with headache pain. Researchers have yet to determine how many people are affected.
What are chronic migraines?
Chronic migraine, a condition characterized by the experience of migrainous headache on at least 15 days per month, is highly disabling. Patients with chronic migraine present to primary care, are often referred for management to secondary care, and make up a large proportion of patients in specialist headache clinics.
What are the side effects of Ubrelvy?
The most common side effects of Ubrelvy are nausea and sleepiness. These are not all of the possible side effects of Ubrelvy. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How long after Ubrelvy can you take a second dose?
A second dose of study medication (Ubrelvy or placebo), or the patient’s usual acute treatment for migraine, was allowed between 2 to 48 hours after the initial treatment for a non-responding or recurrent migraine headache. Up to 23% of patients were taking preventive medications for migraine at baseline.
Is ubrogepant an inhibitor of CYP1A2?
Ubrogepant is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4. Ubrogepant is a weak inhibitor of CYP2C8, 2C9, 2D6, 2C19, MAO-A, and UGT1A1. The in vitro inhibition potential is not expected to be clinically significant. Ubrogepant is not an inducer of CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations.
Is ubrogepant safe for pregnant women?
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of Ubrelvy in pregnant women. In animal studies, adverse effects on embryofetal development were observed following administration of ubrogepant during pregnancy (increased embryofetal mortality in rabbits) or during pregnancy and lactation (decreased body weight in offspring in rats) at doses greater than those used clinically and which were associated with maternal toxicity (see Data).
Is ubrogepant soluble in water?
Ubrogepant is a white to off-white powder. It is freely soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone, and acetonitrile; and is practically insoluble in water. Ubrelv y is available as tablets for oral administration containing 50 mg or 100 mg ubrogepant.
Is Ubrelvy safe for children?
Ubrelvy is not used to prevent migraine headaches. It is not known if Ubrelvy is safe and effective in children.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as G43. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. headache NOS (. ...
Is migraine G43 intractable?
Migraine G43-. the following terms are to be considered equivalent to intractable: pharmacoresistant (pharmacologically resistant), treatment resistant, refractory (medically) and poorly controlled. Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology.
Is ubrogepant soluble in water?
Ubrogepant is a white to off-white powder. It is freely soluble in ethanol, methanol, acetone, and acetonitrile; and is practically insoluble in water. UBRELV Y is available as tablets for oral administration containing 50 mg or 100 mg ubrogepant.
Is ubrogepant safe for pregnant women?
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of UBRELVY in pregnant women. In animal studies, adverse effects on embryofetal development were observed following administration of ubrogepant during pregnancy (increased embryofetal mortality in rabbits) or during pregnancy and lactation (decreased body weight in offspring in rats) at doses greater than those used clinically and which were associated with maternal toxicity (see Data ).
Is ubrogepant an inhibitor of CYP1A2?
Ubrogepant is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4. Ubrogepant is a weak inhibitor of CYP2C8, 2C9, 2D6, 2C19, MAO-A, and UGT1A1. The in vitro inhibition potential is not expected to be clinically significant. Ubrogepant is not an inducer of CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for trali
- 2. icd 10 cm code for post procedural state
- 3. icd 10 code for k2
- 4. icd 9 code for moles
- 5. icd-10-pcs code for transurethral resection of prostate
- 6. icd 9 code for severe peripheral vascular disease
- 7. icd 10 code for g i tube issue
- 8. icd 10 cm code for gamma knife radiosurgery
- 9. icd-10 code for ectopic pregnancy right fallopian tube
- 10. icd 10 code for functional movement disorder